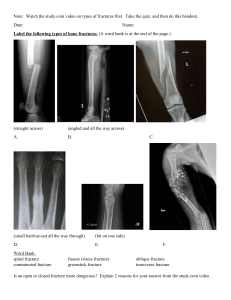
The lower extremity refers to the part of the body from
the hip to toes. The lower extremity includes the hip,
knee, and ankle joint, and the bones of the thigh, leg,
and foot.
Many people refer to the lower extremity, it as leg.
There are three types of
injuries:Acute injuries
Overuse injuries
Chronic injuries.
An acute injury, on the other hand , is an injury that
occurs suddenly and is usually associated with trauma
such as cracking a bone, tearing a muscle or bruishing.
It could result of falling or crashing into another player
during sports.
Chronic/overuse sports injuries out number sudden
acute injuries in almost every athletic activity, but
because these injuries are not instantly disabling , they
attract less medical attention than those that cause a
sudden and obvious loss of function.
An achilles tendon rupture means the tendon behind
the ankle rupture{tears}.
This can happen when, for example the foot bearing
the body’s weight launches powerfully off the ground
while the leg is straight.
All acute and chronic ankle injuries should be
treated using the P.R.I.C.E. principles
(protection, rest, ice, compression & elevation)
as soon as possible after injury. This should be
applied at home for at least the first 2 – 3 days.
The muscle gastrocnemius and soleus commonly
referred to as calf muscles are located on posterior
side of lower leg.
These muscles are particularly vulnerable to strains in
many sports. Especially ball sports.
A common situation that can lead to a strained ball. It
is important to apply the PRICE principle on the acute
phase to help reduce pain, minimise swelling and
prevent further injury.
1. Rest your injured leg. ...
2. Put ice or a cold pack on the
sore muscle for 10 to 20
minutes at a time to stop
swelling. ...
3. After 2 or 3 days, you can try
alternating cold with heat. ...
4. Wrap your lower leg with an
elastic bandage (such as an
Ace wrap) to help decrease
swelling.
An injury of musculoskeleton system the result from the combined
fatigue effect over a period of time beyond the capabilties of the
specific structure.
Symptoms :Gradual onset of pain.
Pain presenting as an ache.
No history of direct injury.
Stiffness or aching after or during training or competition.
Increasing periods of time for pain to go away.
Point tenderness.
Visible swelling.
Examples such as achilles tendinopathy, shin plints ,iliotibial
band,etc…
Treating overuse injuries requires:-
Rest
2. Reducing exercise intensity , frequency and duration.
3. Icing an overuse injury and use PRICE RULE.
4. For more serious conditions physical therapy, over
the counter {OTC} medications,
1.
Many overuse injuries happen over time and often
have subtle symptoms. This can result in a delay in
diagnosis and treatment, and delays can lead to more
serious or disabling injuries.
Signs include;1. Pain when performing an activity
2. A dull ache when at rest
3. Swelling .
Pelvic fracture:Anterior inferior iliac spine avulsion injury
Duverney fracture
Malgaigne fracture
Proximal femoral fractures
Bisphosphonate-related proximal femoral fractures
Until help arrives a person
with a suspected pelvic
fracture should be covered
with a blanket or jacket and
should not be moved by
non-trained personnel,
especially if there is severe
pain. If you are at a serious
road accident and a person
is walking around, get them
to sit still
Segond fracture
Patella fracture
ACL avulsion
PCL avulsion
Tibial plateau fracture
1. Stop your activity
immediately. ...
2. Rest the joint at first.
3. Reduce pain, swelling and
internal bleeding with
icepacks, applied for 15
minutes every couple of
hours.
4. Bandage the knee firmly and
extend the wrapping down
the lower leg.
5. Elevate the injured leg.
Triplanar fracture
Pilon fracture
Bosworth fracture
Tillaux fracture
Wagstaffe-lefort fracture
Maisonneuve fracture
Weber fractures of the ankle.
Avulsion of the 5th metatarsal
March fracture
Jones fracture
Lisfranc injury
Calcaneal fracture
Lover’s fracture
Aviator fracture
Beak fracture
Nutcraker fracture
Snowboarder fracture.
1. Rest: Stay off the
injured foot or limit
weight bearing until it
gets better or can be seen
by a doctor. ...
2. Ice: Immediately apply ice
to the injury to reduce
pain and swelling. ...
3. Compression: Snuggly
wrap the foot in a soft
dressing or bandage
Lower extremity venous stasis ulcers
Arterial (diabetic) wounds
Non- healing post surgery wounds
Traumatic wounds
Pressure related wounds
Advanced technologies for diagnosis and treatment.
Interventional and surgical treatment to improve poor
circulation and heal skin.
Antibiotics, if an infection is present.
following a healthy diet, as recommended, including
plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Wearing appropriate shoes.
Changing the dressing as directed.
Dressing should be kept clean and dry .