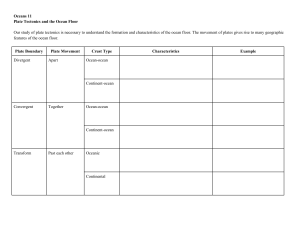
Plate tectonics Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1910) Hypothesized that all the continents were once joined together in a single landmass call Pangaea and have since drifted (like rafts in water) ○ This became known as CONTINENTAL DRIFT ○ Pangaea- supercontinent (350-200 million years ago) (Pangaea means “all lands” in latin) Others had similar ideas, however Wegener was the first to have scientific evidence to support this idea Plate tectonics Evidence for Continental drift 1.)Geologic features Coastlines of some continents seemed to fit together like a jig saw puzzle Mountain ranges in N. America line up with those in Europe Plate tectonics 2.) Fossils- any trace of an ancient organism that is preserved in rock Glossopteris- fern like plant with leaves the shape of a tongue, live 250 million years ago ○ Found in Africa, South America, Australia, India and Antarctica These land masses are now separated by oceans indicating that Pangea once existed Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus- fresh water reptiles ○ Fossils found in places separated by oceans Neither reptile could have swum that great of a distance in salt water - These reptiles lived on a single landmass that split apart Plate tectonics 3.) Climate Fossils of tropical plants found on an island in the arctic ocean Scratches in rocks made by glaciers found in South Africa Coal fields in Europe and North America lined up Coal only forms in tropical swamp areas ****When continents move, north or south, they take the fossils and rocks that formed in the past with them Plate tectonics Continental Drift—REJECTED Wegener provide supporting evidence to the continental drift theory BUT…. Could not identify the mechanism that cause the plates to move (the force that caused the push or pull) because of this, most geologist rejected his theory Plate tectonics The theory of Plate Tectonics Plate- A section of the lithosphere that slowly moves over the asthenosphere, carrying pieces of continental and oceanic crust Theory of Plate TectonicsEarth’s plates are in slow, constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Convection current –A flow of material caused by temperature differences Faults-breaks in the Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other, form along these boundaries Convection Currents Occurs in the asthenosphere of the mantle How Convection Works: Heat from Earth’s core causes the material of the mantle to become a plastic like solid (it can stretch and “flow”) Once heated the material becomes less dense so it rises toward the lithosphere At the lithosphere it cannot move upward any more so it moves to the right or the left As it moves, it drags the lithospheric plate with it and cools. The material becomes less dense and it sinks back toward the core The above process is repeated. Convection Currents Plate tectonics Measurement of plate motion over time Satellites are used to measure plate motion precisely. Plates move very slowly between 1-12 cm per year ○ North American and Eurasian plate move about 2.5 cm/year This is about the same speed in which your fingernails grow ○ Although very slow the plates have been moving for hundreds of millions of years so they have moved great distances. Plate Motion Since the breakup of Pangaea, the continents have taken about 200 million years to move to their present location. 200 million years ago 115 million years go Earth Today As the plates move, they create earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges and deep ocean trenches Plate tectonics 3 Types of Plate Boundaries 1.) Divergent Boundariestwo plates slowly move away from each other In the ocean = Mid Ocean Ridge (MOR) ○ Underwater mountain ranges ○ new crust is added during process of sea floor spreading ex. Mid Atlantic Ridge, Atlantic Ocean On land = Rift Valley ○ ex. East African Rift System, Africa Plate tectonics Sea Floor Spreading- the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor at DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES This occurs at mid-ocean ridges (MOR) How sea floor spreading works: MOR form crack in the oceanic crust, called central valley (see pic. on previous slide) Along the ridge, molten material from inside Earth rises, erupts, cools and hardens to form a solid strip of rock ○ Sea Floor spreading adds more crust to the ocean floor while older strips of rock move outward from either side of the ridge Plate tectonics Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading 1.) Drilling samples Scientists drilled into the ocean floor ○ Farther away the sample was taken from the MOR, the older the rock was ○ Youngest rocks were found at the center of the MOR ○ The rocks age shows that sea floor spreading occurs **As distance from the ridge increases, age increases Plate Tectonics 2.) Magnetic Stripes Lava contains iron Iron is magnetic (points to magnetic north) When the lava solidifies, the iron will be “frozen” in the direction of the magnetic north at the time of the eruption Direction of the iron at the seafloor is not always the same. The patterns are mirror images on either side Width of stripe indicates how long the pole was in the normal or reversed position Wider = longer Ocean Floors Mid-ocean ridges rise from the sea floor like stitches on the seams of a baseball. Diagram of MOR where two plates move apart Plate Tectonics 2.) Convergent Boundary-boundary where two plates collide or come together Density of plates determine which one comes out on top Subduction- the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent boundary New crust is hot—less dense Old crust is cool—more dense Deep ocean trenches-A deep valley along the ocean floor beneath which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle ○ Gravity pulls the older, more dense oceanic crust down beneath the trench into the mantle Plate tectonics Three types of convergent boundaries 1.) Oceanic-Oceanic-the one that is more dense will sink beneath the one that is less dense often forms island arc-volcanoes which erupt through the overriding plate as the descending plate melts below it Ex. Aleutian Islands of Alaska 2.) Oceanic-Continental-oceanic crust is more dense so it will sink below continental Mountains (Andes) and volcanoes can form-Volcanic Mountain Range -Water leaves sinking crust, rises into wedge of mantle above it, the water lowers the melting point of the mantle, mantle partially melts and volcano forms -Ex. Andes Mountains ***Trenches generally run parallel to volcanic island arc’s Plate tectonics Types of convergent boundaries cont. 3.) Continental-Continental-neither is dense enough to sink into mantle, no subduction, no trench, mountains form Ex Indian Plate and Eurasian plate collide to form Himalayans Plate tectonics Sea Floor spreading and subduction: ○ work together ○ change the size and shape of the oceans ○ They move the ocean floor like a large conveyor belt. Size determined by how fast new crust is being created and old crust being swallowed Ocean surrounded by many trenches—may shrink Ocean with few trenches—will probably grow larger Plate tectonics 3.) Transform Boundary-place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions. Plates are rocky and jagged, and get “stuck”, forces inside Earth cause plates to become “unstuck”, sudden release of energy in the form of an earthquake ○Crust is neither created nor destroyed. ○Ex. San Andreas Fault in California Subduction Oceanic crust created along a mid-ocean ridge is destroyed at a deep-ocean trench. During the process of subduction, oceanic crust sinks down beneath the trench into the mantle. Plate tectonics Convergent Boundaries (cont.) 3.) Continental-Continental-neither is dense enough to sink into mantle, no trenches, no subduction, mountains form Ex Indian Plate and Eurasian plate collide to form Himalayans Plate Tectonics Earthquake and Volcanic Activity Most earthquakes and volcanoes occur because of the movement of the plates, especially as plates interact at their edges or boundaries. Plate Tectonics Volcanoes, Earthquakes and Converging Boundaries Volcanoes often form where two plates collide. Hot Spots Sometimes, volcanoes do not occur at plate boundaries BUT in the middle of tectonic plates This is called a HOT SPOT Examples: Hawaii, Yellowstone Hot Spot The Hawaiian Islands have formed one by one as the Pacific plate drifts slowly over a hot spot. This process has taken millions of years The island over the mantle plume is the youngest and the island farthest from the mantle plume is the oldest The Ring of Fire The world's most active volcanoes lie along what's called the Ring of Fire. Lines the Pacific Ocean The "ring" stretches along a 25,000-mile (40,000kilometer) arc from the boundary of the Pacific Plate, to smaller plates such as the Philippine Sea plate, to the Cocos and Nazca Plates Results in 90% of the world’s earthquakes Home to 75% of the planets volcanoes