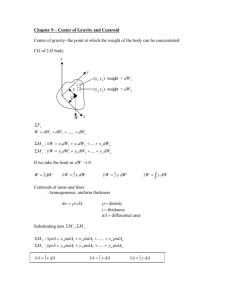
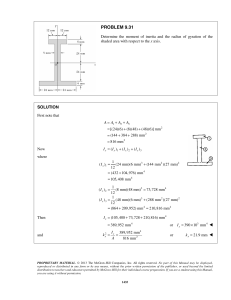
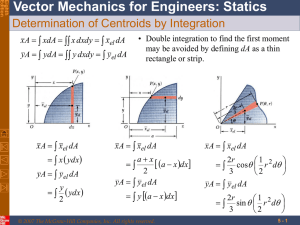
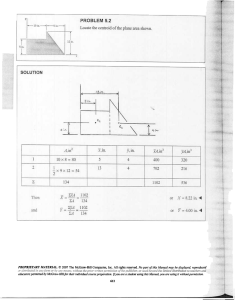
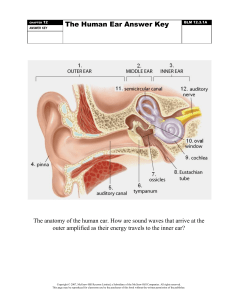
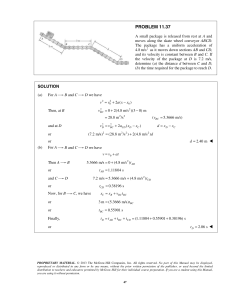
PROBLEM 5.40 Determine by direct integration the centroid of the area shown. Express your answer in terms of a and b. SOLUTION y1 = k1 x 2 but b = k1a 2 y2 = k 2 x 4 but b = k2 a 4 dA = ( y2 − y1 )dx = b 2 x a2 b y2 = 4 x 4 a y1 = b x4 2 x − dx a2 a2 xEL = x yEL = = 1 ( y1 + y2 ) 2 b x4 2 + x 2a 2 a2 A = dA = b a2 a 0 b x3 x5 = 2 − 2 a 3 5a x2 − x4 dx a2 a 0 2 = ba 15 xEL dA = a 0 x b x4 2 − x dx a2 a2 x5 dx a2 = b a2 = b x4 x6 − a 2 4 6a 2 a 0 x3 − a 0 1 = a 2b 12 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission. 596 PROBLEM 5.40 (Continued) yEL dA = = a 0 b x4 b x4 2 2 + − x x dx a2 a2 a2 2a 2 b2 2a 4 a 0 x4 − x8 dx a4 b 2 x5 x9 = 4 − 4 2 a 5 9a a = 0 2 2 ab 45 xA = xEL dA: x 2 1 ba = a 2b 15 12 5 x= a 8 yA = yEL dA: y 2 2 2 ba = ab 15 45 1 y= b 3 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission. 597 PROBLEM 5.41 Determine by direct integration the centroid of the area shown. Express your answer in terms of a and b. SOLUTION y =b First note that symmetry implies At x = a, y=b y1 : b = ka 2 Then y1 = or k= b a2 b 2 x a2 y2 : b = 2b − ca 2 or c= b a2 x2 a2 Then y2 = b 2 − Now dA = ( y2 − y1 )dx2 = b 2 − = 2b 1 − and Then and x2 b − 2 x 2 dx 2 a a x2 dx a2 xEL = x A = dA xEL dA = a 0 a 0 x2 x3 2b 1 − 2 dx = 2b x − 2 a 3a x2 x2 x4 x 2b 1 − 2 dx = 2b − 2 2 4a a 4 1 xA = xEL dA: x ab = a 2b 3 2 a = 0 4 ab 3 a = 0 1 2 a b 2 3 x= a 8 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission. 598