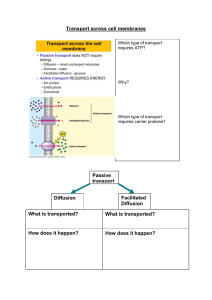
9 week Benchmark Study Guide CELLS PROKARYOTE Pro = No (No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) EUKARYOTES - cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Bacterial Cell Eubacteria Archaebacteria Ribosomes - proteins Nucleic Acid – DNA/RNA Cell membrane Some Cell Wall Animal cell parts: Plant cell parts Cell membrane – phospholipid bilayer Same as Animal plus - controls what enters/leaves cell wall – support – made of cellulose Mitochondria – turn food into energy chloroplasts – capture light energy Ribosomes – make proteins vacuoles – very large ER – transports fat (smooth) or proteins (rough) Golgi body – modifies, packages and transports Lysosomes – clean up Cytoskeleton – structure/support Nucleus – contains genetic info. (DNA/RNA) Cell wall composition No cell wall Bacteria - peptidoglycan Fungi - chitin Plants - cellulose Animals MACROMOLECULES Organic compounds – contain CARBON “C” – major element found in living things - also usually contain hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) The 4 macromolecules (Molecules of Life): Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates monomer = monosaccaride - give quick energy - gives extra support in cell walls (plants) Starches – potatoes, pasta, bread Lipids (single sugar) Sugars – candy, fruits, vegetables monomer – fatty acids - stores energy - Insulates and cushions Butters, oils, animal fat __________________________________________________________________ Proteins monomer = amino acid - build muscle, hair, nails - regulates metabolism(enzymes) - molecular structure contains Nitrogen!!! Meats, nuts ___________________________________________________________________ Nucleic Acids monomer = nucleotide - stores hereditary material in code (messages) The double helix structure was discovered by James Watson & Francis Crick in 1964. DNA & RNA (Phosphate, sugar, base) Enzymes (specialized proteins) help control the rate of chemical reactions (usually speeds it up without being used up). They are effected by Temperature (hotter is faster) and pH (acid/base amounts) -they are effected by concentration (higher concentration the faster it will happen) Catalyst- an enzyme that speeds up a reaction. Cell Transport Cell Transport – How a cell moves material in and out through the cell membrane 2 Types: Passive (no energy required) and Active (requires cell to use energy) -The cell membrane on the outside determines what can enter and leave your cells and keeps you alive. -Cells must interact with the environment to maintain Homeostasis. Transport/Channel Protein Phospholipids bilayer -Substances diffuse across the membrane and flow naturally from a higher concentration to a lower one. -Water diffuses the process is called osmosis. -This means that water would cross a selectively permeable membrane from a dilute solution (less dissolved in it) to a concentrated solution (more dissolved in it). 2 types of cell transport (across the cell membrane) Active Passive - Uses cell energy (ATP) -Endocytosis -Exocytosis -Sodium-Potassium Pump - NO cell energy…it happens because of molecular movement -Diffusion - High to Low concentrations -Osmosis - the diffusion of water -facilitated diffusion Types of Solutions: (Sketch the beakers with cells to represent the correct type of solution like we did in class). A _____Isotonic____ (concentration is equal inside and out) B ___Hypotonic___ (concentration Is higher inside than out) Diffusion – the movement of particles from higher to lower concentration Osmosis – the movement of water from higher to lower concentration Facilitated Diffusion – the movement of large particles with the help of carrier proteins C ___Hypertonic__ (Concentration is higher outside than inside) Pump – the movement (pumping) of ions across the cell membrane against concentration using ATP Endocytosis – how a cell “ingests” or moves large amounts of particles fluids INTO the cell pinocytosis - fluids phagocytosis – solids Exocytosis – opposite of endocytosis, how a cell “spits out” large amounts of fluids or solids Characteristics of Living Things (Biology: the study of living things) Homeostasis – maintaining a balanced internal conditions Organization - Cells Tissue Organs Organ systems Organism (living thing) Growth - gets bigger or adds cells or matures Reproduce - asexual or sexual; making more of one’s species Energy - organisms must make or obtain energy (food) – ‘metabolism’ Cells - all living things are made of cells or at least one cell (unicellular) Respond - responding to stimuli such as temperature, pH, needs such as food,….etc. Viruses - They are NOT alive. They do not meet all of the HOGRECR - Antibiotics do not kill or help a viral infection such as the common cold or influenza. - Viruses are not plants, animals, or bacteria, but they are parasites of the living kingdoms. CELL ENERGY Photosynthesis – sunlight is converted into sugar/food (chemical energy = ATP) - takes place in Autotrophic organisms (ex: plants) usually in the leaves - takes place in the Chloroplast organelle of plants Reactants -------------------------------------------------> 6 CO2 Carbon dioxide + 6 H2O + Water Light Dependent Reactions (sunlight) -takes place in the thylakoids of the chloroplast -Water molecules are split -Energy is stored as ATP --------- Sunlight Enzymes Products C6H12O6 + Sugar (glucose) main product 6 O2 Oxygen gas by-product/wastes Calvin Cycle (light independent – doesn’t require sunlight) -takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast -Carbon is ‘fixed’ in carbohydrate (from gas to sugar molecule) Cellular Respiration – plants and animals convert food into energy - takes place in the mitochondria ATP (energy) C6H12O6 + Sugar (glucose) + 6 O2 --------- Oxygen gas 6 H2O Water + 6 CO2 Carbon dioxide _____________________________________________________ Light Energy Photosynthesis Chloroplast Gives off water and CO2 Mitochondria Cellular Respiration Gives off sugar (glucose) & Oxygen (gas)