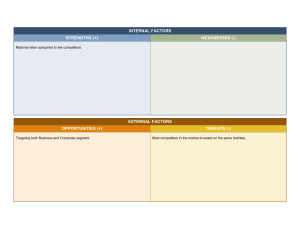
CHAPTER 4 SMALL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AND PLANNING by Mohd Zaini Zainudin MPU22012 – ENTREPRENEURSHIP POLYTECHNIC VERSION 1 Woot! Woot! MOHD ZAINI ZAINUDIN LECTURER Hi Everyone, you are in Entrepreneurship MPU22012 class! INTRODUCTION Definition of business plan, the purpose of business plan, the important elements, and the standard format of the business plan. The characteristics of a good business plan, format and minimum requirement required by financial institutions and government agencies. TOPIC OUTLINES Upon completing this course, students should be able to : 1. Explain the overview of business plan. 2. Explain human resource management for small business. 3. Explain marketing elements for small business. 4. Explain basic operation management for small business. 5. Explain the basics of a financial plan for small business COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completing this course, students should be able to : 1. Develop a viable business plan by organizing business objectives according to priorities. (A4, CLS 4) BUSINESS PLAN “ DEFINITION A formal statement of goals, and plans business reasons they are attainable, for reaching them. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals. 5 BUSINESS PLAN Business Plan Pain “Business Plan: A document investors make you write that they don’t read.” – Steve Blank Silicon Valley entrepreneur 6 what you do today can improve all your tomorrows! Mr Jai - someone smart HERE WE GO! BUSINESS PLAN TIMELINE OVERVIEW ORGANIZATION PLAN MARKETING PLAN HERE WE GO! BUSINESS PLAN TIMELINE PRODUCTION PLAN FINANCIAL PLAN CREATE BUSINESS PLAN OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN 1 OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN BUSINESS PLAN 10 OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN DEFINE BUSINESS PLAN PURPOSE OF BUSINESS PLAN 11 OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN i DEFINE BUSINESS PLAN • A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a marketing, financial and operational viewpoint. • Include: An executive summary - this is an overview of the business you want to start. Your vision and business idea - a short description of who you are, what you plan to sell or offer, why and to whom, your business goals and key selling points - see your business, its products and services. • Written document between 25 to 40 pages. Must be blueprint of company (logical & realistic) • To convinces the reader – business can produce enough revenue or profit and sound investment opportunities. 12 OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN ii PURPOSE OF BUSINESS PLAN • It spells out your purpose, vision and means of operation. It also serves as your company's resume, explaining your objectives to investors, partners, employees and vendors. • 2 primary purposes : o First - used to help run your company with a more cohesive vision. It is your roadmap. By truly analyzing your plan for marketing, sales, manufacturing, website design, etc., you greatly improve your chances for success. o Second - to be the reason most clients request plan. That is, a financial institution or other lender will not invest in your company unless you can demonstrate that you have a roadmap to success. Banks want to mitigate their risk of default and private investors, such as Angel’s, want a realistic forecast for when they will be reaping a return on their capital. 13 OVERVIEW OF BUSINESS PLAN ENTREPRENEUR SHAREHOLDER SUPPLIERS CLIENTS / CUSTOMERS BANKERS / CREDITORS / FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS MANAGEMENT / EMPLOYEES INVESTOR 14 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN 2 BUSINESS PLAN IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN 15 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN IMPORTANT ELEMENT 01 ORGANIZATION PLAN 04 FINANCIAL PLAN 02 MARKETING PLAN Fantastic 4 03 PRODUCTION PLAN 16 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN i VISION & MISSION iii SWOT ANALYSIS 01 ORGANIZATION PLAN ii ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 17 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN - VISION & MISSION Vision & Mission MISSION More specific than your vision. Expresses the "what and how" of your effort, describing what your group is going to do to make your vision a reality. An example of a mission statement: "Our mission is to develop a safe and healthy neighborhood through collaborative planning, community action, and policy advocacy.“ While your vision statement inspires people to dream, your mission statement should inspire them to action. Make it concise, outcome-oriented, and inclusive. VISION Your dream, a picture of the ideal conditions for your community. As a unifying statement for your effort, it also reminds you what you are striving to reach and guides important decisions. A vision statement should be a few short phrases or a sentence that conveys your hopes for the future. Catchy phrases such as "Healthy teens," "Safe streets, safe neighborhoods" and "Education for all" illustrate the common characteristics of a vision statement. STRATEGY Strategies explain how your group will reach its objectives. Broad approaches for making change include advocacy, coalition building, community development, education, networking and policy or legislative change. For example, a child health program could choose a broad strategy of social marketing to promote adult involvement with children. Specific strategies guide an intervention in more detail. To promote the health of children, you might also enhance people's skills (offer training in conflict management), modify opportunities (offer scholarships), or change the consequences of efforts (provide incentives for community members to volunteer as youth mentors). 18 WRITE YOUR Mission & Vision Mission Vision ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………... ………………………………………………………………………………………………... IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE Organizational Structure The typically hierarchical arrangement of lines of authority, communications, rights and duties of an organization. Organizational structure determines how the roles, power and responsibilities are assigned, controlled, and coordinated, and how information flows between the different levels of management. 20 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 4 Common Types Of Organizational Structures •Functional •Divisional. •Matrix. •Flatarchy. Watch first 21 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 1. Functional Also commonly called a bureaucratic organizational structure, the functional structure divides the company based on specialty. This is your traditional business with a sales department, marketing department, customer service department, etc. The advantage - individuals are dedicated to a single function. - clearly defined roles and expectations limit confusion. - The downside is that it’s challenging to facilitate strong communication between different departments. CEO Marketing Financial Operational Information Technology 22 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 2. Divisional Refers to companies that structure leadership according to different products or projects. Gap Inc. is a perfect example, there are three different retailers underneath the heading: Gap, Old Navy, and Banana Republic. Each operates as an individual company, but they are all ultimately underneath the Gap Inc. brand. CEO Product A Product B Product C Sales & Marketing Sales & Marketing Sales & Marketing R&D R&D R&D Purchasing Purchasing Purchasing 23 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 3. Matrix Employees have multiple bosses and reporting lines. Not only do they report to a divisional manager, but they also typically have project managers for specific projects. While matrix structures come with a lot of flexibility and balanced decision-making, this model is also prone to confusion and complications when employees are asked to fulfill conflicting responsibilities. 24 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE 4. Flatarchy A ‘flatter’ structure seeks to open up the lines of communication and collaboration while removing layers within the organization. Flatarchies are organizations that aren't quite flat nor are they hierarchical. They are actually a combination of both types of structures. In other words, an organization can be relatively flat yet can create an ad hoc hierarchy to work on a project or function and then disband 25 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – SWOT ANALYSIS SWOT Analysis SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique used to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning. 26 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – SWOT ANALYSIS OUR SWOT Strength What do you do well? What unique resources can you draw on? What do others see as your strengths? S W Weakness What could you improve? Where do you have fewer resources than others? What are others likely to see as weaknesses? What is your organization's Unique Selling Proposition (USP)? Opportunities What opportunities are open to you? What trends could you take advantage of? How can you turn your strengths into opportunities? O T Threats What threats could harm you? What is your competition doing? What threats do your weaknesses expose you to? 27 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : ORGANIZATION PLAN – SWOT ANALYSIS PROS VS CONS PROS Zero cost Important results New ideas CONS Additional research needed Subjective Analysis Submission not critical coffee break Pizza Hut GROUP SESSION! Domino McDonald KFC Iphone Nokia IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN i MARKET STP ii MARKETING MIX iii MARKETING STRATEGY 02 MARKETING PLAN iv COMPETITORS ANALYSIS 31 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP) is a familiar strategic approach in Modern Marketing. STP is second most popular after SWOT / TOWs matrix. In the 1950s, for example, the main marketing strategy was 'product differentiation'. The STP model is useful when creating marketing communications plans since it helps marketers to prioritise propositions and then develop and deliver personalised and relevant messages to engage with different audiences. 32 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION S Segmentation Market segmentation is the activity of dividing a broad consumer or business market, normally consisting of existing and potential customers, into sub-groups of consumers based on some type of shared characteristics. Marketing term referring to the aggregating of prospective buyers into groups or segments with common needs and who respond similarly to a marketing action. Market segmentation enables companies to target different categories of consumers who perceive the full value of certain products and services differently from one another. 33 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION S DEMOGRAPHIC Segmentation GEOGRAPHIC By personal attributes such as : Age marital status gender, ethnicity Sexuality Education Occupation. PSYCHOGRAPHIC Personality risk aversion Values lifestyle. Country Region State City neighborhood. BEHAVIORAL By how people use the product, how loyal they are, or the benefits that they are looking for 34 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION T Targeting Target Marketing involves breaking a market into segments and then concentrating your marketing efforts on one or a few key segments consisting of the customers whose needs and desires most closely match your product or service offerings. It can be the key to attracting new business, increasing your sales, and making your business a success. 35 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION T Targeting Age What age range am I catering my products/services to, Kids, Adults, Senior, Gen X, Millennials Gender Am I targeting men, women, or both sexes Marital Status Are my target customers married or single Family What is their family structure (number of children, extended family, etc.) Location Where do they live? Am I looking to sell locally? Regionally, Nationally Education How well are they educated Income What is their income Occupation What do they do for a living Religion Are they members of a particular religious group Language Are they members of a particular language group Lifestyle What is their lifestyle like Motivation What motivates them Size What is the size of the target market IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION P Positioning Market Positioning refers to the ability to influence consumer perception regarding a brand or product relative to competitors. The objective of market positioning is to establish the image or identity of a brand or product so that consumers perceive it in a certain way. For example: • A handbag maker may position itself as a luxury status symbol • A TV maker may position its TV as the most innovative and cutting-edge • A fast-food restaurant chain may position itself as the provider of cheap meals 37 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKET SEGMENTATION P Positioning Types of Positioning Strategies A few examples are positioning by: • Product attributes and benefits: Associating your brand/product with certain characteristics or with certain beneficial value • Product price: Associating your brand/product with competitive pricing • Product quality: Associating your brand/product with high quality • Product use and application: Associating your brand/product with a specific use • Competitors: Making consumers think that your brand/product is better than your competitors 38 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX Marketing Mix History The term marketing mix was coined in an article written by Neil Borden called “The Concept of the Marketing Mix.” The marketer, E. Jerome McCarthy, proposed a four Ps classification in 1960. Robert F. Lauterborn proposed a four Cs classification in 1993. 39 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX Marketing Mix Marketing Mix is a combination of marketing tools that a company uses to satisfy their target customers and achieving organizational goals. The marketing mix is probably the most famous marketing term. Its elements are the basic, tactical components of a marketing plan. Also known as the 4 P's. 40 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX OUR 4 P’S Product PRODUCT Price The goods and/or services offered by a company to its customers. Place A product refers to any item that intends to satisfy the needs and wants of a target customer. It can be a tangible good, such a clothing item or piece of software, or intangible, like a service or experience Promotion Contribute : variety, quality, design, features, brand name, packaging, services 41 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX OUR 4 P’S Product PRICE Price The amount of money paid by customers to purchase the product. Place Pricing strategy is an art and a science, in that it involves both market data and careful calculations, as well as skillfully balancing between pricing that is too high or too low, and understanding how skewing either way might damage the brand. Promotion Contribute : list price, discounts, allowance, payment period, credit terms 42 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX OUR 4 P’S Product Price Place Promotion PLACE The activities that make the product available to consumers. Place refers to providing customers access to the product, and it also calls into play convenience for the customer. Marketing, through digital means or otherwise, is about putting the right product, in the right place, at the right price, at the right time, in front of the customer. Contribute : channels, coverage, assortments, locations, inventory, transportation, logistics 43 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING MIX OUR 4 P’S Product Price Place Promotion PROMOTION The activities that communicate the product’s features and benefits and persuade customers to purchase the product. Now, how to make an audience aware of the product? Within the framework of the four Ps, promotion refers primarily to marketing communications. Contribute : advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations 44 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING STRATEGY Marketing Strategy Marketing strategy is the section of your business plan that outlines your overall game plan for finding clients and customers for your business. Sometimes marketing strategy is confused with a marketing plan, but they are different. •Marketing strategy focuses on what you want to achieve for your business and marketing efforts. •Marketing plan details how you'll achieve those goals. 45 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING STRATEGY Identify your business goals Using SMART method: •Specific •Measurable •Achievable •Relevant •Time State your marketing goals Research your market Profile your potential customers Profile your competitors Develop strategies to support your marketing goals Write a successful marketing strategy Use the ‘4 Ps of marketing‘ Test your ideas 46 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – MARKETING STRATEGY Marketing Strategy Plan 5W 1H WHO WHAT WHY WHERE HOW WHEN Buyer Persona Description Who is this person? What problems does this buyer have? Problems you solve for this buyer? Why are they buying from you? Actions you’d like them to take Enquire, order, buy, connect, etc. How are you remarkable? What value do you bring? Proof Credibility indicators, guarantees, testimonial, etc. Where are they? Google, blogs, Facebook, Twitter etc. Your company personality, What kind of company are you? Creative, Look and feel, Tone of voice, Language you’d use Keyword phrase, What buyers type into Google Marketing tactics & Content strategy, etc. Things to do today Things to do next week Things to do next month 47 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – COMPETITORS ANALYSIS Competitors Analysis Identifying your competitors and evaluating their strategies to determine their strengths and weaknesses relative to those of your own product or service. 48 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – COMPETITORS ANALYSIS Once you identify your main competitors, answer these questions about each one. And be objective. It's easy to identify weaknesses in your competition, but less easy (and a lot less fun) to recognize where they may be able to out perform you: What are their strengths? Price, service, convenience, extensive inventory are all areas where you may be vulnerable. What are their weaknesses? Weaknesses are opportunities you should plan to take advantage of. What are their basic objectives? Do they seek to gain market share? Do they attempt to capture premium clients? See your industry through their eyes. What are they trying to achieve? What marketing strategies do they use? Look at their advertising, public relations, etc. How can you take market share away from their business? How will they respond when you enter the market? 49 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – COMPETITORS ANALYSIS Name of Store (and link) HQ Mission Product Statement Offering Sales Channels (i.e. Amazon, eBay, Facebook, physical store, etc.) Strengths Weaknesses Competition Category (Primary, Secondary, Tertiary) 50 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : MARKETING PLAN – COMPETITORS ANALYSIS 1000 800 600 400 200 [COMPANY NAME] [COMPETITOR 1] [COMPETITOR 2] [COMPETITOR 3 [COMPETITOR 4 51 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN i OPERATION AND PRODUCTION PROCESS 03 PRODUCTION PLAN iii LAYOUT PLANNING ii RAW MATERIAL SOURCES 52 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – OPERATION AND PRODUCTION PROCESS Operation And Production Process Production and Operations Management ("POM") is about the transformation of production and operational inputs into "outputs" that, when distributed, meet the needs of customers. 53 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – OPERATION AND PRODUCTION PROCESS Example 54 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – OPERATION AND PRODUCTION PROCESS Example 55 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – RAW MATERIAL SOURCES Raw Material Sources Raw materials are the resources used by a company to produce its finished goods and products. 56 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – RAW MATERIAL SOURCES Raw materials can be divided into 2 groups: Direct materials are used within the final product. Examples include the wood used to make furniture or the fabric used to make clothing. Indirect materials are used throughout the production process, but are not directly included in the final product. Examples include the oils used to maintain machinery or the lightbulbs in a factory. 57 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – LAYOUT PLANNING Layout Planning Deciding on the best physical arrangement of all resources that consume space within a facility. 58 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – LAYOUT PLANNING Example 59 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : PRODUCTION PLAN – LAYOUT PLANNING TIPS TO DO 03 02 01 OFFICE LAYOUT FURNITURE + STORAGE + EQUIPMENT OFFICE ACTIVITIES 60 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN i BUSINESS STARTUP COST ii BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS iii INCOME STATEMENT 04 FINANCIAL PLAN iv CASH FLOW 61 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – BUSINESS STARTUP COST Business Startup Cost Startup costs are the expenses incurred during the process of creating a new business. All businesses are different, so they require different types of startup costs. Online businesses have different needs than brick-and-mortars; coffee shops have different requirements than bookstores do. Advertising and promotion Borrowing costs Employee expenses Equipment and supplies Insurance, license and permit fees Research expenses Technological expenses 62 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – BUSINESS STARTUP COST Example 63 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS Break Even Analysis Break-even analysis is a technique widely used by production management and management accountants. Total variable and fixed costs are compared with sales revenue in order to determine the level of sales volume, sales value or production at which the business makes neither a profit nor a loss (the "break-even point"). 64 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS Example Break Even Point = 𝑭𝑭𝑭𝑭𝑭𝑭 𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪 𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺𝑺 𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷𝑷 −𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽𝑽 𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪𝑪 65 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS 66 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – INCOME STATEMENT Income Statement An income statement or profit and loss account is one of the financial statements of a company and shows the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period. It indicates how the revenues are transformed into the net income. 67 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – INCOME STATEMENT Example 68 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – CASH FLOW Cash Flow the total amount of money being transferred into and out of a business, especially as affecting liquidity. 69 IMPORTANT ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS PLAN : FINANCIAL PLAN – CASH FLOW 70 keep your head in the cloud international community innovations job descriptions god bless scientist we know how to make it right monthly staff trainning people first knowledge celebrate together teambuilding regular check we are real pro’s CREATE A BUSINESS PLAN 3 CREATE A BUSINESS PLAN BUSINESS PLAN 72 CREATE A BUSINESS PLAN a. Table Of Content b. Execute Summary LETS CREATE! c. Introduction d. Purpose Of Preparing A Business Plan e. Business Background f. Owners Background g. Organizational Plan h. Marketing Plan i. Operational Plan j. Financial Plan k. Project Implementation Schedule l. Conclusion 73 CREATE A BUSINESS PLAN PROJECT TIMELINE planning writing submit Group discussion Content power Binding well week phase 1 – planning phase 2 – writing phase 3 – submit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 LET’S PLAY THANKS! Does anyone have any questions? mozaspace@gmail.com.com 76