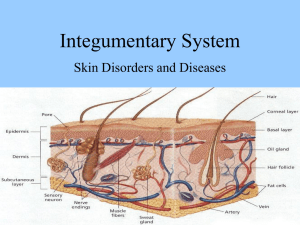
Digestive system / biochemistry Digestion & absorption of proteins 1- With relate to digestion and absorption processes of food :a. Digestion is a purely chemical breakdown of food. b. Digestion is produced by the action of enzymes that are present in all length of the GIT except in the mouth. c. NO absorption occurring in the stomach d. None of the above 2- With relation to gastric juice all the following is true except : a. Mucous, proteases and HCL are the main component. b. Mucous is secreted by the chief cells c. Parietal cells is responsible for secretion of HCL d. Gastric secretion is under feedback control 3- With related to mucous of the gastric juice .. a. It must be continuously produced, hence it can be degredaded by the action of pepsin b. It is secreted from the parietal cells and surface epithelium c. NO bicarbonate in it d. It can be inhibited by Ach 4- With relation to gastric acid secretion a. H+ is delivered to stomach through secondary active transport. b. HCO3- is delivered to the stomach too c. It is produced by the neck cells d. Carbonic anhydrase is responsible for catalyzing the reaction of formation of the week carbonic acid 5- Factors that control gastric acid secretions are :- a. b. c. d. Ach Histamine Gastrin and secretin All of the above 6- With related to factors that affected the secretion of gastric juice .. a. Adrenergic stimulation will inhibit HCO3- secretion in the mucosa b. Secretin is produced in duodenum due to signal stimulation from gastric acid and it will inhibit the secretion. c. Gastrin is produced by G-cells of stomach and it cause stimulation of gastric acid secretion like the action of Ach d. All of the above 7- With relation to alkaline tide, all of the following is true except … a. It occurring after eating a huge meal of proteins. b. Caused by elevated HCO3- concentration in blood. c. The PH of plasma will be reduced d. The PH of the urine will be elevated 8- The main buffer systems that maintain the excess amount releasing of OH in blood after gastric acid secretion in stomach is :a. Phosphate buffer system b. Bicarbonate buffer system c. Lactate buffer system d. All of the above 9- With related to gastric proteases a. Pepsin work at optimum PH = 1.2 b. Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin by the action of auto-activation c. Pepsin is a serine protease d. Pepsin and chymotrypsin work on different amino acid 10- With relation to pancreatic proteases, all of the following is true except : a. They are serine proteases b. Trypsin activates chymotrypsin, elastase and have a partial auto-activation activity c. Trypsin is activated by auto-activation only d. Chymotrypsin and pepsin works on the same amino acid 11- With relation to absorption of amino acid .. a. Di- & tri-peptides can be absorbed and may hydrolyzed inside the enterocytes b. All types of amino acid is absorbed by the same type of receptors c. Small peptides absorption receptors have a dependent mechanism on amino acid absorption d. NO small peptides can enter blood 12- With relation to milk protein “ casein “ a. Can be absorbed in neonated by M-cells covering peyers patches b. Have a role in the immune development of neonates c. In adults, it is hydrolyzed by pepsin & chymotrypsin d. All of the above 13- With relation to hartnup disease a. The core clinical problem related to it is diarrhea b. It is an AD metabolic disorder c. There is defect in absorption of positively charged amino acids d. There is no defect in the absorbtion of nicotin amide ( niacin or vit B3 ) but a defect in the endogenous source of it. 14- Tryptophan a. Is a neutral amino acid b. Accumulation in gut may cause diaper blue syndrome c. Is concider as an endogenous source of niacin, serotonin and melatonin d. All of the above 15- With relation to tryptophan metabolism a. BH2 & BH4 are responsible for converting (Try) to (5-OH try) b. AADC converts ( 5-OH Try ) to serotonin c. Mono amine oxidase converts serotonin to ( 5-OH indolacetic acid ) d. All of the above 16- Which statement is true ? a. Try have NO role in protein synthesis b. BH2 & BH4 deficiency may cause PKU and serotonin deficiency c. A persistent try in gut will cause elevated nicotinc acid concentration in blood d. All of the above statements are true 17- In celiac diseases .. a. Weight loss, diarrhea & failure to thrive are the main symptoms b. There is immune reaction to de-aminated gliadin, tissue transglutaminase & endomysium c. NK2GD receptors of CD8+ T cells will react with enterocytes expressing the stressor molecule MIC-A d. All of the above 18- The main cause(s) of celiac disease is .. a. The auto-immunity b. Enzymatic deficiency c. The antigenic proteins d. All of the above 19- Which of the following is an “ exopeptidase “ ? a. Trypsin b. Chymotrypsin c. Carboxypeptidase d. Pepsin 20- Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bond between valine & tryptophan? a. Trypsin b. Chymotrypsin c. Carboxypeptidase d. Pepsin 21- Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bond between valine & serine? a. Trypsin b. Chymotrypsin c. Carboxypeptidase d. Pepsin 22- The mechanism underlying H. pylori to escape the mucosal protection and gastric acidity protection of stomach is by :a. Containing flagella b. Have an urease activity that will produce ammonia around the microorganism c. Toxins produced by the micro-organism itself d. a&b 23- Which of the following is a neutral amino acid? a. leucine b. lysine c. arginine d. histidine Digestion & absorption of carbohydrates 24- salivary amylase is also called :a. B-amylase b. Protein splitting enzyme c. Ptyalin d. Amylopsin 25- Which statement regarding a amylase is untrue ? a. Exist in both saliva and pancreatic juice b. Its function is restricted by PH c. Salivary amylase products can be a single sugar molecules d. Pancreatic amylases products can be disaccharides 26- Which statement is untrue a. There is enzymatic digestion of CHO exist in stomach b. Biochemical digestion of CHO in stomach is done by pepsin c. Salivary & pancreatic amylases work in different PH d. Only sucrose can be cleaved in stomach 27- The optimum PH for pancreatic amylase function is :a. 7.1 b. 6.7 c. 6.8 d. 6.9 28- Brush border enzymes includes all the following except :a. Lactase b. Maltase c. Pepsin d. Tri- & di- peptidase 29- With regarding the absorption of sugar molecules :A. Glucose transporter is Na+ - dependent protein carrier that require 2NA+ to transmit 1 molecule of glucose B. Usually glucose molecule is transported by simple diffusion C. Fructose transporter is co-transported with sodium D. The same carrier protein can transmit different types of sugars 30- In Lactose intolerance a. There Is absent or deficiency in the lactase enzyme b. The main symptoms is diarrhea with abdominal pain c. It can be due to inactivation of the enzyme or gene mutation or aging d. All of the above 31- Which of the following can transmit fructose from the intestinal lumen to enterocyte? a. SGLUT1 b. GLUT1 c. GLUT6 d. GLUT5 32- GLUT2 can transmit : a. Glucose b. Galactose c. Fructose d. All of the above 33- The way of transmitting fructose is by :a. Simple diffusion b. Active transpotrt c. Fascilitated transport d. a&c 34- which of the following can be transported by simple diffusion ? a. Mannose b. Fructose c. Pentoses, glucose & galactose d. All of the above 35- Which molecule is transported by co-transport system ? a. Fructose b. Glucose c. Galactose d. b&c 36- Which of the following sugars is faster to be absorbed a. Glucose b. Fructose c. Mannose d. Pentoses 37- The 1st location in which there is de-branching enzymes in CHO digestion is a. Mouth b. Pancreatic juice c. Small intestine d. Stomach 38- All of the following enzymes can be found in intestine except : a. Terminal a 1-4 glyosidic linkage enzymes b. Deep a 1-4 glycosidic linkage cleaving enzymes c. Disaccharides d. Aminopeptidases Digestion & absorption of fat 39- Hydrolysis of triglycerides (TGs) is initiated by: a. Lingual lipase b. Gastric lipase c. Pancreatic lipase d. a&b 40- With regarding to lingual lipase, which statement is false ? a. It does NOT work in stomach b. Work in PH range from 2 to 7.5. c. Has a role in digestion of short FAs in milk. d. Secreted from the dorsal surface of tongue. 41- With regarding to gastric lipase, choose the most appropriate answer: a. It is important in digest backflow chyme from the duodenum b. Its optimum PH is 2. c. Usually digest long chain FAs. d. Have no role in digestion of egg yolk. 42- Short chain FAs: a. Could be absorbed directly from stomach to portal vein. b. Could be digested by lipases secreted from tongue & stomach c. Usually found in milk fat & egg yolk d. All of the above. 43- Micelle is composed of all the following except: a. FFAs b. monoacylglycerol c. Bile salts d. Diacylglycerol (DAGs) 44- FFAs conjugated with ---------- could by absorbed by ---------- to ---------a. Bile salts, stomach, portal vein b. Bile salts, small intestine, portal vein c. Bile salts, small intestine, lymph d. Bile salts, stomach, lymph 45- Which is not appropriate? a. FFAs = portal vein b. Cholesterol = lymph c. Resynthesized TGs ( chylomicron ) = portal vein d. Phospholipids = lymph 46- With regarding to bile salts functions: a. 3 molecule of co-lipase enhance the lipase activity in prescence of bile salts. b. Proper digestion and absorption of fat is critically dependent on both pancreas and liver secretions. c. Have NO role in emulsification of fat aggregations. d. Could not transport lipids because it has NO aqueous component. 47- Bile acid: a. Is composed of cholic acid & glycine b. Glycine is the hydrophilic component c. Cholic acid is the lipophilic component d. All of the above. 48- Which is the most appropriate statement? a. NO bile acid is presented in systemic circulation b. 85% of bile acid will be recycled to liver c. NO bile acid is present in feces. d. Bile acid is secreted from the gallbladder 49- Which of the following is used as indicator for hepatic disease? a. Feces bile acid level b. Systemic circulation bile acid level c. Portal vein bile acid level d. None of the above 50- Chylomicrons contains all the following except a. TGs b. Cholesterol & phospholipids c. Apo-lipoprotein B48, CII, CIII d. Apo-lipoprotein A 51- Abetalipoproteinemia is a mutation in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein resulting in a. Absence of apo-B48 b. Absence of apo-100 c. Chylomicrons & VLDL will not form d. All of the above. Detoxification in liver 52- With regarding to toxins: a. Most of the toxins are water soluble substances. b. Toxins could be excreted from body by urine and sweating. c. Toxins could be released to body in time of exercise, stress or fasting. d. They have a high affinity for fatty tissues only. 53- With regarding to detoxification pathways: a. Phase I could directly neutralize substances with no need to phase II. b. Both Phase I & phase II require enzymes. c. Both phases happened in the liver. d. All of the above. 54- The major sites in the body for biotransformation of xenobiotics are: a. Kidney, liver, pancreas b. Kidney, liver, intestine c. Kidney, liver, skin d. Kidney, liver, circulation 55- Sulfate used in conjugation process in phase II is obtained from: a. Methionine b. Cysteine c. Glycine d. a&b 56- ------------- are determinants in oxidative, peroxidative, and reductive degradation of exogenous & endogenous toxins: a. cytochrome P450–dependent monooxygenase enzymes b. cytochrome P450 c. cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase d. a&c 57- with regarding to cytochrome P450 a. They are hemoproteins NOT enzymes! b. Their reaction is catalyzed by cytochrome P450 reductase enzyme. c. The most common reaction catalyzed by cytochromes P450 is a monooxygenase reaction d. All of the above 58- A reaction when we incorporate one atom of oxygen into a substrate to creating a hydroxyl group, and other oxygen atom is being reduced to water is called : a. Oxidation b. Monooxygenase c. Oxygenation d. Oxygenase 59- With regarding Cytochrome P450 system, all the following is true except: a. It found on cell membrane b. It is a membrane associated proteins NOT enzymes. c. It found in mitochondria d. It found in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 60- Cofactors for monoxygenase reactions will include: a. NADP,H+ b. NADH, H+ c. NADPH, H+ d. NAD+, H+ 61- Whist statement is most appropriate? a. Hyper activity of CYP 450 system have a great role in detoxification. b. When Phase I work correctly and there is insufficiency in phase II, a state of carcinogenesis will develop. c. CYP 450 system is a system that have no variability between individuals. d. There is NO variability between individuals in detoxification process. 62- CYP 450 system variability is due to: a. Genetics b. Nutritional state c. Exposure to toxins ( inducible state ) d. All of the above 63- A significant side effect of phase I is the production of: a. H2O b. NADP+ c. free radicals d. none of the above 64- with regarding the process of neutralizing free radicals produced by Phase I a. It is NOT done by phase II reactions b. Glutathione is NOT important in this process c. This process happened in the gut wall d. None of the above 65- All these cofactors are required for fully functioning detoxification process except: a. B vitamins b. Cysteine c. Selenium d. A vitamin 66- Which of the following mechanisms play a prominent role in phase II detoxification? a. Conjugation b. Oxidation c. Hydrolysis d. Reduction 67- People with a very active phase I detoxification system coupled with slow or inactive phase II enzymes are: a. Pathological detoxifiers b. suffer unusually severe toxic reactions to environmental poisons. c. Do not prone to toxicity overall d. a&c 68- With regarding to glutathione a. It is a tetrapeptide b. It consist of glycerin, cysteine & glutamic acid. c. It is the primary reaction occurring in Phase I d. All of the above. 69- Glutathione conjugation produces water-soluble ------------------ which are excreted via the -----------. a. Xenobiotics, kidney b. Mercaptates, liver c. Xenobiotics, liver d. Mercapates, kidney 70- Glutathione: a. It is useful to detoxify heavy metals like mercury & Iron b. Its synthesis is depends on cysteine & glutamic acid. c. a deficiency of methionine can, in itself, liver cancer without the presence of a carcinogen d. can be obtained from diet only. 71- ----------- is the most commonly utilized in phase II amino acid detoxification. a. Glycine b. Cysteine c. Taurine d. Arginine 72- Most important note that could be considered in amino acid conjugation system is that: a. It have no variability between individuals. b. It is highly depend on protein-diet. c. This system do NOT occur in liver. d. Depletion in this system will lead to NO toxicity. 73- Methylation process in phase II require all the following except: a. Methyl group obtained from (SAM) b. Vitamin B12 c. Folic acid d. Vitamin E 74- Major source for amino acid containing sulfur like glycine and taurine is a. Methionine b. Methylation c. Vitamin B d. Glutathione 75- Toxins from intestinal bacteria are neutralized by: a. Methylation b. Sulfation c. Glutathione d. Acetylation 76- Sulfation pathway a. Is the main pathway to eliminate thyroid & steroid hormones. b. Depeletion of this system may lead to nervous system disorders c. A diet low in methionine & cysteine will have an impact on this system. d. All of the above. 77- Main way in HOW body eliminate sulfa drugs is via: a. Methylation b. Sulfation c. Acetylation d. Glutathione 78- All the following are required in acetylation process except: a. Methionine b. Thiamine c. pantothenic acid d. vitamin C. 79- poor acetylation system could lead to: a. Nervous system disorders b. More susceptible to sulfa drugs and other antibiotics c. Carcinogenesis d. None of the above 80- Most important point in glucouronic acid conjugation pathway is: a. Have genetic variability. b. Could be reversed by Beta glucuronidase enzymes produced by pathological bacteria and cause toxins to be reabsorbed increasing toxicity. c. It has major role in detoxcify aspirin, menthol & synthetic vanilla, benzoates. d. All of the above. 81- All the following regarding sulfoxidation is true except: a. Sulfite oxidase (molybdenum dependentenzyme) metabolizes sulfa containing substances. b. Sulfates is less toxic than sulfite c. Sulfates /sulfites ration is high in people will sulfoxidation insufficiency d. There is variability in functioning of this system. Pancreatic secretions 82- With related to pancreatic secretions, which statement is true? a. HCO3- is produced by acinar cells of the pancreas b. Digestive enzymes are produced by epithelial cells lining the ducts. c. They present the major, but not the final step in digestion processes. d. They are endocrine secretions. 83- Elastases, cut the peptide bond between: a. Valine & serine b. Valine & tryptophan c. Alanine & serine d. Alanine & leucine 84- Presence of acid in the duodenum will cause secretion of: a. Secretin b. Gastrin c. CCK d. GIP 85- Presence of fat in the duodenum will cause secretion of: a. Gastrin b. Secretin c. CCK d. VIP 86- Trypsinogen is converted to trypsin by: a. Enterokinase b. Trypsin c. Chemotrypsin d. a & b 87- The pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis in bile stones include: a. Hyper stimulation of pancreas. b. Activation of phospholipase c. Increasing Ca++ concentration d. None of the above. 88- The cause underling alcoholism induce acute pancreatitis is through: a. Hyper stimulation of pancreatic enzyme b. Blockage of ducts by protenicious plug. c. All of the above d. None of the above 89- In which case, increasing Ca++ level will lead to acute pancreatitis a. Hyperparathyroidism b. Hypoparathyroidism c. Alcoholism d. Bile stones 90- The different between alcoholism and cystic fibrosis disease which both cause chronic pancreatitis is that: a. Alcoholism cause hyperstimulation of pancreas but CF do NOT. b. Alcoholism cause hyperconcentration of proteins but CF do NOT. c. Inflammation is associated with CF but NOT with alcoholism. d. In contrast to alcoholism, in CF there is pure atrophy of the exocrine pancreas, without pain. 91- Symptomatic malabsorption in pancreatitis does not occur until pancreatic enzyme secretion is reduced to less than ------------ of normal. a. 20% b. 10% c. 5% d. 3% 92- -------------- is the only plasm enzyme physiologically found in urine. a. Amylases b. Trypsin c. Chymotrypsin d. Pancreatic amylase 93- See figure below, then what it estimates? Enzyme Urine Amylase Elevated a. Macroamylasemia b. Pancreatic pseudocyst c. All of the above d. None of the above 94- See figure below, then what it estimates? Enzyme Urine Amylase Low a. Macroamylasemia Plasma Elevated Plasma Elevated b. Pancreatic pseudocyst c. All of the above d. None of the above 95- With related to lipase a. It is usually NOT filtered through the glomeruli. b. It is NOT normally present in urine. c. It is decreased in serum in acute pancreatitis . d. None of the above. 96- See figure below, then what it estimates? Enzyme Urine Amylase elevated Lipase NO a. Macroamylasemia. b. Pancreatic pseudocyst. c. Pancreatitis. d. None of the above. Serum Elevated Elevated Bilirubin metabolism 97- Which of the following test is used to determine the amount of breakdown of hemoglobin ? a. Serum ferritin b. Breath CO2 c. Serum bilirubin d. urine bilirubinogen 98- which statement is true? a. Heam breaking down is done by Heam reductase enzyme. b. Unconjugated bilirubin is water soluble c. Bilirubin is NOT water soluble and it is an important anti-oxidant d. Biliverdin is normally found in serum. 99- Regarding the pathway of bilirubin metabolism a. There is trace amount of unconj. Bilirubin in bile. b. HOX and biliverdin reductase are found in reticular endothelial cells. c. If there is bilirubin in urine, then it is of conjugated type. d. All of the above. 100- Regarding urobilinogen a. It is formed in intestine due to converting of conjugated bilirubin into nonconjugated type (de-conjugation) b. Its rate of absorbtion by small intestine increased in fasting, and in bile acid mal-absorption ( due to intestinal diseases and resections ) c. It is usually captured ONLY by liver d. All of the above. 101a. b. c. d. Which statement is true? Intestinal diseases and resection may lead to gallstone formation. Bilirubin when de-conjugated it will give urobillinogen In gallbladder, some amount of unconjugated bilirubin is present. All of the above 102- Regarding bilirubin metabolism : a. bilirubin will oxidise back to biliverdin after excretion – hence the green colour of bile. b. Bilirubin is synthesized from cholesterol c. Normal bilirubin pigment is green d. All of the above. 103- Wich of the following suggest increase urine urobilinogen? a. Hemolysis diseases b. Liver diseases c. All of the above d. None of the above 104- Regarding hemoglobin: a. Heme is a porphyrin that composed of four pyrrole rings that connect to each other by methane bridge (CH). b. Heme is usually coupled with metal (Fe+2) c. No recycling could be done to heme, and it must be eliminated d. All of the above. 105- A 2 week baby male present with jaundice, pallor and difficulty in breathing, laboratory assessment reveals a serum bilirubin level that exceeded 20mg/100ml, the most appropriate diagnosis is a. Type I Criglar-Najjar syndrome b. Type II Criglar-Najjar syndrome c. Gilbert’s disease d. Dubin-Jhonson syndrome. 106- In patient with type II Criglar-Najjar syndrome, they show improvement when treated with : a. Phenobarbital b. sulfobromopthalein c. sulfasalazine d. methyldopa 107- With relating to Gilbert’s disease a. The main defect is failure of uptake of bilirubin by liver that can be exacerbated by hemolysis. b. It is an autosomal recessive disorder. c. There is normal UDP-GT enzyme activity d. All of the above. 108- Regarding the chronic idiopathic jaundice ( dubin-johnson syndrome ) all the following is true except: a. The excretory pattern of porphyrins in urine is also abnormal in these people. 80-90% of coproporpyrins excreted are of Type I instead of the normal type III. b. It is inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder. c. The hyperbilirubinemia may occur in childhood or in adult life and is due to a defect in the-liver cell in the secretion of conjugated bilirubin into bile. d. The excretion of conjugated hormones (like estrogens) and dyes (like sulfobromopthalein) is also impaired. Dyes which do not require conjugation before excretion (eg. Rose Bengal) are excreted without any difficulty. 109a. b. c. d. Normal level of conjugated bilirubin in serum is: 0.0 – 0.4 mg/dl 0.2 – 0.8 mg/dl 0.4 – 1 mg/dl 1 – 2 mg/dl 110- Normal level of unconjugated bilirubin in serum is: a. 0.0 – 0.4 mg/dl b. 0.2 – 0.8 mg/dl c. 0.4 – 1 mg/dl d. 1 – 2 mg/dl 111- Normal level of total bilirubin in serum is: a. 0.1 – 2 mg/dl b. 0.5 – 1 mg/dl c. 0.2 – 1 mg/dl d. 1 – 2 mg/dl 112- Bilirubin is usually detectable when serum level reaches : a. 1 mg/dL b. 2 mg/Dl c. 2.5 mg/dl d. 3mg/dl 113- Clinical and labrotary features of hemolytic jaundice is characterized by all the following except: a. Bilirubinurea. b. Anemia. c. Normal LFTs. d. Dark stool & urine 114- With regarding to hepatocellular jaundice, all of the following is true except: a. This results from an inability of the liver to excrete and/or conjugate bilirubin, as a result of liver tissue damage. b. There is both increase in conjugated & unconjugated bilirubin. c. This type of diseases could be inherited d. Fecal urobilinogen will decrease. 115a. b. c. d. Which of the following drugs are known to cause hepatocellular jaundice. Halothane Paracetamol Sulfasalazine a&b 116a. b. c. d. the most common cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer is: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis E 117- In post hepatic jaundice a. Usually there is dark stool & urine. b. It may caused by many conditions, such as pancreatic head tumours and intestineal malabsorption and resection. c. There is elevated levels of bilirubin in urine. d. Elevated levels of urobilinogen will present also in urine. 118a. b. c. d. Normal level of urobilinogen in urine 40-80 mg/day 0.4 mg/day 0.8 mg/day O.2-0.8 mg/day 119a. b. c. d. Normal level of urobilinogen in feaces is : O.4 mg/day 40-280 mg/day 0.4 – 0.8 mg/day 0.1 – 0.4 mg/day 120- An absent of urine bilirubin, with very elevated urine urobilinogen is suggestive for : a. Hemolytic jaundice b. Cholestatic jaundice c. Intrahepatic obstruction d. Alcoholic hepatitis 121a. b. c. d. The forward reaction of AST gives : Pyridoxal 5-p and ATP Aspartate and oxoglutarate Pyruvate and glutamate Oxaloacetate and glutamate 122- Co-factor for transaminase enzyme activity is: a. B2 b. B5 c. B6 d. B12 123a. b. c. d. In hepatocyte: There is no mitochondrial AST ALT is more abundant than cytoplasmic AST. ALP is the most abundant enzyme found in cytoplasm of cell. GGT is only detected on cytoplasmic membrane. 124a. b. c. d. AST/ALT ratio more than 2 indicates: Cholestatic liver disorder Alcoholic hepatitis Viral hepatitis None of the above 125- Why AST is more elevated than ALT in alcoholic hepatitis ? a. AST is mitochondrial enzyme and since the alcohol work on damaging the mitochondrial membrane, it will elevated more than ALT. b. transaminase imbalance occurs in alcoholics secondary to a hepatic deficiency of pyridoxal-6-phosphate (a cofactor for ALT enzymatic activity). c. All of the above d. None of the above 126a. b. c. d. e. AST is found mainly in Liver Skeletal muscle Kidneys Heart 127- ALT is found in all the following except: a. Liver b. Skeletal muscles c. Pancreas d. Erythrocyte 128a. b. c. d. Non-alcoholic liver diseases is usually secondary to : Hyperlipemia & increase BMI Insulin resistance Type 2 diabetese mellitus All of the above 129a. b. c. d. Clinical picture for patient with cholestasis disorder is mainly: Pruritus Jaundice All of the above None of the above 130a. b. c. d. Serum bilirubin above 2mg/dL is very suggestive for : Hepatic liver disorder Prehepatic jaundice Cholestatic liver disorder Other 131- Which statement concerned GGT is true? a. A patient should never be labeled an alcoholic because of a high plasma GGT activity alone. b. GGT is present in female more than in male. c. A prostate and/or prostate related conditions are not related to elevated GGT. d. NO enzyme induction occurs leading to elevated of the amount of this enzyme in plasma e. None of the above. 132- which of the following enzymes is more sensitive and specific for detection of hepato-cellular injury : a. ALT b. AST c. ALP d. GGT 133- Regarding ALT, all the following is true except: a. b. c. d. Is the first enzyme to elevate in alcoholic hepatitis Is more than AST in cirrhosisi Is more P-6-P dependent than AST. Is more specific for hepatocellular injury. 134- Regarding transaminases, all of the following is true except: a. b. c. d. e. Are used to assess the conditions of late presentations. Used to differentiate between cardiac and hepatocellular injuries. Are convenient to measure. Elevation give us NO hint about the severity. 135- ALP a. b. c. d. Is the specific marker for cholestasis Do Not elevated in alcoholic hepatitis Is very sensitive for biliary tract injury Have equal ranges in male and female 136- Which of the following statemnts are true? a. b. c. d. AST is more in the liver than ALT. Cytoplasmic AST is more elevated than Mast IN alcoholic hepatitis Low AST/ALT ration is very suggestive for alcoholic hepatitis. The half life of AST is more than that of ALT. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A B B D D D C D B C 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 A D D D D B D B C D 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 A D A C C A A C A D 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 D D D C D A C B D A 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 A D A B C B D B B D 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 D C D B D D D B 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 A C B D C D D A 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 D B D C A B D A 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 B D C A B B C C 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 C A C D B C B D 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 B A B A D C B C 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 D B D A C D A A 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 A B A B C B A D 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 D B C B B A D C 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 B B C D D D C C 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 A A A A A 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146