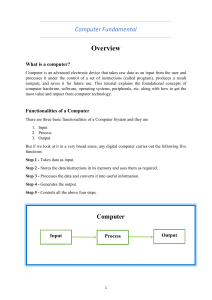
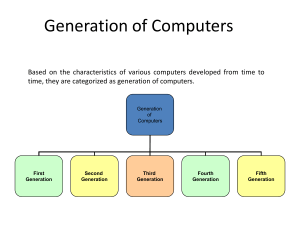
COMPUTER DEFINITION A computer is an electronic device that accepts user input (data) and processes it under the influence of a set of instructions referred to as programs to produce the desired output generally referred to as information. Data are the raw facts may not make much meaning to the user. Programs are set of instructions that instruct a computer what to do. Information is result after data has been processed CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS The ever-increasing use of computer is due to its special characteristics. Computer is not just a calculating machine; they also have the capability of doing complex activities and operation. Main characteristics of the computer are given bellow: 1. Speed: Computer is very fast and accurate device. Since electronic pulses travel at incredible speed and they are electronic device its internal speed is virtually instantaneous. A microcomputer can process millions of instructions per seconds over and over again without any mistake. 2. Accuracy: Computers physical circuits rarely make errors, if the data and instruction are correctly fed. Most errors which occur in computers are either hardware error or human error 3. Storage: Computers have a large amount of memory to hold a very large amount of data, we can store large amount of data information in the secondary storage device. 4. Programmability: A computer is programmable; i. e. what computer does depend on the lines of instruction (Program) it is using. 5. Diligence: Computer is free from problems like lack of concentration, and confusions etc. Computer is never confused like humans and it can perform instruction again and again without failing or getting bored. 6. Versatility: We can perform many different types of tasks on computer, one moment it might be busy in calculating the statistical date for annual performance evaluation of a business organization and next moment it might be working on inventory control. GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS First Generation (1940-1956): Vacuum Tubes First generation computers were vacuum tube / thermionic valves-based machines. These computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. A magnetic drum a metal cylinder coated with magnetic iron-oxide material on which data and programs can be stored. Input was based on punched cards and paper tape, and output was displayed on printouts First generation computers relied on binary-coded language (language of 0s and 1s) to perform operations and were able to solve only one problem at a time Second Generation Computers (1956-1963): Transistors In 1946, Willam Shockley and a few of his colleagues invented transistors, the transistor was used as the internal components of the second-generation computer. Transistors were much smaller, faster, and reliable than vacuum tubes. They consumed less electrical energy and needed no warm-up time. Third Generation Computers (1964 - early 1970s): Integrated circuits In second generation computers, one could recognize the circuit components such as transistors, resistors and capacitors distinctly. integrated circuits began to replace transistors as the internal components used to construct the computer. Even the entire circuit board of transistors can be replaced completely with one chip (integrated circuit). This chip can be much smaller than one transistor. Integrated circuits are made of silicon chip. Fourth Generation Computers (Early 1970s – till date): Micro processors The fourth generation is just an extension of the third –generation technology. This next technological development is to put more power and capabilities in one chip called microprocessor. More and more circuits were packed in a microprocessor. The components were integrated further and very large-scale integration (VLSI) technology revolutionized computer field further. Microprocessor is considered as the brain of the computer. It is where almost all computations and operations of the computer circuitry are being done and coordinated. Fifth Generation Computers (Present and beyond): Artificial Intelligence Up to fourth generation, the classification was based purely on hardware. Fifth generation computers are classified based on software also. VLSI technology is used in fifth generation computers. They have large main memories. The speed is also high. In addition to all this, Fifth generation computers run software called ‘expert systems. VARIOUS TYPES OF COMPUTER SYSTEMS Hybrid computers: The computer which possess the features of both analog and digital computers are called hybrid computers. That is, the hybrid computers have the good qualities of both analog and digital computer. Micro Computers Because of its small size and the use of micro-processor, this computer is called micro computer. All the computers have three units namely input, output and central processing unit, (CPU). The entire CPU is contained in a single or a few microchips. When equipped with memory and input/output control circuitry, it is called micro computer Mini Computers The size of the mini-computer is in between the size of micro and main frame computers. It is more powerful than a microcomputer. Mini computers are usually designed to serve multiple users. Super Computers The super computers are very costly. Hence it is rarely used. Its capacity is abnormally high, it cannot be compared with any other computers in capacity, function, speed, accuracy, language etc., Laptop computer: Laptop computer, simply laptop (notebook computer or notebook), is a small mobile computer, which usually weighs 2-18 pounds (1-6 kilograms), depending on size, materials, and other factors.