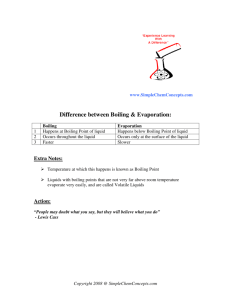
Heat is a form of energy which results in the sensation of hotness or coldness. It is the total amount of energy in a substance. Transfer of Heat Heat always flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature .This phenomenon is called heat transfer. The transfer of heat continues till the two bodies attain the same temperature and then maintain a constant temperature They are then said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. Temperature on the other hand, is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body. It is a measure of average energy of a molecular motion in a substance. A hot body is at a higher temperature than a cold body Heat S.I. UNIT OF HEAT IS JOULE S.I. UNIT OF TEMPERATURE IS KELVIN The SI unit of heat is joule (J). However, the traditional unit of heat is calorie (cal). Units of Heat Relationship between Various Units of Heat One calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 C 1 kilocalorie = 1000 calories I calorie =4.184 joules = 4.2jouIe 1 kilocalorie = 4184 joules = 4200 joules I joule = 0.24 calories Melting/Fusion Freezing or Solidification Boiling or vaporisation Condensation Melting or fusion is the change of a substance from its solid state to liquid State at a fix temperature due to absorption of heat. Melting of Ice and melting of wax Freezing or Solidification is the change of a substance from liquid state to its solid state at a fixed temperature due to liberation of heat energy. Change of water into ice Boiling or vaporisation ¡s the change of a substance from liquid into its vapour state (gas) at a fixed temperature by absorbing heat Water on boiling changes to steam Condensation is the change of substance from vapour or gaseous state to its liquid state at a fixed temperature Evaporation Evaporation is the change of a substance from its liquid state to its gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point. Drying of clothes in sunlight Sublimation Sublimation is the change of a substance from solid state to its gaseous state directly, without changing to its liquid state. Camphor and naphthalene undergoes sublimation Deposition Deposition is the process of change of a gas into its solid state, without changing to its liquid state, Snow formation in clouds Evaporation The change of a substance from its liquid state to its gaseous state by absorbing heat from the Surroundings at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation . Evaporation takes place from the surface of a liquid, i.e., it is a surface phenomenon and takes place at all temperatures The liquid absorbs heat from the surroundings and evaporates thereby decreasing the temperature of the liquid In the process. This is why when you pour perfume or spirit on your hand, it immediately evaporate giving you a cool sensation. It is because of evaporation only that we place Strips of cold water on forehead during high fever. The water in the strip evaporates by absorbing heat from the patient’s body thereby reducing the body’s temperature. Reason: In liquids, the molecules are not as tightly packed as in solids. As a result the intermolecular forces are weaker. However, these forces are stronger than in gases and so the liquids have a defined volume, Therefore, the molecules in a liquid are in a continuous but random motion throughout the liquid. When a molecule reaches the surface of the liquid it is pulled back inside the liquid. However, if the molecules on the surface acquire enough kinetic energy to overcome the pull of the other molecules it escapes and leaves the surface of the liquid. This is the process of evaporation Boiling The process during which a liquid changes into its vapour state (gas) at a fixed temperature by absorbing heat is called boiling . The fixed temperature at which a liquid starts to boil is boiling point. When a liquid is heated all its molecules acquire sufficient kinetic energy so as to gain enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction binding them to the liquid. Unlike evaporation boiling is not a surface Phenomenon; it affects the entire liquid. It is also accompanied with the formation of bubbles that can be seen in the liquid. Factors Affecting Boiling 1. Nature of liquid 2. Atmospheric pressure 3. Presence of impurity Thermal Expansion When temperature of a substance is increased, it results in expansion of the substance. This ¡s known as thermal expansion. o We know that matter is composed of molecules. These molecules are constantly vibrating. When we substance, its molecules start vibrating at a faster pace as they gain energy. Due to this, the molecular distance increases which lead to expansion of the substance. However, the extent of expansion is different substance. Gases expand the most on heating whereas solids the least. Types of Expansion Applications in Daily Life When the railway tracks made of steel are laid, some gap is always left between the successive rail tracks for allowing the expansion of the tracks in summers and their contraction in winters. But if the same is not done, the railway tracks are likely to bend outwards in the summers due to expansion. This expansion of tracks may lead to derailment of a train. During summers, the electricity and telephone wires are seen to expand and during winters, they contract. Therefore, these wires are laid a little loose which leaves a scope for thermal expansion and contraction. • In order to fit the iron rim on a wooden wheel of the cart, the iron rim is heated in order to expand it. Due to this heat, the iron rim becomes slightly bigger in size and is fixed on the wooden wheel. When the rim is cooled, it contracts and fits properly onto the wooden wheel. . In order to seal the metallic wire into the glass, platinum wires are used. The platinum wires have the same rate of thermal expansion as the glass. In case the other metals of different thermal expansion rate are used, they will either expand or contract more than the glass and will result in breaking of the glass Expansion in Liquids The molecules in liquids are free to move when temperature increases the molecule gain energy. Thus there is an increase in the average kinetic energy of its molecules. Due to this there is an increase in intermolecular spaces. This results in the expansion of liquids on heating. Factor effecting the Cubical Expansion of liquid The following factors affect the cubical expansion of a liquid. . Original volume of a liquid: There is more increase in the volume of a liquid on heating when a larger volume of liquid is taken. . Rise ¡n temperature: There is more increase in the volume of a liquid when there is a greater rise in temperature of a liquid. . Nature of liquid: Equal volumes of different liquids on being heated at a same temperature undergo different increase in their volumes. Factor effecting the Cubical Expansion of gas 1. Gas undergoes cubical expansion 2. The extent of expansion is greatest