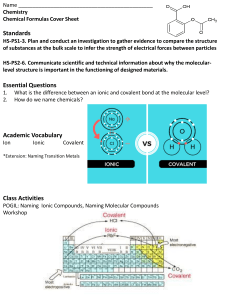
Chemistry warm - up Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds. calcium sulfide tin (IV) fluoride sodium sulfate 2. Write names for the following ionic compounds. FeCO3 (NH4)2O 1. Answers Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds. calcium sulfide = CaS tin (IV) fluoride = SnF4 sodium sulfate = Na2SO4 2. Write names for the following ionic compounds. FeCO3 = iron (II) carbonate (NH4)2O = ammonium oxide 1. Today in Chemistry Class Today’s Goal . . . • To be able to write molecular compound formulas and name molecular compounds Ionic vs. molecular compounds ◼ Ionic – – – – ◼ Occurs between metals and non metals Positive and negative ions attract and balance Electrons are traded Strong bond. Mostly solids* Molecular (covalent) – – – – Occurs between non-metals No need to worry about charges Electrons are shared Weaker bonds. Mostly liquids and gases* * At “room” temperature and sea level Molecular Compounds Occurs between non-metals Top right hand part of periodic table No metals Can often combine in more than one way (NO, NO2, N2O5, etc.) Traditional System The traditional naming system uses Latin prefixes to show how many of each element there is in the compound Prefixes 1 = mono 2 = di 3 = tri 4 = tetra 5 = penta 6 = hexa 7 = hepta 8 = octa 9 = nona 10 = deca Binary molecular compound If there is only one atom of the first element, it doesn’t get a prefix All other elements, or if there is more than one atom of the first element, they get a prefix First element name doesn’t change Second element ending changed to -ide CO2 carbon dioxide P2O4 diphosphorous tetraoxide Examples Naming molecules NO = nitrogen monoxide NO2 = nitrogen dioxide N2O5 = dinitrogen pentoxide Writing molecular formulas carbon tetrachloride = CCl4 dinitrogen trioxide = N2O3 The diatomic seven ◼ Seven elements must combine with another atom of the same element when there are no other elements – These are H, N, O, F, Cl, Br, and I – When we talk about oxygen and hydrogen in the air, it is O2 and H2 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Not H + O → H2 O Chemistry ◼ Write the following formulas: Tricarbon heptafluoride Nitrogen tetrachloride ◼ Write the following names: SO3 NO4 How do formula 2. How do formula 1. you recognize whether a chemical is an ionic compound? you recognize whether a chemical is a molecular compound? Answers 1. How do you recognize whether a chemical formula is an ionic compound? – There is a metal and a non-metal 2. How do you recognize whether a chemical formula is a molecular compound? – There are two or more nonmetals and no metals Chemistry ◼ Write the following formulas: Tricarbon heptafluoride Nitrogen tetrachloride Calcium phosphate Write the following names: (NH4)2SO3 SO3 NO4 Acids Have an H at the start of their formula (HCl, HF, H2SO4) Compounds that produce hydrogen ions in water Compounds are molecular but act ionic in water meaning charges must be balanced Binary (only 2 elements) ➢ Given the prefix “hydro“ to indicate they are binary ➢ The name is modified with an “ic” ending Examples Hydrogen + chlorine Hydrogen + sulfur HCl (aq) = hydrochloric acid H2S (aq) = hydrosulfuric acid Ternary (3+ elements) NO prefix If the anion ends in “- ite” the acid ends in “-ous” If the anion ends in “-ate” the acid ends in “-ic” Example: Hydrogen + nitrite ion HNO2 Nitrous acid Hydrogen + sulfate ion H2SO4 Sulfuric acid Examples H2SO4 = sulfuric acid (because SO42- is sulfate) HNO2 = nitrous acid (because NO21- is nitrite) ◼ What would be the name of HBr? ◼ What would be the formula of acetic acid? ◼ Hydrobromic Acid – only 2 elements, so name starts with “hydro”, – bromine changed to bromic ◼ HC2H3O2 – No “hydro” in name so more than 2 elements – “acetic” ends in “ic” so anion must end in “ate” ▪ Acetate which is -1, so we need only one to balance the +1 charge of the hydrogen