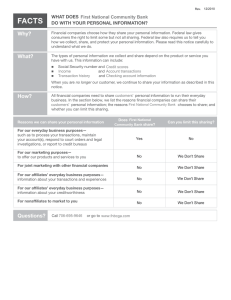
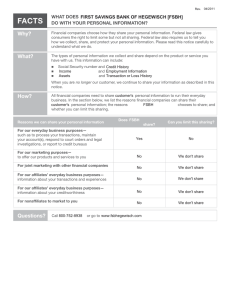
ACCOUNTING FOR MANAGERS CHAPTER ONE A GENERAL OVERVIEW Introduction Accounting vs Finance: A distinction Financial vs Management Accounting: User perspective Finance INTRODUCTION “Accounting is the art ofrecording ,classifying andsummarizing in a significant manner and in terms ofmoney transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.” AICPA “It is the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information topermit informed judgments and decisions by users of the information.” AAA Its purpose is tocommunicate orreport the results of business operations and its various aspects. CONT’D On analyzing the above definitions, the following characteristics of accounting emerges: Accounting is the art of recording and classifying different business transactions. Generally the business transactions are described in monetary terms. In accounting process, the business transactions are summarized and analyzed so as to arrive at a meaningful interpretation. The analysis and interpretations thus obtained are communicated to those who are responsible to take certain decisions to determine the future course of business. OBJECTIVES OF ACCOUNTING To record the business transactions in a systematic manner. To determine the gross profit and net profit earned by a firm during a specific period. To assess the taxable income and the sales tax liability. To know the financial position of a firm at the close of the financial year by way of preparing the balance sheet. To facilitate management control. To provide requisite information to different parties, i.e., owners, creditors, employees, management, government, investors, financial institutions, banks etc. USERS OF ACCOUNTING INFORMATION Internal Users External Users •Lenders •Consumer Groups •Managers •Sales Staff •Shareholders •Employee Unions •Officers •Budget Officers •Governments •Potential Investors •Internal Auditors •Controllers 1-7 CONT’D • Accounting Information(AI): A Means to an End Accounting information is not an end , but is a means to an end i.e. its final product is decision which is ultimately enhanced by the use of accounting information, whether that decision made by owners, management, creditors, government bodies, labor unions ,etc. • Why accounting is being called as “the language of business”? • Why Accounting information is a means to an end, not the end in itself? FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING & MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Financial Accounting: • Financial accounting information provides information about the financial resources, obligations, & activities of an enterprise that is intended for use primarily byexternal decision makers. • Financial accounting information appears in financial statements that are intended for external use. • The primary questions about an organization’s success that decision makers want to know are: • What is the financial picture of the organization on a given day? • How well did the organization do during a given period? CONT’D • Accountants answer these primary questions with three major financial statements. •Balance sheet - Shows financial picture on a given day. •Income statement- shows performance over a given period. •Statement of cash flows- shows performance over a given period. CONT’D Management Accounting: Management accounting involves the development and interpretation of accounting information intended specifically to assist managing in operating the business. Management accounting information is for internal use & provides special information for managers. Managers use this information in setting companies goals, evaluating the performance of departments and individuals, deciding whether to introduce a new line of products, and making virtually all types of managerial decisions. CONT’D • Management accounting generates information that managers can use to make sound decisions such as: •Financial, •Resource allocation, •Production & •Marketing decisions FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING VS MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING • Financial accounting is aimed to provide accounting information to external users. • Managerial Accounting is aimed to provide accounting information to internal users. • Although there is a difference in the type of information presented in financial and managerial accounting, the underlying objective is the same; to satisfy the information needs of the user. MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING VS FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Criteria Management Accounting Financial Accounting Purpose of information Help managers make decisions to fulfill an organization’s goals Primary users Managers of the organization Communicate organization’s financial Position and operating results to investors, banks, regulators, and other outside parties External users such as investors, banks, regulators, and suppliers Focus and emphasis` Future-oriented (budget for 2014 prepared in 2013) Past-oriented (reports on 2013 performance prepared in 2014) Rules of measurement and reporting Internal measures and reports do not have to follow GAAP (IFRS) but are based on cost-benefit analysis and usefulness to managers Varies from hourly information to 15 to 20 years, with financial and nonfinancial reports on products, departments, territories, and strategies Financial statements must be prepared in accordance with GAAP (IFRS) and be certified by external, independent auditors Annual and quarterly financial reports, primarily on the company as a whole Designed to influence the behavior of managers and other employees Primarily reports economic events but also influences behavior because manager’s compensation is often based on reported financial results Time span and type of reports Behavioral implications 1. What is the purpose of the 3 major financial statements? 2. How are the three major financial statements related? 3. Discuss the differences between managerial and financial accounting. FINANCE Virtually all individuals and organizations earn or raise money and spend or invest money. Finance is concerned with the process, institutions, markets, and instruments involved in the transfer of money among individuals, businesses and governments. The general areas of finance are business, personal and public finance. Finance is important to individuals, business and government to achieve their economic objectives. CONT’D Finance plays a pivotal role to every general person to earn and invest money; for business to raise and invest funds; and to the government to plan expenses and incomes, to execute goals of government and to achieve development of a country. FINANCE uses accounting information as inputs to decision-making. The study of how to raise money and invest it productively. CONT’D Financial management defined: It is an integral part of overall management. concerned with the efficient use of an important economic resource namely, capital funds” “Financial Management deals with procurement of funds and their effective utilization in the business” In simple words, Financial Management as practiced by business firms can be called as corporation Finance or business Finance. CONT’D Financial decisions in a firm There are four broad areas of financial decision making in a firm. These are: 1. Investment decisions (Capital budgeting) 2. Financing decisions (capital structure) 3. Liquidity decisions (working capital management/short term asset mix decision) 4. Dividend decisions CONT’D 1. Investment decisions: A firm’s investment decisions involve capital expenditures. They are, therefore, referred as capital budgeting decision. Capital investment isthe allocation of capital to investment proposals Involves commitment of funds to long term assets that would yield long term benefits Two important aspects of investment decision are: 1. The evaluation of the prospective profitability of new investment, and 2. The measurement of acut-off rate against that the prospective return of new investments could be compared. Investment proposal should be evaluated in terms of both expected return and risk. CONT’D 2. Financing decisions: Once a firm has decided the investment projects it wants to undertake, it has to figure out ways and means of financing them. This is the function of raising funds. The central issue here is to determine the appropriate proportion of equity and debt; the mix of debt and equity is called capital structure. The financial manager must strive to obtainthe best financing mix or the optimum capital structure. The use ofdebt affects the return and risk of shareholders ; it may increase the return on equity funds, but it always increases risk as well. CONT’D 3. Working capital management (Liquidity) decision: Also referred as short term financial management that deals with current assets and current liabilities. Investment in current assetsaffect the firm’s profitability and liquidity . Current assets should be managed efficiently for safeguarding the firm against the risk of illiquidity. If the firm does not invest sufficient funds in current assets, it may become illiquid and therefore, risky; but it would lose profitability, as idle current assets would not earn anything. Conflict exists between profitability and liquidity while managing current assets and hence it deals with proper trade-off between liquidity and profitability . CONT’D 4. Dividend Decision: The financial manager must decide whether the firm should distribute all profits, or retain them or distribute a portion and retain the balance. The proportion of profits distributed as dividends is called the dividend payout ratio and the retained portion of profit is known as the retention ratio . The optimum dividend policy is that onemaximizes the market value of the firm’s shares 1. Distinguish Accounting and Finance. 2. Explain the Four key decision areas of financial Management. 3. How can you explain the contribution accounting & finance in administering business/managing projects? End of Chapter One!