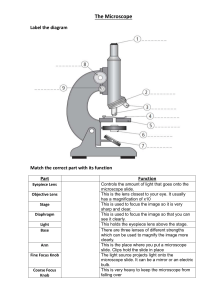
ACTIVITY 1 Parts of the Microscope TheThe Compound Compound Microscope is an Microscope is an optical tool that is is optical tool that used to observe used to observe things that areare things that beyond ordinary beyond ordinary vision. It isIt one of of thethe vision. is one basic instruments of of basic instruments a microbiologist. a microbiologist. Table 1 Characteristics of the Microscope Features Scanner Low Power High Power Focal Length (mm) 16mm 4mm 1.8mm Working Distance (mm) 4mm 0.5mm 0.1mm Linear Magnification (X) 4X 10X 40X 0.27 0.60 1.34 2.0mm 0.4mm 0.2mm Numerical Aperture (N.A.) Diameter of front lens (mm) Table 2 movement of specimens If the letter e on the stage is move d to: If the image in the eyepiece is moved to: 3 o’clock 9 o’clock 9 o’clock 3 o’clock 12 o’clock 6 o’clock 6 o’clock 12 o’clock The Letter “e” e What can be see with an unaided eye SCANNER (4X) Low power (10x) DEPTH FOCUS Which colored thread comes into focus first, second, and third (as observed under 10x) The order of the threads are as follows: pink comes first, which is in the bottom, then the blue one, and lastly, yellow which is at the top. Based on our observation, the yellow thread comes into focus first, then the middle one which is the blue thread, and finally the pink thread. DEPTH FOCUS As observed under 40x and 4x objectives. When viewed under the HPO (40x magnification), yellow thread was on top among the other two colored threads. They showcase hairy-like projections. In addition, the surrounded parts were somewhat blurry to successfully observe. On the other hand, when viewed under 4x, we saw all the three colored threads and their arrangements were from the yellow thread being on top then blue thread in the middle and pink thread as the last one. OTHER QUESTIONS Other questions What does it mean when a microscope is parfocal? Parfocal microscopes maintain focus throughout real-time magnification changes. These microscopes also remain focused when the user rotates objectives. Other questions Which objective focuses closely to the slide? The objective focuses closely to the slide is the High Power (40X) What controls the amount of light reaching then ocular lens? The Iris diaphragm and the light intensity adjustment. Other questions Name two ways in which you can enhance the resolving power. • Adjusting the intensity of light that enters the condenser through the iris diaphragm. • Adjusting the coarse adjustment knob when viewed under the Low Power Objective. And for the High Power Objective we use the fine adjustment knob. Terms associated with Microscopy • Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument. • A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. • Total magnification is the final magnification of the microscope is the result of objective magnification x eyepiece magnification with consideration of the tube factor • Resolution is a measure of the ability of a lens to image closely spaced objects so they are recognized as separate objects. • Resolving power is the capacity of any optical system to distinguish and separate details in a specimen. • Depth of Field is the distance along the optical axis throughout which the object can be located and yet be imaged with satisfactory clarity. This is used in stereo microscopy. • Magnification is the enlargement of an object through the lens system. This is determined by multiplying the magnifying power of the objective by the eyepiece. • Parcentered is When all the elements of the optical system are aligned on a single axis thus reducing aberration. • Parfocal (parfocality) is a term used describing the property of a microscope where the subject stays in focus when the objective lenses are changed. Less then 1/2 of a revolution from the fine adjustment is usually acceptable. HOW IMAGES ARE FORMED UNDER THE MICROSCOPE 1 Formation of image occurs at the intermediate plane by interference between direct light that has pass through the specimen unaltered and light diffracted by features present in the specimen. 2 The intermediate image projected by the objective is enlarged by the eyepiece. There was an inversion of image when the specimen was observed at different objectives. 3 Objective lens inverts the image because of the lens' curvature. The inverted image is made from a positive lens, which means the image formed after light passes through the lens is a real image. 4 This real image is inverted at the focal length. When the letter "e" is put rightside up in the slide to the observer, it is projected upside down in the tube. 5 The image is refracted through the objective lens, and it travels up the body tube where the ocular lens magnifies the image a little more. 6 Then objective lens is where most of the magnification occurs, and many microscopes have rotating lenses that increase magnifications. Proper ways on taking good care of a microscope •Always carry with 2 hands •Never touch the lenses with your fingers. •Only use lens paper for cleaning •Do not force knobs •Keep objects clear of desk and cords •When you are finished with your "scope", rotate the nosepiece so that it's on the low power objective, roll the stage down to lowest level, rubber band the cord, then replace the dust cover. CONCLUSION After performing the activity, we were able to learn the parts and functions of a microscope and how to properly use it. We were able to identify its characteristics, how images are formed when viewing specimens using it and how its depth of focus works. Through this activity, we were able to acquire additional knowledge on enhancing microscope’s resolving power, on other terms related to microscopy and on how to handle proper ways on taking good care of a microscope.