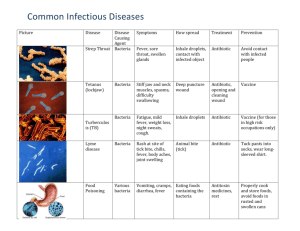
Airborne Disease: Measles (viral infection) Provide details on how the disease is transmitted between members of a community. The disease spreads through the air by respiratory droplets produced from coughing or sneezing. Impact on the Human Body Research the signs and symptoms of the selected disease and describe how the human body responds to becoming infected. Signs and symptoms can take up to 12 days to appear and may consist of; fever, cough, runny nose, sore or red eyes, and also skin rash. The human body responds to the disease by experiencing fever which can inactivate the virus due to the rise in temperature. Waterborne Disease: Cholera (bacterial infection) The disease spreads through contaminated water (and food) that contains the bacteria known as Vibrio Cholerae. Common symptoms of Cholera may include pain in the abdomen, vomiting, watery diarrhoea, dehydration and lethargy. The body responds to the disease by excreting an increased amount of diarrhoea which becomes watery due to the effects of the toxin produced by the bacteria. Vector borne Disease: Malaria (parasite – which is different from bacteria and viruses) The disease spreads through a parasite carried by mosquitoes. Mosquitoes pick up the parasite from an infected person and pass it to other people when the mosquito bites them. Signs and symptoms of the disease may include chills, fever and sweating which usually begins a few weeks after being bitten. Another symptom which can occur is pallor appearance due to anaemia which is the result of the parasite infecting red blood cells in the bloodstream. Contact (direct/indirect): Influenza (viral infection) The disease mainly spreads through droplets made when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Influenza can also be spread through touching surfaces where infected droplets have landed. Symptoms may include fever, chills, coughing, congestion of the airways, runny nose, and sneezing. The body responds to the disease by coughing out mucus (from the nose) or phlegm (from the throat and lungs) that contains the virus. The body also responds to the infection by fever which increases the temperature to kill the virus. Ingestion: Gastroenteritis (can be caused by viruses or bacteria) The disease can be spread from person to person by sharing food, water, or contact with food/surfaces infected by another person’s diarrhoea or vomit. Symptoms may include pain in the abdomen, diarrhoea, stomach cramps, vomiting and loss of appetite. The human body responds to the disease by the process of inflammation which prevents the infection from spreading and removes unwanted material. Droplet: Meningitis The disease can be spread by transmission of the bacteria from person to person through droplets or respiratory secretions. Symptoms may include inflammation of the brain and spinal cord, headache, neck stiffness, vomiting and fatigue. The human body responds to the disease by the process of inflammation which prevents the infection from spreading and removes unwanted material. Difference between airborne and droplet transmission: Airborne – droplets remain in the air for long periods of time and can be transmitted to others over long distances Droplet – occurs when a person is in close contact with someone who has respiratory symptoms