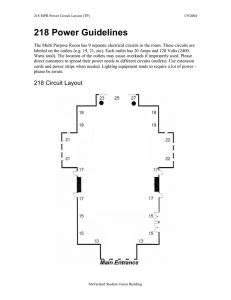
INTERIOR WIRING 9.324 DIVISION NINE Outlets per Circuit Maximum Location Number Barbershops, beauty parlors, etc. 2 Medical, dental, and similar offices 2 Store show windows (for spotlights) 3 Store show windows (at floor) 6 Display areas in retail stores 6 School classrooms 6 Manufacturing spaces 6 Office spaces 8 Storage spaces 10 5. CIRCUIT CONTROL Suitable provision shall be made for the control of all circuits except those supplying convenience outlets only, and control of the latter circuits is recommended. Circuits may be controlled individually, in groups, or by a combination of both methods. In a retail store, individual control at the panelboards by means of circuit switches or circuit breakers is usually preferable. In most other occupancies, control should be provided by means of local switches or circuit breakers. Frequently it is necessary to provide two or more switches for the local control of outlets supplied by a single branch circuit. Provision shall be made for control of all circuits supplying a single sign by means of an external manually operable switch or circuit breaker, and in each case a suitable time switch shall also be provided to effect the same control. In a retail store, each circuit supplying outlets in one or more show windows shall be individually controlled, and provision shall be made for the installation of a time switch for group control of all such circuits. Group control of circuits for general illumination or for special decorative effects, by means of remote-control switches, is desirable in certain large spaces such as large offices, large reading rooms, museums, art galleries, and ballrooms. 6. PANELBOARDS The number and location of panelboards shall be based on the number of branch circuits and the distance or runs as specified in Par. 4 of these adequacy standards. On each panelboard one spare circuit shall be provided for each five circuits utilized in the initial installation. When flush-type cabinets are used, provision shall be made for bringing a corresponding number of circuit conductors to the ceiling of the story served, the ceiling of the story immediately below, or both points. Such provision may consist of circuit conductors or of empty raceways terminating in boxes suitably located for future extensions. Provision shall be made for control of show-window lighting by such grouping of circuits to a panelboard as to enable a time switch to be suitably installed. 7. FEEDERS a. Carrying capacity. The carrying capacity of each feeder or subfeeder shall be based on the number of separate circuits which it supplies, computed as follows: (1) Overhead lighting circuits. These are assumed as having 1000 W for each 15-A circuit and 1500 W for each 20-A circuit. (2) Convenience-outlet circuits. The assumed load is 1000 W per circuit. (3) Spare panelboard circuits. The assumed load is 500 W. (4) Nonitemized and heavy-duty additional circuits. The capacity is based on the specific load for which they are designed. To the total of these four, such demand factors as permitted by the NEC may be applied. Refer to Div. 3 for additional information. Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com) Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.