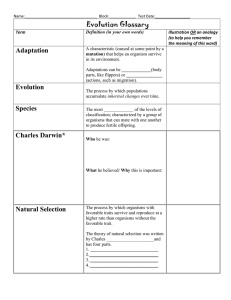
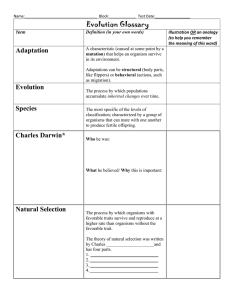
Unit 2 – Evolution – Review KEY 1. Objective Page 2. Lamarck: Use or disuse Acquired a trait in your lifetime you could pass it on Not completely accurate or faulty Darwin: “Father of Evolution” Variations More offspring – compete and struggle Survival of the fittest Natural selection 3. Evidence of Evolution: Fossils – impressions/remnants of ancient organisms, use fossils to show how an organism or species change over time. Homologous structures – same structure but different function, ex: batwing, human arm, flipper, show connections to common ancestor. Vestigial Structures – ex: appendix, no longer in use, connected to the past. Embryology – embryo study, if embryos look the same then they must share a common ancestor. Biochemical Comparisons – ATP used, DNA language the same. Widespread distribution of Org. – some organisms come to look the same due to the same environmental pressures – convergence. Analogous Structures – same function, different bones (structures), ex: dragonfly – bird wing 4. Gene – part of a chromosome and controls traits. 5. Body Cells – somatic cells – 46 chromosomes Sex Cells – gametes (sperm/egg) – 23 chromosomes 6. Homozygous – same alleles, purebred – BB or bb Heterozygous – different alleles, hybrid – Bb Selective Advantage – you have an advantage over others to be selected. 7. Genotype – genes/alleles – Bb Phenotypes – physical appearance – brown eyes Monohybrid Cross Segregation X B B B BB Bb b Bb bb P = parents Bb X Bb F1 Generation Genotypic Ratios – 25% BB: 50% Bb: 25% bb or 1BB: 2Bb: 1bb Phenotypic Ratios – 75% brown: 25% blue or 3 brown: 1 blue Punnett Square – chance or probability of an occurrence. P = RrYy X RrYy Use foil = first outside inside last 8. Law of Segregation: Mendel's Law of Segregation states that every organism has two alleles per trait and that these alleles separate during meiosis, so each gamete gets one allele. 9. Reproductive Isolation: isolating mechanisms Behavioral – act differently, ex: mating dance Time/ Temporal – different mating season Geographical – physically separated, ex: mtn or island Ecological – different habitats, ex: desert verses arctic 10. Gradualism – gradual change in species, SLOW Punctuated Equilibrium – slow and steady is interrupted with a rapid change, ex: asteroid and mass extinctions 11. Father of Taxonomy = Linnaeus 2 name naming = binomial nomenclature (genus and species) 12. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species (most natural) 13. Dichotomous Key: 14. 3 DOMAINS: D Bacteria Archae Eukarya K Eubacteria (cell wall, pep) Archaebacteria (cell wall, no pep) Animali, Fungi, Plantae, Protista 15. Molecular Clock: Neutral mutations happens regularly Use these mutations to group organisms Same mutations they are more closely related 16. Phylogeny – study of evolutionary relationships among organisms. Example: African Vulture………..American Vulture………..…Stork Physically same Genes are closer matched Phylogenetic Tree: is a Cladogram diagram Paraphyletic (some) Monophyletic (one common ancestor) ((one common ancestor) Polyphyletic (does not include common ancestor)