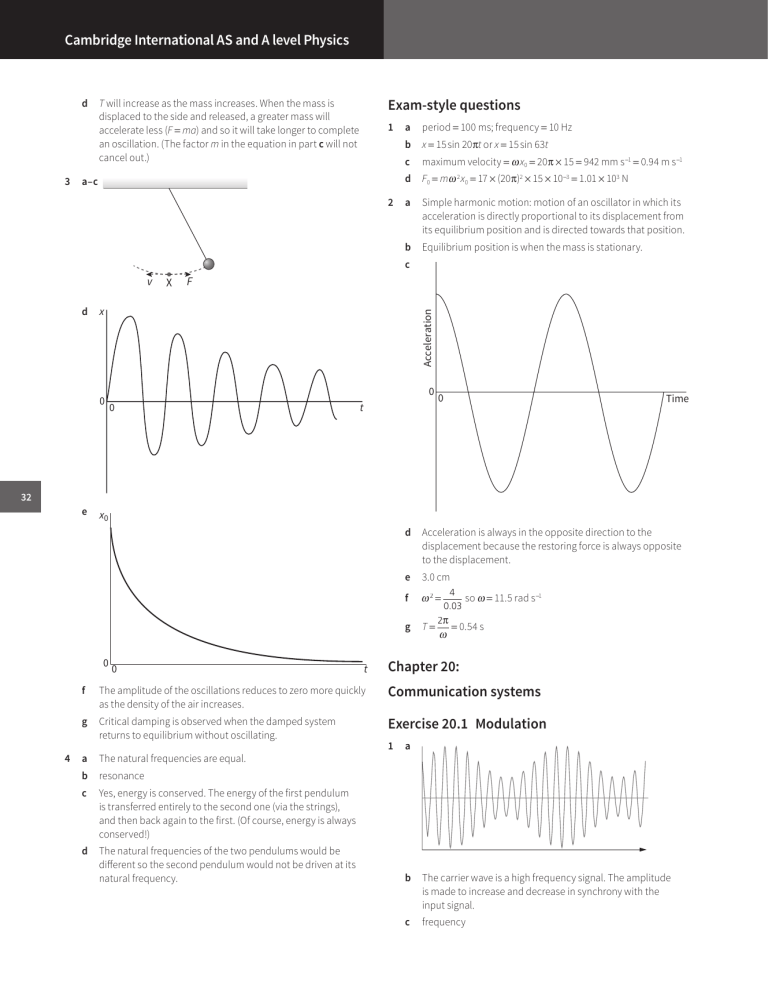
Cambridge International AS and A level Physics d 3 T will increase as the mass increases. When the mass is displaced to the side and released, a greater mass will accelerate less (F = ma) and so it will take longer to complete an oscillation. (The factor m in the equation in part c will not cancel out.) Exam-style questions 1 a–c 2 a period = 100 ms; frequency = 10 Hz b x = 15 sin 20πt or x = 15 sin 63t c maximum velocity = ω x0 = 20π × 15 = 942 mm s −1 = 0.94 m s −1 d F0 = mω 2 x0 = 17 × (20π)2 × 15 × 10 −3 = 1.01 × 103 N a Simple harmonic motion: motion of an oscillator in which its acceleration is directly proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position and is directed towards that position. b Equilibrium position is when the mass is stationary. c v F x 0 Acceleration d X 0 0 t 0 Time 32 e x0 0 0 t Acceleration is always in the opposite direction to the displacement because the restoring force is always opposite to the displacement. e 3.0 cm f ω2 = g T= 4 so ω = 11.5 rad s −1 0.03 2π ω = 0.54 s Chapter 20: f The amplitude of the oscillations reduces to zero more quickly as the density of the air increases. Communication systems g Critical damping is observed when the damped system returns to equilibrium without oscillating. Exercise 20.1 Modulation a The natural frequencies are equal. b resonance c Yes, energy is conserved. The energy of the first pendulum is transferred entirely to the second one (via the strings), and then back again to the first. (Of course, energy is always conserved!) d The natural frequencies of the two pendulums would be different so the second pendulum would not be driven at its natural frequency. 1 4 d a b The carrier wave is a high frequency signal. The amplitude is made to increase and decrease in synchrony with the input signal. c frequency Answers 2 a 3 a Record a value (usually of voltage) of the signal at one instant. b 2.07 × 109 c To recover the analogue signal in its original form from the digital signal. a a signal that is continuously variable within limits b, c 3 4 b The carrier wave is a high frequency signal. The frequency is made to increase and decrease in synchrony with the input signal. c amplitude a less interference or less noise; larger bandwidth or better quality b smaller bandwidth means more stations in a given frequency range; cheaper radio sets as electronics less complex; covers a greater area as wavelengths used are longer a 2.0 × 10 s b 2.0 × 10 −4 s c Power −5 4 0 5 6 7 b 3 0 c Time 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 d digital-to-analogue converter e The largest 4-bit number is 1111 = 15 and so, including 0, there are 16 possible values. f If S changes V1 in between the samples it has no effect on the ADC. g have more bits and sample more frequently h The parallel-to-serial converter takes the 4 bits of each digital sample and then emits it as a series of bits, one after the other. The serial-to-parallel converter takes the series of bits and converts them into the 4 separate bits. a random and unwelcome power that distorts the transmitted signal b as long as the noise does not make a 0 too close to a 1 or a 1 too close to a 0 then 0 and 1 can be recognised c needs fewer amplifiers or they can be further apart Exercise 20.3 Channels of communication 45 50 55 Frequency / kHz 1 a polar orbit geostationary orbit d a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, produced as a result of the modulation process e 45 and 55 kHz f 10 kHz a 8600 Hz b weather forecasting; spying; monitoring the surface b 31 c one day or 24 hours a 6.0 V d b 860 kHz The satellite orbits in the same time as the Earth rotates and is fixed over a point on the equator. c 740 kHz e Polar regions d 20 Hz a a 6.5 V linking a ground station to a satellite; t.v. from a satellite; mobile phones b 5.5 V b connecting an aerial to a television; computer network connections; audio and video connections c 800 kHz c d 5000 older telephone and computer connections; linking hi-fi to a loudspeaker a wire pair: two wires twisted together coaxial cable: copper braid on outside, core is a copper wire separated from the core by an insulator b Signal in one wire pair is picked up by a neighbouring wire pair. c Outer of coaxial cable is earthed and shields the core from noise or external signals. Exercise 20.2 Analogue and digital signals 1 Voltage / V 2 a a basic unit of information storage stored as a binary digit 0 or 1 b 1011 c three d the first one e five 2 3 33 Cambridge International AS and A level Physics 4 5 a They pass through the ionosphere with little reflection and can carry large amounts of information. b To prevent the satellite’s high power transmitted signal swamping reception of the very low power signal received from Earth. c Space wave to satellite, sky wave reflected from ionosphere, surface wave travels direct. d Ionospheric reflection varies as layers of ions vary in height and density according to the time of day. iii iv b Optic fibres have a wide bandwidth and large transmission capacity. Signal power losses are relatively small and allow longer distances between regenerator amplifiers. The diameter, weight and cost of fibre optic cables are much less than those of metal cables. Optic fibres have negligible ‘cross-talk’ and do not pick up electromagnetic interference. c 2 34 a 2.0 b 15.8 a 190 or −190 dB b Logarithm provides a smaller number or attenuation in series is added when using logarithms. increases as the signal reduces and the noise remains, approximately, constant i 1.52 mW ii 27 dB iii 4.5 km i less attenuation with fibre optic cable; longer distance before signal attenuated to minimum acceptable signal; also, noise may be lower on an optic fibre ii larger bandwidth; larger transmission capacity; smaller diameter, weight and cost; negligible ‘cross-talk’; less electromagnetic interference/noise Chapter 21: 20 dB 4 3.0 × 10 −14 W 5 a 6.0 × 10 −2 mW or 6.0 × 10 −5 W b 49.6 km 7 Thermal physics Exercise 21.1 Kinetic model and internal energy 1 3 6 a 4.6 × 10 −4 W b 7.3 × 10 −3 W a 240 dB b six 2 Exam-style questions 1 a most closely together: solid farthest apart: gas b They vibrate with greater amplitude; their velocity is greater as they oscillate through the midpoint of their oscillation. c attractive d Potential energy increases as particles are pulled apart; energy is being added to the material. e greater separation: greater potential energy greater speed: greater kinetic energy a greater amplitude of oscillation b greater separation c The potential and kinetic energies of the atoms have increased. a Amplitude of carrier wave varies in synchrony with the displacement of the information signal. a B b i spectrum A as only the carrier wave is present b ii spectrum C as the carrier and one signal in the two sidebands is present More molecules in B have sufficient kinetic energy to escape from the surface of the water. c iii spectrum B as the carrier and two sidebands are present; music has a number of different frequencies and thus different lines in the sidebands Evaporation means that the molecules with the highest kinetic energies escape, so the average kinetic energy of the molecules remaining in the liquid decreases. d More molecules escape initially from B (see answer to b), so the average kinetic energy of the molecules remaining in the liquid decreases more quickly. c d 2 ⎛ signal power ⎞ 10 lg ⎜ ⎝ noise power ⎟⎠ v Exercise 20.4 Attenuation 1 thermal vibrations of the atoms of the material; electrical interference (for example, wire acts as aerial); induced emf caused by change in magnetic field a i 200 kHz ii 3.0 kHz iii 12 kHz 3 a average speed of the particles increases disadvantages: more noise; more interference; less bandwidth; lower quality b total kinetic energy increases c temperature of the gas increases advantages: longer range; fewer repeaters or transmitters needed; less complex electronics; cheaper d a force is doing work e 2.4 J i the gradual loss of power along a wire ii thermal energy lost in the wire 4