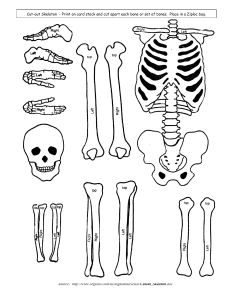
جامعة البصره_____________ _____________كلية الصيلة إشراف : د .فال ح سن شر إعداد الطالب: مونى عبد العزيز عبد الزهره عبد الله السجاج المجموعة الثانية شعبة- G- INTRODUCTION The skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. Each bone is a complex living organ that is made up of many cells, protein fibers, and minerals. The skeleton acts as a scaffold by providing support and protection for the soft tissues that make up the rest of the body. The skeletal system also provides attachment points for muscles to allow movements at the joints. New blood cells are produced by the red bone marrow inside of our bones. Bones act as the body’s warehouse. The skeletal system in an adult body is made up of 206 individual bones. These bones are arranged into two major divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton runs along the body’s midline axis and is made up of 80 bones in the following regions:)Skull,Hyoid,Auditory ossicles,Ribs,Sternum,Vertebral column). The appendicular skeleton is made up of 126 bones in the folowing regions:(Upper limbs,Lower limbs,Pelvic girdle,Pectoral (shoulder) girdle). MEDICAL TERMS OF SKELETAL SYSTEM: Sacrumk / (sac.rum) : is a large bone located at the terminal art of the vertebral canal, where it orms the posterior aspect of the lvis. It is remarkably thick, which ds in supporting and transmitting the weight of the body. Femur/ (fe.mur): is the only bone located within the human thigh. It is both the longest and the strongest bone in the human body, extending from the hip to the knee. Radius/(ra.di.us): in anatomy, the outer of the two bones of the forearm when viewed with the palm facing forward. All land vertebrates have this bone. In humans it is shorter than the other bone of the forearm, the uln. Tibia/(tib.i.a): (shin bone) is a long bone of the leg, found medial to the fibula. It is also the the weight bearing, bone of the leg. Ulna /(ul.na): is a long bone in the forearm. It lies medially and parallel to the radius the second of the forearm bones. The ulna acts as the stabilizing bone, with the radius pivoting to produce movement. Humerus /(hu.mer.us): is a long bone of the upper limb, which extends from the shoulder to the elbow. Scapula/( scap.u.la): form the posterior portion of the shoulder girdle (pectoral girdle), the part of the appendicular skeleton that connects the bones of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton. Patella :(pa.tal.la): is also known as the kneecap. It sits in front of the knee joint and protects the joint from damage. It is the largest sesamoid bone in the body, and lies within the quadriceps tendon. Sternum/( Ster.num): A long, narrow, and flat bone commonly known as breastbone occurring in the midsection of the anterior thoracic segment or chest region, which stabilizes the rib cage and serves as the point of origin for several muscles that move the arms, head and neck. Spine/( spaɪn): The column of bone known as the vertebral column, which surrounds and protects the spinal cord. Zygoma/(zy.go.ma): Either of a pair of bones that form the prominent part of the CHEEK and contribute to the ORBIT on each side of the SKULL. Thoracic / (tho.rac.ic): The chest, properly called the thorax, is the superior part of the trunk located between the neck and abdomen. Rib / (rib): The vertebrosternal ribs (true ribs) are the first seven pairs (01-07) of ribs that form the thoracic cage. The false ribs (08-12) are the five inferior pairs of ribs that form part of the thoracic cage and give it flexibility. Bone marrow/ (mar.row): Bone marrow fills the cylindrical cavities in the bodies of long bones and occupies the spaces inside spongy bone. It also extends into the larger bony canals (central canals) that contain blood vessels. Pelvis / (pel.vis): The lower portion of the trunk, bounded anteriorly and laterally by the two hip bones and posteriorly by the sacrum and coccyx. Skull : ( skull): The skull comprises most of the bones of the head region. It is divided into two parts: the eight bones of the neurocranium and the fourteen bones of the facial skeleton. REFERENCES: [1] Morgan, Elise F., George L. Barnes, and Thomas A. Einhorn. "The bone organ system: form and function." Osteoporosis. Academic Press, 2013. 3-20. [2]Moore, Keith L., and Arthur F. Dalley. Clinically oriented anatomy. Wolters kluwer india Pvt Ltd, 2018 [3] Pellegrini, Massimo, et al. "Agenesis of the scapula in Emx2 homozygous mutants." Developmental biology 232.1 (2001): 149-156. [4] Kumlin, T., M. Wiikeri, and P. Sumari. "Radiological changes in carpal and metacarpal bones and phalanges caused by chain saw vibration." Occupational and Environmental Medicine 30.1 (1973): 71-73. [5] Logan, Bari M., and Ralph T. Hutchings. McMinn's Color Atlas of Foot and Ankle Anatomy E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2011. [6] Steele, D. Gentry, and Claud A. Bramblett. The anatomy and biology of the human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press, 1988. [7] Cragg, A. H. (2003). U.S. Patent No. 6,575,979. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.