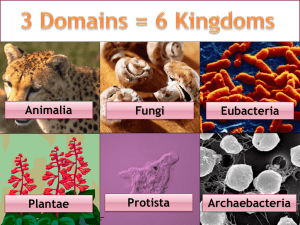
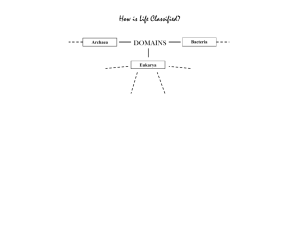
NAME:_________________________________ Taxonomy Practice: 1. Three Domains: All organisms belong to one of three domains, depending on their characteristics. A domain is the most inclusive taxonomic category. A single domain can contain one or more kingdoms. Fill in the table below. Domain Domain Characteristics Kingdoms Included in Domain Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Practice with Domains and Kingdoms: DOMAIN KINGDOM Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Eukaryote Animalia CELL TYPE Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote CELL STRUCTURES Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls of Cell walls of chitin; no cellulose; chloroplast chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts NUMBER OF CELLS Unicellular Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most Multicellular multicellular ; some unicellular Multicellular MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals Figure 18-3 2. According to the figures, what is the main difference between the domain Bacteria and the domain Archaea? 3. If you know an organism has a cell wall and is a multicellular autotroph, could you use Figure 18-3 to determine the kingdom to which it belongs? _____________________Why or why not? 4. If you were told only that an organism is unicellular and has chloroplasts and a nucleus, could you use Figure 18-3 to determine the kingdom to which it belongs? ________________Why or why not? Taxonomy Practice: 1. Define a species: 2. List 4 ways that new species can develop: ________________________________ ___________________________________ ________________________________ ___________________________________ 3. Define taxonomy: 4. Who is known as the "Father of Taxonomy"? ____________________________________ 5. Describe binomial nomenclature? 6. What two parts constitutes a "scientific name"? ____________________ and the __________________ 7. If your name were a scientific name, which part would be the genus? __________________ 8. Which part would be the species identifier? _______________________________________ 9. Number the major classification groups (taxa) in order from the most specific (1) to the least specific (7). ___class ___family ___order ___genus ___phylum ___kingdom ___species Circle the scientific name that is LEAST like the other 2. 10. Canis familiaris 11. Felis domesticus Canis lupis Mus domesticus Use the table to answer the questions that follow: Animalia Kingdom Chordata Phylum Mammalia Class Cetacea Order Mysticeti Family Balaenoptora Genus B. physalus Species Common Name Blue Whale Felis domesticus Felis concolor Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Mustelidae Mustela M. furo Ferret Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Felis F. domesticus Domestic cat Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Felis F. rufus Bobcat 12. How does the table indicate that a cat is more closely related to a bobcat than a ferret? 13. Which two animals are most closely related? ______________________ and ___________________How do you know? 14. What kind of animal is Balaenoptora borealis? _______________________ How do you know?