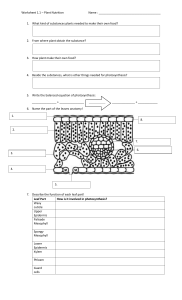
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make carbohydrates from raw materials, using energy from light. During photosynthesis: light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll - a green substance found in chloroplasts in green plant cells and algae absorbed light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide (from the air) and water (from the soil) into a sugar called glucose oxygen is released as a by-product The following equations summarise what happens in photosynthesis: carbondioxide+water→chlorophylllightglucose+oxygen 6CO2+6H2O→chlorophylllightC6H12O6+6O2 Some glucose is used for respiration, while some is converted into insoluble starch for storage. The stored starch can later be turned back into glucose and used in respiration. Leaf structure The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis effectively. A leaf needs: a way to transport water to the leaf, and glucose to other parts of the plant a way to exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen the ability to absorb light energy efficiently Transport Xylem tissue delivers water from the roots to the leaf, and phloem tissue transports glucose away from the leaf. These tissues form vascular bundles in the plant. Gas exchange Gas exchange happens in the spongy mesophyll tissue of the leaf. Spongy mesophyll cells are covered by a thin layer of water and loosely packed. When the plant is photosynthesising during the day, these features allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the spongy mesophyll cells, and oxygen to diffuse out of it. To get to the spongy mesophyll cells inside the leaf, gases diffuse through small pores called stomata. They also open or close to control the loss of water from leaf by the process of transpiration. Absorbing light energy Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll tissue of the leaf. Palisade cells are column shaped and packed with many chloroplasts. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. A cross-section through a leaf Features of leaves and their functions Feature Function Large surface area Maximise light absorption Thin Short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf cells Thin waxy cuticle This protects the leaves without blocking out light Thin transparent epidermis Allows light to reach the palisade cells Factors affecting photosynthesis Three factors can limit the rate of photosynthesis: light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature. Light intensity Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly - even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide. Increasing the light intensity will boost the rate of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide concentration Even if there is plenty of light, a plant cannot photosynthesise if there is insufficient carbon dioxide. Temperature If it gets too cold, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease. Plants cannot photosynthesise if it gets too hot. If you plot the rate of photosynthesis against the levels of these three limiting factors, you get graphs like the ones shown above. In practice, any one of these factors could limit the rate of photosynthesis. Plants and mineral ions Plants need minerals for healthy growth. They are absorbed through the roots by active transport as mineral ions dissolved in the soil water. Magnesium and nitrate Magnesium ions and nitrate ions are needed by plants. A plant will not grow well if it cannot get enough of these ions, and it will show symptoms of mineral deficiency. Mineral ion Needed for Effects of deficiency Magnesium Making chlorophyll Leaves turn yellow Nitrate Making amino acids Stunted growth Nitrogen fertilisers Fertilisers are used to replace minerals used by plants. Nitrogen fertilisers - such as ammonium nitrate and ammonium phosphate - provide plants with water-soluble sources of nitrogen that they can absorb through their roots. They allow farmers to increase the yield and quality of their crops. However, overuse can cause problems. Eutrophication happens when excess nitrate (or phosphate) enters rivers or lakes from fields. This can lead to the death of fish and other aquatic animals. Eutrophication can cause problems in rivers and lakesInvestigating photosynthesis – gas exchange Photosynthesis can be investigated to show gas exchange at different light intensities. Making oxygen The production of oxygen by photosynthesis is most easily seen in water plants such as Elodea and Cabomba. The number of bubbles released in a given time can be counted as a measure of the rate of photosynthesis. The apparatus in the diagram shows how the volume of oxygen produced in a given time may be measured instead. In this experiment, move the syringe to draw the oxygen produced into the capillary tubing. Then measure the length of the oxygen bubble. You can move the lamp towards the pond weed to increase the light intensity. Carbon dioxide uptake Hydrogen carbonate indicator is used to show carbon dioxide concentration in solution. It is: yellow in high concentrations of carbon dioxide red in equilibrium with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere purple in low concentrations of carbon dioxide Place a leaf from a plant in a stoppered boiling tube containing some hydrogen carbonate indicator. You can then investigate the effect of light over a period of a few hours. The table shows some typical results. Tube Contents Conditions Indicator turns Conclusion Tube Contents Conditions Indicator turns Conclusion 1 Leaf Light Purple There is an overall absorption of carbon dioxide by a leaf in light 2 Leaf Dark Yellow There is an overall release of carbon dioxide by a leaf in the dark 3 No leaf Light Red This is the control – the two other tubes can be compared with it Plant cells respire in the light and the dark, releasing carbon dioxide. In the light, photosynthesis can also happen, and carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air. If the light is bright enough, the rate of absorption becomes greater than the rate of release. Investigating photosynthesis – starch and chlorophyll Photosynthesis can be investigated to show the production of starch and the importance of chlorophyll. Starch testing Iodine solution is used to test leaves for the presence of starch. You need to: 1. heat a plant leaf in boiling water for 30 seconds (this stops its chemical reactions) 2. heat it in boiling ethanol for a few minutes (this removes most of its colour) 3. wash with water and spread onto a white tile 4. add iodine solution from a dropping pipette After a few minutes, the parts of the leaf that contain starch turn blue-black. Note that ethanol is heated using a hot water bath. Ethanol boils at 78°C, so a tube of it boils when placed in a beaker of hot water. This is safer than using a Bunsen burner because ethanol is flammable. Variegated leaves have green parts (where the cells contain chlorophyll) and white parts (where there is no chlorophyll). Only the parts that were green become blue-black with iodine solution, showing the importance of chlorophyll in photosynthesis. A plant can be ‘de-starched’ by leaving it in the dark for a few hours. Parts of its leaves are covered with dark paper, and the plant is left in the light for a few hours. Only the uncovered parts become blue-black with iodine solution, showing the importance of light in photosynthesis. Which of these is the correctly balanced equation for photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 CO2 + H2O → CH2O + O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O 2 Which mineral ions are needed for chlorophyll in plants? Calcium Magnesium Copper 3 Why do plants need nitrate ions? For denitrification as part of the nitrogen cycle To regulate the opening and closing of the stomata For making amino acids 4 In a greenhouse, tomato plants grow faster if the temperature is increased. What does this show? Temperature must be a limiting factor Light intensity must be a limiting factor Carbon dioxide concentration must be a limiting factor 5 In an investigation into photosynthesis in a water plant, why are the number of bubbles of gas it produces counted? To see how fast the plant used up carbon dioxide To see how fast the plant produced oxygen To see how fast the plant produced starch 6 Which tissue in the leaf absorbs the most light for photosynthesis? Upper epidermis Palisade mesophyll Spongy mesophyll 7 Which tissue in the leaf is adapted for efficient gas exchange? Upper epidermis Palisade mesophyll Spongy mesophyll 8 Why do leaves have a waxy cuticle? To protect the leaf without blocking out light To allow water vapour to diffuse out of the leaf To keep oxygen in the leaf 9 Which tissue transports water and minerals from the root to the leaves? Phloem Veins Xylem 10 Which useful energy transfer or conversion happens overall in photosynthesis? Light → chemical Chemical → light Light → heat