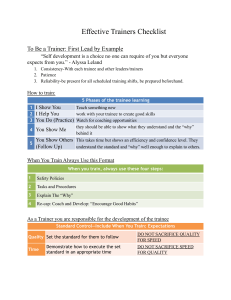
QUALIFICATION: EVENTS MANAGEMENT SERVICES NCIII SECTOR: TOURISM ( HOTELS AND RESTAURANTS ) UNIT OF COMPETENCY: Basic Competency Common Competency Core Competency CORE COMPETENCIES: EVENT PLANNING SERVICES Plan and develop event proposal or bid Develop an event concept Develop an event program Select event venue and site Develop and update event industry knowledge ON –SITE EVENT MANAGEMENT SERVICES Provide on-site event management services Manage contractors for indoor events Develop and update knowledge on protocol WHAT IS COMPETENCY? involves applying knowledge, skills and attitudes to perform work activities to the standard expected in the workplace What is Competency-Based Technical Vocational Education and Training? It is an approach to deliver training that focuses on the development of competence in the learner as a result of the training. Principle One The training is based on curriculum developed from the competency standards Learning is based on the curriculum modules Principle Two Learning is competency based or modular in Job Analysis structure Skills, knowledge and attitudes (competencies) Competency profile TNA Course design and delivery Principle Three Training delivery is individualized and self-paced Learning is done by the learner at their own pace Principle Four Training is based on work that must be performed Learning is based on the actual workplace practice Principle Five Training materials are directly related to the competency standards and the curriculum Training materials are self-paced and experiential Principle Six Assessment of learners is based in the collection of evidence of the performance of work to the industry or organizational required standards Traditional Students are judged againts each other (norm referenced Assessment) CBTVET Each student is assessed against the required standard Students are not judged against each other Principle Seven Training is based both on and off the job components Learners are aware of the activities that has to be completed based on the curriculum Principle Eight The system allows Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) Workers and Students can have prior skills recognised towards awards competencies gained in life or work RPL Competencies assessed and accredited for promotion and learning Principle Nine The system allows for learners to enter and exit programs at different times and levels and to receive an award for modules (competencies) attained at any point (Multiple Entry) There is flexibility for entry and exit from programs Principle Ten Approved training programs are nationally accredited Learners and providers of training are recognised in a national system •CBT Process Flow •Trainee enters •program • Administer RPL • Orientation • Role of trainer/trainee •Review learning •package •View multimedia •materials •YES •Trainer •observes •Trainer •Rates •performance •performance •Use manuals •Trainee selects •competency •and receive •instructions • Administer Learning Contract • Organize learning strategy • Provide materials • Introduce CBLM materials • Introduce the Use of • Achievement Progress • Report •Satisfactorily •Performed •Competency? •NO •Have completed •all the •competencies? •NO •Observe •demonstration •Trainee •practices task •Trainee •Rates own •performance •Practice skills in •workshop •Receive •assistance and •advise •Trainee exits •program •Trainee exits •program •Have enough •Competency/ies •been •achieved? •NO •YES •Undergo Nat’l •Assessment •YES 1.Serves as a team Role member to of the determine what is to Trainer be learned. 2.Stimulates trainees ‟motivation”. 3. Manages learning: a Role consultation rather of the than a provider of Trainer information; a facilitator of the of the facilitator of the learning Role of the 4. Diagnose and solves Trainer learning problems. 5. Evaluates learner’s achievement. Role 6. Assist learner’s to of the obtain individualized rewards. Trainer 7. Assist each learner in designing a personalized plan of study. Role 8. Installs confidence in of the the learner by Trainer providing experiences where learners may succeed. Role 9. Serves as a model for of the desirable work habits, Trainer attitudes and tasks performance in the occupational field. Role 10. Spends more time of the interacting with Trainer students on a 1:1 or small group basis. 11. Helps those learners who really need help. Role of the Trainer 12. Accepts responsibility along with the learner for the tasks learned or not learned. Role 1. Trainees may select of the what they want to Trainee learn and when they want to learn it, within reason. Role 2. Trainees learn at of the their own rate within Trainee program guidelines. They may speed up, slow down, stop or even repeat a task. 3. Trainees may request to receive credit for what they already know. Role of the Trainee This is done either through pre-testing or through a review o a task list completed at another training site. Role 4. Trainees may choose of the how they want to learnindividually, on a one-toTrainee one basis, in small group, in large groups or with audio-visuals. Role 5. Trainees are of the responsible for what they learn and when they Trainee learn it. Role 6. Trainees decide when they are ready to perform each of the task or demonstrate mastery Trainee of learning to a job-like level of proficiency before receiving credit for the task. Role of the Trainee 7. Trainees help develop personalized prescription for learning worked out cooperatively and based upon what the students already knows, his preference for learning, learning style and other needs. Role of the Trainee 8. Trainees compete against present job standards and not against other students and are graded on achievement of the standards or criteria of each task. Role of the Trainee 9. Trainees know “up front”, before instruction begins what they are expected to know and do to complete the program. 9. Trainees know “up Role front”, before instruction of the begins what they are Trainee expected to know and do to complete the program. Role of the Trainee 10. Trainees evaluate their own progress to see how well they are doing. 11. Trainees move freely in the workshop, laboratory and or training center. Role of the Trainee 12. Trainees know they will be rated mainly on performance, while paper and pencil tests will be used mainly to check their knowledge of the task. 13. Trainees learn Role according to their of the interest, needs and Trainee abilities – not according to teacher timelines and expediency.