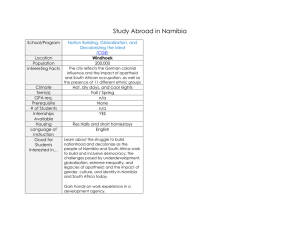
Project Management Chapter 2 Project Management Cycle Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Some more terms……. • Project life cycle • Phases of a project • Phase exits or stage gates • Stakeholders Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Project Life Cycle • Project management is about acquiring or achieving the project goal • Most projects need to be broken down into a logical sequence of ‘phases’, known as the project life cycle. Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Phases of a Project • • • Organisations normally break a project down into several project phases for better management control Collectively, the project phases are known as the project life cycle Each project phase is marked by the completion of one or more deliverables. Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 How do you eat an elephant? Stage Gates • • Each phase ends with a review of the deliverables and performance in order to detect and correct errors and to decide if the project should continue into the next phase. The phase end reviews are often called phase exits or stage gates. Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 4 Phases of a Project • • • • project initiation project planning project execution and control project closure Collectively these four phases represent the ‘project life cycle.’ Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 4 Phases of a Project Project Initiation Project Planning Project Project execution closing and control Scope identification Team set up Project definition WBS OBS Scheduling Network diagrams Reporting Project life cycle Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Hand over Commission Cost and staffing level Project Life Cycle Initiation Planning Execution and control time Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Closing Cost and staffing level Project Life Cycle - Ideal v Typical Initiation Planning Execution and control time Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Closing Exercise What does the chart tell you about typical v ideal project life cycle? Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Answer Cost and staffing level • Many projects don’t get adequate resources in the early stages • Low resourcing in the planning stage results in delays in completing the project on time, to the right quality and within the budget Initiation Planning Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Execution and control time Closing Allocation of time and money……. 10% 25% Initiation Planning 20% 30% 60% Implementation 40% 5% 10% Closing Typical Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Initiation Planning Implementation Closing Successful projects Sydney Opera House • Good or bad project? Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Sydney Opera House • Planned • Actual - 1959 to 1963 (4 years) $7 million 1959 to 1973 (14 years) $100 million Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Project Life Cycle (PLC) as a Tool • • • PLC is a management tool to make it easier to manage the project sequence The choice of phases vary from industry to industry and the PLC will vary to suit the needs of the participants Different project managers choose different PLC’s, depending on the nature of the task i.e. Engineering, software development etc. Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Project Life Cycle (PLC) Uses • • • • • • To maintain an overview of the project To help identify tasks Break the project into manageable parts Integrate activities (bite sized chunks) To help with the timing of decisions (go/no go) To guide the level of contingency needed Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Common characteristics of PLCs • Cost and staff levels low in early phases of the project • Probability of failure, risk and uncertainty are highest in the early phases • Ability of stakeholders to influence the outcome of the project are highest at the beginning of the project • Although many projects have similar phase names, with similar work requirements, few are identical • Sub-projects within a project also have distinct project life cycles Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Project Stakeholders • Project stakeholders are individuals and/ or organisations who are actively involved in the project and whose interests are directly affected by the outcome of the project • Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Key Stakeholders • the project advocate or champion (promotes the idea) • the project sponsor (for funding) • the project manager (for the execution) • customer or client (the user) • the performing organisation (the team) • Other categories of stakeholders can be identified such as internal and external clients, team members & families, suppliers, contractors, Government etc. Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 The Project Management Dilemma Managing stakeholders expectations can be difficult because of the sometimes widely different objectives of the various groups of stakeholders Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Your understanding of the project needs to match stakeholders’ Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic understanding. Work to make sure it is what you end up with! of Namibia, 2012 Stakeholders Identification • Let’s take you completing this course as a project (some people might argue that it isn’t a project – but it is – it has a start and an end date, a clear goal and some phases to it • Who are all the stakeholders? Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Stakeholder Cycle Identify Stakeholders Implement Stakeholder Management Strategy Gather Information on Stakeholders Project Management Team Predict Stakeholder Behavior Identify Stakeholder Strategy Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Identify Stakeholders' Mission Determine Stakeholder Strengths and Weaknesses More information • Chapter 2 – Project Management for Success, Knipe et al Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 For the next session – homework • Think about a project you have undertaken – with your studies, at home, at work or anywhere else • Identify the phases of the project - did you follow each of the 4 phases? • Identify the stakeholders for that project Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 Common characteristics of PLCs • Cost and staff levels low in early phases of the project • Probability of failure, risk and uncertainty are highest in the early phases • Ability of stakeholders to influence the outcome of the project are highest at the beginning of the project • Although many projects have similar phase names, with similar work requirements, few are identical • Sub-projects within a project also have distinct project life cycles Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 In class ‘Mock Test’ 1. What is meant by the term ‘deliverable’? 2. What is meant by the term ‘stakeholder’? 3. List the 4 different phases of a project life cycle 4. List at least 3 benefits from using project life cycle to manage projects Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 In class ‘Mock Test’ 1. What is meant by the term ‘deliverable’? • an output from a stage of the project 2. What is meant by the term ‘stakeholder’? • individuals and/ or organisations who are actively involved in the project and whose interests are directly affected by the outcome of the project 3. What is meant by the term ‘contingency’? • The buffer or safety margin built into a project Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012 In class ‘Mock Test’ 3. List the 4 different phases of a project life cycle – project initiation – project planning – project execution and control – project closure 4. List at least 3 benefits from using project life cycle to manage projects – To maintain an overview of the project – To help identify tasks – Break the project into manageable parts – Integrate activities (bite sized chunks) – To help with the timing of decisions (go/no go) – To guide the level of contingency needed Dr. Jana Jagodick Polytechnic of Namibia, 2012