Lipids Lecture Notes: Structure, Function, and Classification
advertisement

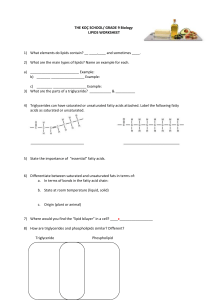
NUR8103LEC NOTES- Lipids Lipids ➢ Heterogeneous class of biological molecules classified on the basis of common solubility E.g. fats and oils ➢ Soluble in organic solvents such as diethyl ether, chloroform, methylene chloride, and acetone but insoluble in water ➢ Amphipathic molecule Molecule that has hydrophilic (water loving) and hydrophobic regions Lipids Open-chain 1. fatty acid 2. triacylgycerols 3. phosphoacylglycerols 4. sphingolipids 5. glycolipids Ring- fused 1. cholesterol 2 .steroid hormoes 2. bile salts Fatty Acids ➢ Unbranched chain of carboxylic acids 12–20 carbons long ➢ Derived from hydrolysis of animal fats, vegetable oils, or phosphodiacylglycerols of biological membranes ➢ Amphipathic compounds ➢ Types Saturated fatty acids Unsaturated fatty acids ➢ Saturated fatty acids -hydrocarbon chain single-bonded with carboxylic acids -have even number of carbon atoms because these fatty acids are built from acetic acid - solid at room temperature, high melting point because of close and regular packing of hydrocarbon chain -found in animal fats and resist oxidation ➢ Unsaturated fatty acids -cis isomer predominates while trans isomer is rare -cis double bond puts a kink in the long-chain hydrocarbon tail -shape of a trans fatty acid is like that of a saturated fatty acid in its fully extended conformation -double bonds are isolated by several singly bonded carbons -have lower melting points than their saturated counterparts, liquids at room temperature -greater the degree of unsaturation, lower the melting point -essential fatty acids- linoleic (C18) and arachidonic (C20); polyunsaturated, not synthesized in the body, must be obtained from the diet -usually found in vegetable oils and can undergo oxidation producing short chain aldehydes and carboxylic acids - can undergo hydrogenation reaction producing saturated fatty acids ➢ Fatty Acid Nomenclature: - named according to the number of C atoms and to the number and position of any double bonds. - systematic name: add ‘oic acid’ on the name of the parent hydrocarbon - but fatty acids at physiological pH are ionized and name ending with ‘ate’ than ‘oic acid’ and represented as RCOO- shorthand notation: 18:0= fatty acid with 18 carbon and 0 double bonds 18:2= fatty acid with 18 carbon and 2 double bonds cis, cis- Δ9, Δ12 … =first C=C is between C 9 and 10 and the second C=C is between C12 and 13 ➢ Omega-3 fatty acid - polyunsaturated fatty acids found abundantly in marine animals: linolenic (18:3Δ9,12,15), eicosapentaenoic acid /EPA (20:5-Δ5,8,11,14,17), docosahexaenoic acid/ DHA (22:6Δ4,7,10,13,16,19) - associated with low occurrence of atherosclerosis and heart attacks even in a high-fat diet and high levels of cholesterol (HDL) - lower the ability of platelets to form blood clots - omega-3: double bond at C3 farthest from the -COOH group - omega-6: polyunsaturated fatty acids found abundantly in vegetable oils such as linoleic (C18) and arachidonic acids (C20) Prostaglandins ➢ Derived from fatty acids ➢ First detected in seminal fluid, which is produced by the prostate gland ➢ Arachidonic acid Metabolic precursor of all prostaglandins Contains four double bonds, which are not conjugated Have five-membered rings Differ from one another in numbers and positions of double bonds and oxygen-containing functional groups Physiological effects of prostaglandins: 1. Activation of inflammatory response in joints 2. Production of fever 3. Production of pain 4. Induction of blood clotting Triacylglycerols(triglycerides) ➢ formed by esterification of three fatty acids to glycerol ➢ ester groups are polar part and the tails are nonpolar part of the molecule ➢ stored in adipose tissues and give means of storing fatty acids ➢ lipases hydrolyze ester bonds when fatty acids are used by organisms ➢ act as concentrated stores of metabolic energy ➢ Acrolein test - presence of glycerol ➢ Br2- unsaturation test ➢ Saponification ➢ Reaction of glyceryl ester with NaOH or KOH to produce glycerol and respective Na or K salts (soaps) ➢ ➢ Soaps form water-insoluble salts when used in hard water, which contains Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe3+ Glycerol is used in creams and in the manufacture of nitroglycerin Phosphatidic acid ➢ ➢ ➢ Compound in which two fatty acids and phosphoric acid are esterified to the three hydroxyl groups of glycerol Phosphoric acid is triprotic in nature One molecule can form ester bonds to glycerol and to some other alcohol to create phosphatidyl esters Phosphatidyl ester Figure 5. Structure of phosphatidyl ester ➢ Structure ➢ Long, nonpolar, hydrophobic tails Polar, highly hydrophilic head groups Nature of fatty acids in a molecule varies widely Amphipathic Classified as phosphoacylglycerols Classification depends on the second alcohol that is esterified to the phosphoric acid Phosphoacylglycerol ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ Polar head is charged Phosphate group is ionized at neutral pH Positively charged amino group is contributed by an amino alcohol esterified to the phosphoric acid Phospatidylserine- (+) in Ninhydrin test Structures of phosphatidylcholine(lecithin); phosphatidylserine; phosphatidylethanolamine(cephalin) Waxes ➢ Complex mixtures of esters of long-chain carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols ➢ Serve as protective coatings for plants and animals Sphingolipids ➢ Contain sphingosine, a long-chain amino alcohol ➢ Found in plants and animals ➢ Abundant in the nervous system ➢ Sphingomyelin Primary alcohol of sphingosine is esterified to phosphoric acid, which is esterified to choline Glycolipids ➢ Lipid bonded to a sugar ➢ Ceramides= parent compounds of glycolipids ➢ Cerebroside= compound formed-primary alcohol group of the ceramide and a sugar residue (glucose or galactose) ➢ Gangliosides=glycolipids with a complex carbohydrate moiety that contains more than three sugars (one is always a sialic acid ) =acidic glycosphingolipids because of their net negative charge at neutral pH Steroids ➢ Lipids with a fused-ring structure Three six-membered rings (the A, B, and C rings) One five-membered ring (the D ring) ➢ ➢ Important steroids include sex hormones and cholesterol Cholesterol: Occurs in cell membranes Highly hydrophobic Acts as a precursor of other steroids Plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis Bile Salts ➢ Synthesized in the liver from cholesterol and stored in the gall bladder ➢ Acts as emulsifying agents ➢ Gallstones: high levels of cholesterol in the gall bladder causing precipitation ➢ Jaundice:gallstones obstructing the bile duct, bile cannot be secreted and bile pigments (bilirubin) enter the blood Lipoproteins ➢ Lipids must be transported through the bloodstream for: 1. Energy storage 2. Synthesis of cell membranes, nerve tissues, hormones and bile salts 3. Carriers of insoluble lipids ➢ LDL (low density lipoproteins): bad cholesterol, deposit excess cholesterol in the arteries (artherosclerosis) and a risk of myocardial infarction ➢ HDL (high density lipoproteins): good cholesterol, remove excess cholesterol from tissues, carry them back to the liver, for the elimination as bile salts ➢ High-fat diet (saturated fatty acids) causes: 1. Reabsorption of cholesterol from bile salts 2. Liver to increase its synthesis of cholesterol Lipoproteins Origin chylomicrons VDL Intestinal mucosa liver LDL liver HDL liver Compounds transported Exogenous lipids Targeted cells/ Tissues adipose Endogenous lipids adipose, extrahepatic tissues Extrahepatic tissues, arteries(excess cholesterol) liver Cholesterol and other endogenous lipids Cholesterol (as products of metabolism) Function/s Store energy Store energy Synthesis of cell membrane, hormones and bile salts Elimination as bile salts Biological Membranes ➢ Every cell has a cell (plasma) membrane ➢ Membrane-enclosed organelles (nuclei and mitochondria) present in eukayotes ➢ Lipid and protein components= molecular basis of membrane structure ➢ Separate cells from the external environment and transport specific substances into and out of cells ➢ Membrane function is determined by interaction between lipid bilayers and membrane proteins ➢ Contain many important enzymes whose function depends on the membrane environment ➢ Hydrophobic interaction= major force driving the formation of lipid bilayers is ➢ Differ from lipid bilayers as they contain proteins as well as lipids Lipid bilayer ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ ➢ Aggregate of a lipid molecule- polar head groups are in contact with water and the hydrophobic parts are not Polar surface contains charged groups Hydrocarbon interior consists of saturated and unsaturated fatty acid chains and cholesterol Arrangement is held together by noncovalent interactions-van der Waals and hydrophobic interactions Bulkier molecules tend to occur in the outer layer Smaller molecules tend to occur in the inner layer HW- LIPIDS 1. Discuss why a saturated fatty acid like lauric acid has a good anti-oxidant property. 2. Why are the essential fatty acid associated with low incidence of heart disease? Cite some clinical signs of essential fatty acid deficiency. 3. Explain how aspirin can block the synthesis of prostaglandins? 4. Discuss how soap can help in the fight against the coronavirus. 5. What structural features do a triacylglycerol and a phosphatidyl ethanolamine have in common? How do the structures of these two types of lipids differ? 6. Refer to the lipid structure below. A. Identify the lipid structure, give its role, function, and enumerate its hydrolysis products. B. Explain which hydrolyzed component will test positive in the Acrolein test? Ninhydrin test? 7. Explain which hydrolyzed component of the lipid structure below will test positive in the Br2 test. 8. What tests will identify lipids A and B? A B 9. Egg yolks contain a high amount of cholesterol, but they also contain a high amount of lecithin. From a diet and health standpoint, how do these two molecules complement each other? 10. Briefly discuss the structure of myelin and its role in the nervous system. 11. In terms of structure, how ischolesterol different from bile salts? Cite causes of bile duct obstruction and symptoms. 12. Explain the cell membrane’s lipid bilayer. What are the lipids cell membrane? found in the