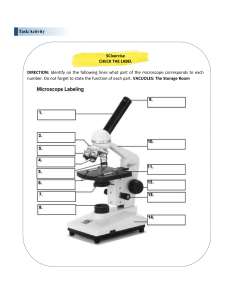
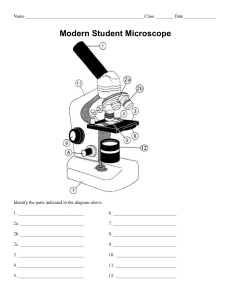
TYPES OF MICROSCOPES JANSEN MICROSCOPE (1950) first microscope was known as the Jansen microscope. It had three draw tubes with lenses placed at the ends of the tubes. COMPOUND MICROSCOPE 1. 2. A compound microscope is illuminated with the use of light. The light source can be sunlight or an electric bulb. TWO TYPES OF COMPOUND MICROSCOPE LIGHT COMPOUND MICROSCOPE ELECTRIC COMPOUND MICROSCOPE A light compound microscope uses mirrors to collect sunlight that illuminates the image. LIGHT COMPOUND MICROSCOPE electric compound microscope uses electric bulb as light source. It can create two dimensional images of the sample being examined. ELECTRIC COMPOUND MICROSCOPE Dissection Microscope It is used for dissection to obtain a better view of the specimen by creating three-dimensional images. The magnification capacity of dissection microscope is usually limited until 4 times its original size (4x) making it only applicable in observing large samples. DISSECTION MICROSCOPE phase-contrast microscope is highly similar to the usual electric compound microscope in terms of appearance except for its capability to change the position of light as it passes through a transparent sample. The changes brought by phase shift in light causes changes in the brightness of formed image. PHASE- CONTRAST MICROSCOPE fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that requires the use of fluorescence dye to create magnified images. This is usually used to study reflection and absorption properties of organic or inorganic substances within a minute organism or cells. FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE confocal microscope uses a laser light instead of normal light. Laser at specific wavelength allows more details in the images created by a confocal microscope. A confocal microscope is used in the field of material science to study structure and properties of materials to be used for various purposes. CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses beam of electrons for to illuminate images. High magnification and resolution of specimens being examined is possible because the wavelength of electron beams is shorter than visible light. An electron microscope can provide up to 1000x magnification. It can reveal detailed structure of smaller objects. scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that can produce images by scanning the surface of the sample using electron beams. A SEM is usually used to determine surface structure of cells or small compound particles. SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (SEM) IMAGES FROM A SEM MICROSCOPE transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is another type of electron microscope that transmits beam of electrons through the sample to form an image. It is used in examining very thin section of samples. It is being used to examine inner structure of the cells and other thin materials. TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) IMAGES FROM A TEM MICROSCOPE MATCH THE GIVEN TYPES OF MICROSCOPE WITH THEIR SPECIAL FUNCTION/S Compound microscope Scanning electron microscope Confocal microscope Phase-contrast microscope steromicroscope Observing live specimen Observing cell surface structure Observing cell internal structure Observing chemical processes Observing fixed samples Observing conducting materials