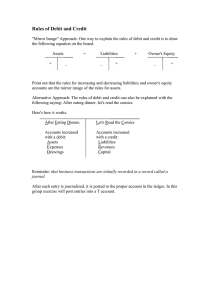
MIDTERM SUMMARY Defin Bryan Eliezer Prionggo – 0106022010011 #Accounting in Action Accounting Vs Finance Finance -> is cash sufficient to pay dividends to shareholders? Marketing -> what price for our product will maximize net income? Finance = related to the future, predicting the future Ex: Creditors = will the company be able to pay its debts? stock and shares, it has to have a based/fundamental, Ethics in Financial Reporting which is accounting. Accounting = the process of recording financial Ethics are the standards of conduct by which actions are transactions related to the past. Three activities : judged as : right or wrong, honest or dishonest, fair or identify, record and communicate. not fair. ACCOUNTING IS THE FUNDAMENTAL OF FINANCE Purpose of Accounting = creating financial statements Accounting Standards International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) -> International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) Financial statement = Reflects the company condition, either the company gain the profit(good condition) or not(bad condition/gaining loss). Financial statement will Focuses on accounting standards on global standards (international) be the reference for people to invest their money in Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) -> stock and shares. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) How do we know if a report is fraud or not? It has to be Focuses on accounting standards in the United States checked by auditor as an independent party (financial statement-audited) 2 types of company = public-listed & private company. Public-listed company = stock and shares can be bought Accounting Users : (ex: PT telkom, bank BCA tbk -> the tbk reflects that the a. Internal Users : b. External Users : - Finance - Taxing Authorities - Marketing - Customers - Human Resources - Regulatory Agencies - Management - Labor Unions themselves. - Creditors Private -> Public (Bursa Efek Indonsesia registration) - Investors Public -> Private (Ex. Aqua, previously it’s private, it company is public listed) (tbk stands for terbuka). It sells % ownership to the public. Private company/family business company = normally stock and shares cannot be bought (PT Wonokoyo Human resource -> can we afford to give employees a pay rise? Investors -> did the company earn a satisfactory income? Management = should any product lines be eliminated? Group). 100% ownership, gain the profit and loss by turned public then private again) Requirements from public to private = buy every paper/slot from the shareholders. TERMS : Transactions = business’s economic events, a deal between two parties, one wants to sell, one wants to buy Gross income = the amount you earn before taxes and other payroll deductions. Net income = take-home pay after taxes and other 2. Partnership = owned by 2 or more, retail or servicetype business, unlimited personal liablity. 3. Corporation = ownership divided into shares, separate legal entity organized under state corporation law, limited liability. ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY payroll deductions. Assets Creditors = someone who lends money a. Current assets = cash, accounts receivable, prepaid Assets = resources a company owns Liabilities = what the company owes Equity = what its owners invest Capital = sum of money to start a business, or which you invest in order to make more money. Dividend = distribution of profit to the shareholders expenses, supplies b. Fixed assets = property, land, equipment, machinery Liabilities a. Current liabilities = notes payable, accounts payable, salaries payable, bills b. Long-term liabilities = bonds payable, long-term loan based on the number of shares they own. Equity The company doesn’t have to pay dividend. Why the Share Capital + Retained Earnings (Rev-Exp-Div) company wants to keep the profit, not share to Financial Statement shareholders : Income 1. they want to expand the business next year 2. the company thinks that next year they will face a big problem 3. the profit is too small statement = revenue – expense (net income/loss) Retained earnings statement = income statement – dividends Statement of financial position = assets = liabilities + Assumptions equity a. Monetary Unit Assumption = expressed in terms of Statement of cash flows = transactions within cash money. account b. Economic Entity Assumption = activities of the entity are kept separate from the activities of the owner and #The Recording Process Double Entry accounting system other economic entities. - each transactions must affect two or more accounts to Forms of Business Ownership : 1. Proprietorship = owned by 1 person, smal business type, receives any profits, suffers any losses, personally liable for all debts. keep the equation in balance - recording done by debiting at least one account and crediting another DEBITS must equal CREDITS. Expense Recognition Principle (Matching Principle) DEBIT VS CREDIT Match expenses with revenues in the period when the company makes efforts to generate those revenues. Adjusting Entries Needed to ensure that the revenue recognition and expense recognition are followed Deferrals Prepaid Expenses = CASH PAYMENT before EXPENSE RECORDED Journalizing : the process of recording accounting transactions in chronological order. increases expense, decreases asset Posting : the process of transferring amounts from the Unearned Revenue = journal to the ledger accounts. CASH RECEIPT before REVENUE RECORDED Trial Balance : a list of accounts and their balances at a increases revenue, decreases liability (unearned fees) given time. Proves that debits = credits Accruals Limitations of a Trial Balance Accrued Revenues = The trial balance may balance even when REVENUE RECORDED before CASH RECEIPT 1. a transactions is not journalized increases revenue, increases accounts receivable 2. a correct journal entry is not posted Accrued Expenses = 3. a journal entry is posted twice 4. incorrect accounts are used in journalizing or posting 5. offsetting errors are made in recording the amount of a transaction. #Adjusting the Accounts EXPENSE RECORDED before CASH PAYMENT increases expense, increases accounts payable The Adjusted Trial Balance After adjusting entries are journalized and posted, the company prepares another trial balance from the ledger Revenue Recognition Principle accounts (Adjusted Trial Balance) Companies Its purpose is to prove the equality of debit balances recognize revenue in accounting period which it is earned. the in and credit balances in the ledger. Unadjusted vs Adjusted Trial Balance Things to pay attention to : Unadjusted trial balance is the first list of ledger account •Transferred cash from personal bank account to be balances, compiled without making any period end used for business = Cash debit, share capital credit adjustments. Adjusted trial balance is the trial balance compiled after considering adjustment entries at the close of the accounting period. #Completing the Accounting Cycle Worksheet Income statement is prepared from the income statement columns •Paid creditors on cash/account(udh pasti cash kynya) = account payable debit, cash credit •Determine the supplies used = debit supplies expense, credit supplies (used supplies cost) •Withdrew cash from business for personal expense = personal expense/drawing debit, cash credit •Received cash on account from previous transaction = cash debit, accounts receivable credit Statement of financial position and retained earnings statement are prepared from the •Returning defective equipment (yg awalnya bayar on statement of financial position columns. account) = accounts payable debit, equipment credit Summary of the Accounting Cycle •Customer pays a sales invoice = cash debit, accounts receivable credited 1. Transactions are analyzed and recorded in the journal •Pioneer advertising agency signed a 3-month note 2. Transactions are posted to ledger 3. An unadjusted trial balance is prepared 4. Adjustment data are assembled and analyzed 5. Adjusting entries are journalized and posted to the ledger 6. An adjusted trial balance is prepared payable for $5000 on October 1. The note requires to pay interest at annual rate 12% = $5000 x 12% / 12 = $50 = Debit interest expense, credit interest payable •Insurance expired = debit insurance expense, credit prepaid insurance •Unbilled fees/fees earned but unbilled = accrued revenue = debit acc receivable, credit fees earned 7. An optional end of period spreadsheet is prepared •Unexpired rent = credit prepaid rent, debit rent 8. Financial Statements are prepared expense (use the number of difference) 9. Closing entreis are journalized and posted to the •Rent Unearned = debit liability (unearned rent), credit ledger fees earned •Equipment 10. A post-closing trial balance is prepared equipment withdrawn = debit drawing, credit