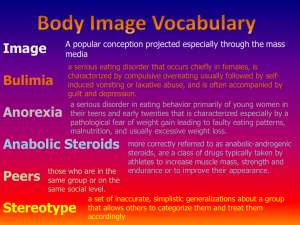
2020 CP PSYCHOLOGY FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE DISORDERS: Anorexia Nervosa- this eating disorder is characterized by caloric restriction, overexercising, and a low BMI. Antisocial Personality Disorder- this personality disorder is characterized by the disregard of the basic human rights of other people. Attention Deficit with Hyperactivity Disorder [ADHD] - this neurodevelopment involves reduced attention, an increase in impulsive behavior, and an overly active and chatty nature. Autism Spectrum Disorder- this neurodevelopment disorder involves deficits in social communication and interaction that begin in infancy/early childhood (ages 2-4) and cause developmental delay. Binge Eating Disorder [BED]- this eating disorder is characterized by eating large amounts of food in a short period of time followed by physical discomfort, guilt, and a dangerously high BMI. Bipolar I Disorder- this disorder is characterized by a pattern of depressed AND fullblown manic episodes. Bipolar II Disorder- this disorder is characterized by patterns of depressed and hypomanic episodes. MINUS full-blown manic episodes. Body Dysmorphic Disorder- this disorder involves a preoccupation with one or more perceived physical defects that are either not seen by others or appear very slight. It can impair social activities, and result in depression, isolation, and eating disorders. Borderline Personality Disorder- a pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and affects, and marked impulsivity. Bulimia Nervosa- this eating disorder is characterized by eating binges followed compensatory activities (“purges”) that may involves self-induced vomiting, laxative use, or other damaging activities. Dissociative Identity Disorder [DID] - this disorder is characterized by two or more distinct and enduring identities or dissociated personality states expressed by the same client. Generalized Anxiety Disorder [GAD] - Excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation), occurring more days than not for at least 6 months, about a number of events or activities (such as work or school performance). Intellectual Disability [ID] - this neurodevelopmental disorder is characterized by an I.Q. below 70 and difficulties in adaption to daily life activities. Histrionic Personality Disorder- a pattern of excessive emotionally and attention seeking. Major Depressive Disorder- this disorder is characterized by a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities and a significant impairment in daily life. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder [OCD] - disorder characterized by recurrent unwanted thoughts and repetitive behaviors. Paranoid Personality Disorder- this personality disorder is characterized by suspiciousness and distrust about the motives of others. Post-traumatic stress disorder [PTSD] - suffering from a traumatic experience and suffer with insomnia, nightmares, and shaky nervousness. Schizoid Personality Disorder- this personality disorder involves a detachment from all social relationship. Schizophrenia- this disorder characterized by disordered and fragmented thinking, delusional beliefs, and hallucinations. CLINICAL TERMS & TESTS: Clinical presentation- these are characteristics of a disorder that are apparent upon examination by a medical or mental health professional. Comorbidity- this is when a patient has a medical and a mental disorder, or two or more mental disorders at the same time. Delusion- false beliefs DSM-V- Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental illness – fifth edition Dual diagnosis- this is when a patient has substance abuse and a mental disorder at the same time. Extravert- people who have this personality trait enjoy spending time with others, and report positive emotions afterwards. Hallucination- skin senses, visual disturbances, or hearing sounds that do not exist. Introvert- people who have this personality trait enjoy solitude or close one-on-one relationships, and are seen as reserved. They do not prefer to be the center of attention. Mental disorder- when behavior atypical, maladaptive, emotionally uncomfortable, and socially unacceptable. Personality-enduring or lasting behavior pattern, throughout your life and all circumstances. Phobia- an intense fear of something Prevalence- this is how many people in a given population are likely to experience a disorder. Psychology- the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Stress- the physical, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral response to threatening or challenging events. Traits- a consistent, enduring way of describing how we think, feel, or behave. Word salad- to speak in an incoherent jumble of words. TREATMENTS Altruism- positive behavior done with no expectation of personal reward. Biological therapy- therapy methods that include medication and surgery. Group therapy- this type of therapy has clients regularly meet in a group setting to discuss their problems under the guidance of a trained professional. Humanistic therapy- therapy method founded by Carl Rogers that includes unconditional positive regard, genuine acceptance, and active listening Pharmacotherapy- this therapy method primarily involves drugs prescribes by a psychiatrist and monitored by a medical team. Psychotherapy- this Freudian method involves engaging in free association, and talking about your childhood, your past, and your dreams. PEOPLE Solomon Asch- While Asch's work illustrated how peer pressure influences social behavior (often in negative ways), Asch still believed that people tended to behave decently towards each other. Sigmund Freud- the founding father of psychoanalysis, a method for treating mental illness and also a theory which explains human behavior. Freud believed that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality. Kitty Genovese (Bystander Effect)- The murder of Kitty Genovese showed that crowd presence negatively impacts the human desire to help those in need. Carl Rogers- This psychologist founded humanistic therapy, which includes unconditional positive regard, genuine acceptance, empathy, and active listening. Elisabeth Kübler-Ross- the five stages of death and dying, which are denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance Abraham Maslow- developed a hierarchy of needs to explain human motivation. His theory suggested that people have a number of basic needs that must be met before people move up the hierarchy to pursue more social, emotional, and self-actualizing needs. Stanley Milgram- His research demonstrated how far people are willing to go to obey authority. His experiments are also remembered for their ethical issues, which contributed to changes in how experiments can be performed today. Psychiatrist- These professionals have four year degrees, have been to medical school, and can write prescriptions. Psychologist- These professionals have four year degrees, masters degrees, and can provide many kinds of clinical and therapeutic services to clients. They cannot write prescriptions or order and interpret medical testing. Wilhelm Wundt- He developed the first psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany. His nickname is "The Father of Psychology". Phil Zimbardo (Stanford Prison Experiment)- This social psychology experiment was terminated prematurely after violent behavior by the guards caused a prisoner revolt.