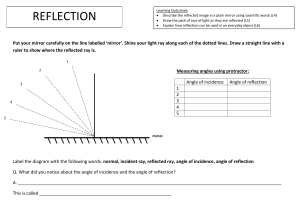
Light What will you learn ….. ■ Reflection of light ■ Refraction of light ■ Dispersion of light ■ Color Light Light is way of transferring energy Light sources give out light. We say that luminous An object that don’t give out light called non - luminous Energy from the sun to the earth by light waves. It called thermal heat Light intensity can be measured by light meter. The unit of it is lux. Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 km/s At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second. Travel of light Light travels in straight line (rectilinear) You can not see the light unless all the three holes are exactly line up Shadows Shadows are dark area where something blocks out light The shadow appears behind the object. The size and shape of it depend on position and size of the light source compare to the object We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework Properties of Light summary 1) 2) 3) 4) Light travels in straight lines (rectilinear) Light travels much faster than sound We see things because they reflect light into our eyes Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object Reflection Types of materials Transparent Will let all the all light rays through Translucent Will let some of the light rays through Opaque Will let no light rays through Reflection in a mirror • The flat mirror is a good reflector of light and is also called a plane mirror. • Look at yourself in a mirror. What you see is an image of yourself. • You can see your image in the mirror because light rays from your body are regularly reflected by the mirror into your eyes. object image RAY DIAGRAM (REFLECTION) • • The incident ray AO strikes the mirror at point O. Incident ray AO makes an angle of incidence, i, with the normal. A incident ray i r N B • • • reflected ray The reflected ray OB travels into the boy’s eye. Ray OB makes an angle of reflection, r, with the normal. Angle i = angle r O • When a ray of light is reflected from a surface, there is a rule that govern its reflection, which is known as the law of reflection. The law of Reflection • Incident ray : a ray of light falling on the surface • Reflected ray : the incident light ray bouncing back after striking the reflecting surface Normal Incident ray i r Reflected ray • Normal ray : the line is drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface mirror The angle of incidence = The angle of reflection The law of reflection • Angle of incidence (i) : the angle between normal and and incident ray • Angle of reflection (r) : the angle between normal and the reflected ray The law of reflection The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection Reflection in a mirror • Characteristics of plane mirror images o The distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the distance of the object from the mirror. o The image and the object are the same size. o The image is upright. o The image is laterally inverted. This means the left and right side of the image are reversed. o The image is virtual. This means that the image cannot be projected onto a screen behind the mirror. Refraction Refraction • Light bends when a light ray travels from one medium to another medium of different density (such as from air to water). • This bending of light is known as refraction Refraction ■ It is caused by different speeds of light in different media ■ The light change angles and speed of travel ■ The greater density of medium, the slower the speed of the light, so the light will be refracted more In air, light travels about 300 million km/s but in water only 230 million km/s Why does refraction happen? • The rows of a soldier changes the direction because there is a change in speed when they enter two different region from concrete to sand • The more dense (higher density) material will slow down the light more, so the light will be refracted more Refraction : air to water ■ If light goes from a less dense medium (air) to more dense medium (water), It slows down ■ The direction of the ray will move towards the normal The angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence Refraction : water to air ■ If light goes from a more dense medium (water) to less dense medium (air), it speeds up. ■ The direction of the ray will bend away from the normal. The angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence DISPERSION Dispersion ■ Dispersion is the separation of light into different colour ■ When the ray light enter a triangular glass called prism, it slows down and get refracted. ■ Dispersion happen because different colours of light are refracted in different amounts. ■ Red light is refracted the least while violet is refracted the most.. Colours All the colours of light can be made up by 3 primary colours : Red, Blue and Green If two primary colours are combined any two of primary colour, it will make secondary colour. When all the three primary colour being mixed, it made white light. RGB & RGY Colours ■ Coloured filters are used to produce different colour from white light ■ Coloured filter only let the colour pass that they are, another colours are absorbed. Eyes identify colours Eye can detect different colours of light because of light sensitive cells in retina called rods and cones. 1 in 20 people have cones that do not work properly so they don’t see colours accurately called colour blindness.