Hospital Pharmacy Final Exam: Fluid, Electrolytes, Nutrition
advertisement

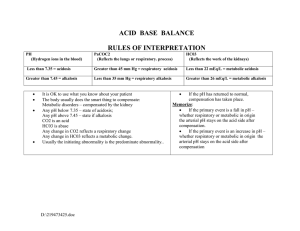
Hospital pharmacy final exam round1 template2 1. Many clinical trials, such as SAFE trial, have found that albumin is not superior for hypovolemic patients compared to crystalloids. a. True b. False 2. 1 L normal saline is clinically equipotent to 1 L albumin 5%. a. True b. False 3. Treatment of both severe hypovolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia should include administration of hypertonic saline whereas severe hypervolemic hyponatremia should only treated by water and salt restriction. a. True b. False 4. When hypokalemia occurs in the setting of acidosis, KCl is the preferred as a potassium supplement, whereas in alkalosis, potassium acetate is preferred. a. True b. False 5. It is possible to use IV continuous infusion of insulin mixed with dextrose 50% to treat hypokalemia. a. True b. False 6. Main difference/s between TBW depletion and ECF depletion is/ are: A. TBW depletion developed more gradually. B. More water is lost than sodium in ECF depletion. C. Dizziness, orthostasis, and tachycardia are of the most common signs of TBW depletion. D. Low oral intake is the most common cause of TBW depletion whereas hemorrhage is one of most common causes of ECF depletion. E. A and b F. A and d 7. The main contributor/s to serum osmolality is/are: A. Sodium B. Potassium C. Phosphate D. Bicarbonate E. F. G. H. Glucose A and d A and e All of them 8. Which of the following is the best choice for initial treatment of moderate symptomatic hypercalcemia? a. Normal saline b. Normal saline plus furosemide c. Furosemide d. Bisphosphonate e. Normal saline plus bisphosphonate f. None of them 9. Which of the following information is/ are helpful to determine the appropriate treatment for metabolic alkalosis? a. Chloride level b. Sodium level c. Potassium level d. Phosphate level 10. Which of the following considered as part of parenteral nutrition? a. Fluids b. Electrolytes c. Fatty acids d. Amino acids e. Vitamins f. Trace elements g. All of them h. All except b 11. Both hypernatremia and hyponatremia should not be corrected by a rate greater than 0.5 meq/l/hr. a. True b. False 12. Generally, one third to half of sodium deficit can be replaced in first 12-24 hr of administration in hyponatremia. a. True b. False 13. Hypomagnesemia often occurs concurrently with hypokalemia and/or hypocalcemia. a. True b. False 14. Total parenteral nutrition is clearly indicated if the patient is malnourished and: a. NPO b. cannot tolerate oral or enteral nutrition c. has intestinal failure or obstruction (no absorption of nutrients) d. will be in need for nutrition support for more than 7 days e. a or b f. a, b, or c g. any of them 15. All of the following medications may be associated with hypomagnesemia except; a. Aminoglycosides b. Furosemide c. Amphotericin B d. Insulin e. A and b f. All 16. Disturbances in sodium concentration most often represent disturbance in total body water. a. True b. False 17. In hyperkalemia, dextrose and insulin are given concurrently with calcium to decrease potassium body content. a. True b. False 18. In hypovolemic shock, initial volume of 1000 to 2000 mL of an isotonic crystalloid in adult patients is administered over the first day of treatment. a. True b. False 19. Treatment of hyponatremia in condition of volume overload is/ are: a. Sodium restriction b. Fluid restriction c. Normal saline infusion d. 3% saline infusion e. A and b f. A and c 20. Fresh frozen plasma is indicated in hemorrhagic shock when bleeding is ongoing and patient has PTT more than ____ times normal. 21. Using a hemostatic agent such as tranexamic acid or factor VII is cornerstone of hemorrhagic shock (bleeding). a. True b. False 22. Vasopressor agent should be tapered down and discontinued as blood pressure restored and stabilized (SBP>90). a. True b. False 23. Dobutamine has: a. Positive inotropic effect and vasodilation effect b. Positive inotropic effect and vasoconstriction effect c. Negative inotropic effect and vasodilation effect d. Negative inotropic effect and vasoconstriction effect e. A and b f. None of them 24. The following is/ are target/s of treatment of hypovolemic shock, except; a. Systolic blood pressure above 90 b. Mean arterial pressure above 50 c. increased urine output to greater than 0.5 mL/kg/hour d. resolution of metabolic acidosis e. b and d f. none of them 25. Which of the following acid- base imbalances usually accompanies hypovolemic shock? a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory acidosis d. Respiratory alkalosis e. None of them 26. Order the following blood products according to their safety to patients; من األكثر لألقل أمانا Whole blood. / Fresh frozen plasma. / Packed RBCs. 27. A healthy 24-year-old pharmacy student is having an ABG drawn as part of her clinical pulmonary rotation. Her ABG shows a pH of 7.50, a Paco2 of 29 mm Hg, and a bicarbonate of 21 mEq/L. What is the primary acid–base disorder? a. Metabolic alkalosis with proper compensation b. Metabolic alkalosis without proper compensation c. Respiratory alkalosis with proper compensation d. Respiratory alkalosis without proper compensation e. No disorder 28. Although dextrose has the lowest energy density among TPN, it is the primary source of energy for patients. a. True b. False 29. In TPN, the maximum dextrose infusion rate of adult patients is _____ mg/kg/min. 30. In TPN, the maximum IVFE infusion rate of adult patients is _____ mg/kg/hr. 31. You can use IVFE after opening its original container within up to 24 hours only. a. True b. False 32. You can use IVFE after opening its original container and transferring it to another container or mixing it with other solution within up to 12 hours only. a. True b. False 33. Thiamine (B1) lacked-TPN is associated with: a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory acidosis d. Respiratory alkalosis e. All of them f. None of them 34. A 48-year, 110 kg, 160 cm male patient is in ICU due to second degree burn. He is in coma and should be maintained on TPN due to intestinal obstruction. Assuming adequate energy is supplied for this patient from dextrose and IVFE, how many grams of amino acid does he need daily? ____ gram/ day. (hint; use the given table in your slides which copied from Pharmacotherapy Principles and Practice 4th edition). 35. Administering PN for long periods is preferred to be through a central vein rather than a peripheral vein because risk of: a. Extravasation b. Thrombophlebitis c. Lactic acidosis d. A and b e. B and c 36. It is preferred to administer IVFE separately from 2-in-1 admixture. a. True b. False 37. EN formula delivery into the intestine (duodenum or jejunum) is generally preferred. a. True b. False Choose the proper type of EN polymeric formula according its protein content for the following patients: Formulas; G. Low protein content II. Standard protein content III. Very high protein content Patients; 38. Postoperative- NPO patient without compelling diseases__. 39. Patient with renal failure __. 40. Critically ill patient ___. 41. Patient with large burn ___. *************************************** 42. High caloric density polymeric EN solutions (1.8- 2 kcal/ ml) are preferred for patient with: a. Congestive heart failure b. Pulmonary congestion c. Peripheral edema d. A and b e. B and c f. All 43. The most prevalent microbe/s that may contaminate extra-abdominal surgeries is/ are: a. Staphylococcus aureus bacteria b. Staphylococcus coagulase -ve bacteria c. Candida albicans d. E. coli e. A and b f. A and d 44. Which of the following is the first choice for surgical prophylaxis prior to extraabdominal operations (e.g., appendectomy)? a. Cefazolin b. Cefuroxime c. Ceftriaxone d. Cefotetan e. Vancomycin f. Ertapenem g. None of them 45. Antibiotic infusion should be started 1 hour before the first incision to get proper prophylaxis. a. True b. False 46. If a procedure duration exceeds ____half-lives of the administered antibiotic, then another dose should be given. 47. Status epilepticus is convulsions that last for more than 5 minutes. a. True b. False 48. Refractory status epilepticus is that did not response to the first line treatment. a. True b. False 49. Midazolam has the advantage of safe IM administration, whereas lorazepam has the advantage of long duration of action. a. True b. False 50. Levetiracetam used as 3rd line adjunctive treatment of SE in refractory cases. a. True b. False A 79-year-old woman with a history of hypertension, diabetes, and arthritis was admitted with traumatic subdural hematoma after sustaining a fall down a flight of stairs in her home. She underwent surgery 2 days ago to evacuate the hematoma and is currently recovering in the ICU. She was started on fosphenytoin for seizure prophylaxis upon admission along with her home medications. She has only one peripheral IV line and has very poor vascular access. Her nurse reports that a few minutes ago she was alert and awake, but now she is unarousable and is having jerky, convulsive movements on both sides of her body. The doctor evaluates her and the jerky activity stops, but then starts again about 1 minute later. She never regained consciousness between these episodes. Her diagnosis is status epilepticus. Ht 165 cm (5´5˝), Wt 133 kg (293 lbs). VS: BP 178/92 mm Hg, pulse 109 beats/min, RR 26 breaths/min, T 39.0°C (102.2°F) CNS: Unresponsive, unarousable Pulm: Tachypneic; oxygen saturation 88% (0.88) on room air Exts: Rhythmic tonic-clonic movements of all extremities GU: Incontinent of urine and stool Current Meds: Fosphenytoin 100 mg PE IV every 8 hours; famotidine 20 mg IV every 12 hours; metoprolol 50 mg by mouth every 12 hours; insulin glargine 25 units subcutaneous at bedtime; insulin aspart 5 units subcutaneous with meals; acetaminophen/hydrocodone 325 mg/5 mg tablet by mouth every 4 hours as needed for pain. Labs: Sodium 132 mEq/L; potassium 4.1 mEq/L; phenytoin 2.7 mcg/mL; albumin 3.5 g/dL (35 g/L); chloride 105 mEq/L; carbon dioxide 12 mEq/L; serum creatinine 0.9 mg/dL; glucose 54 mg/dL; WBC 15 × 103/mm3; hemoglobin 9.6 g/dL; platelets 235 × 103/mm3. 51. What is your assessment of the cause of this patient's condition? 52. Identify your goals of therapy for this patient. 53. What pharmacologic interventions need to be performed at this time? 54. What therapies must be instituted next after stabilization (on discharge)? ************************* 55. BONUS Question A 56-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by rescue squad after several complaints were called in to 911 for a “profoundly intoxicated” individual in a city park. Shortly after arrival in the emergency room she has several episodes of emesis with witnessed aspiration. She is transferred to the ICU where she develops progressive hypoxia during the ensuing hours. Following elective intubation her blood work shows a pH of 7.50, a Paco2 of 20 mm Hg, a bicarbonate of 15 mEq/L, a sodium concentration of 145 mEq/L and a chloride level of 100 mEq/L. What acid–base disorders do this patient has? __________________________________________ . (Briefly)