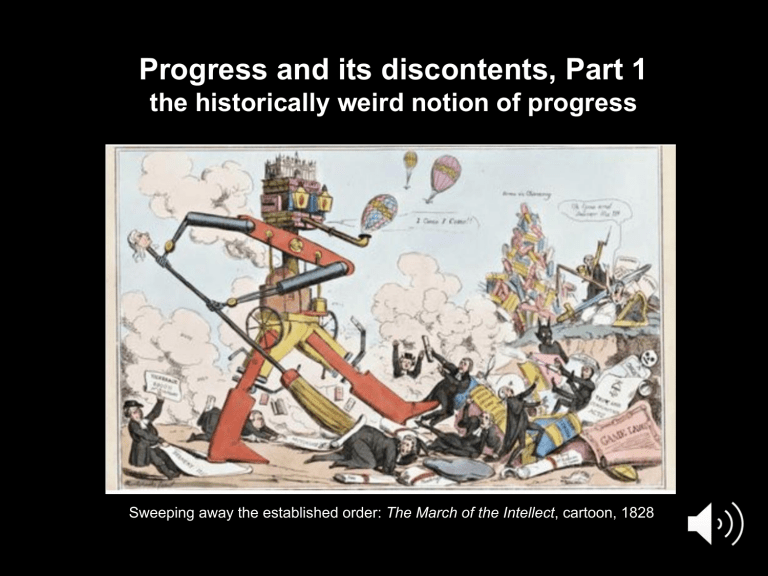
Progress and its discontents, Part 1 the historically weird notion of progress Sweeping away the established order: The March of the Intellect, cartoon, 1828 The great steps in the human experience • opposable thumbs? • fire? • domestication of dogs (or cats if you prefer) • spirits and gods? • agriculture? • money? • Newton’s laws of motion? • antibiotics and vaccines? • indoor plumbing? • Wikipedia and control F? 2 J. B. Bury’s two great steps in the human experience self-consciousness the idea of progress 3 The idea of progress • human history has been a rise from ignorance to knowledge, primitive to skilled, impoverished to wealthy, savagery to civilized behaviour, etc. • human improvement is - possible and perhaps even inevitable - enabled by applied science, technology and economics • there are no serious limits 4 Progress as a modern idea – a phenomenon of the last few hundred years Albert Rohida • sedentary life: wealth as wellbeing • nature as resources: the world is material; we are above it • the world is knowable and manipulable through applied science and technology • economic life organizes directing material self-interest (or collective material interest) as a motivator for innovation and advance • ever improving industrial production and distribution provide more and more 5 Before progress: hunting, gathering, foraging • nomadic life: wealth is a burden • life in nature: the world is alive; we are part of it • the world has mysteries and surprises • social life requires means of ensuring cooperation and avoiding or dealing with conflict on the essentials • what has worked in the past is less risky than innovation • 90 some percent of the human experience Inuit family travelling near Chesterfield Inlet 6 Before progress: agriculture Scene from the Tomb of Sennedjem and Iyneferti, Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain • sedentary life • potential for material accumulation • hierarchical social order • customary places, roles, practices • reliance on the regularity of rains, or annual floods, or dry seasons • chaos of war and invasion • desire for stability 7 Before progress: cyclical time ancient Egypt: • reviving Nile floods • scarab (dung beetle) as eternal renewal; sun god Ra rolling across the sky every day Mayans: • death-rebirth symbols • calendar cycles India: • Jain, Hindu & Buddhist wheel of life 8 Before progress: the glorious past earlier different times, with previous peoples/beings: • maybe giants (Titans) • maybe ideal (Golden Age) or at least heroic • maybe magical (elves, unicorns) • maybe innocent (Eden) all better, or at least more capable or more exciting, than people and life in the present St. George and the Dragon, Rogier van der Weyden, 1432 9 Before progress: a world in decline • in Europe, medieval view of decline - evidence of richer, more sophisticated past (ruins) - the architecture of the past/plagues of the present - assumed wisdom of the ancients (Bible, Aristotle) • focus on perfection of whole, maintenance of hierarchy, stability and balance Pont du Gard aqueduct, Roman, ~50 AD, 17m drop over 50km, no mortar, 20,000 m3/day, operated without maintenance from 4th to 9th c 10 Before progress: ambiguity about gains • rise of selfconsciousness led to banishment from Eden • technological innovations also brought big losses (Daedelus/Icarus) • no anticipation of material betterment • change is risky Peter Bruegel, Landscape with the Fall of Icarus, 1560? 11




