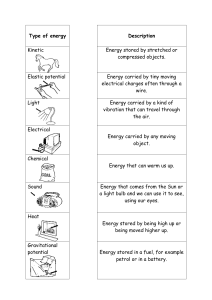
Energy Transfers (PHYSICS) KWLH CHART K _____/01/18 L1: L2: W _____/01/18 L1: L2: L _____/01/18 L1: L2: H _____/01/18 L1: L2: __/11/20 Topic: Understanding potential energy and kinetic energy Learning Objective: To recognise energy transfers due to falling objects. Learning Outcome: Will be able to explain how energy is transferred using gravitational potential energy, Kinetic Energy. Vocabulary Bank: gravity, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy STARTER COMPARE AND CONTRAST BETWEEN KINETIC ENERGY AND POTENTIAL ENERGY TASK 1: Analyze the type of energies possessed by a falling object at position A, position B and Position C dropping from some height. MID PLEANARY • Join at gospiral.ac with code XSQWD AFL 1. Explain about conservation of mechanical energy? 2. TASK 2: Deduce law of conservation of energy: Breakout rooms https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/energy-skate-park-basics/latest/energyskate-park-basics_en.html http://www.solpass.org/5s/images/roller.gif Potential and Kinetic Energy | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children – YouTube Reading : Energy from Gravity of Falling Objects by Ron Kurtus - Physics Lessons: School for Champions (school-for-champions.com) TASK 2: Deduce law of conservation of energy: TASK 2A: Identify the type of maximum energy at position 1, 2,3 and 4? Eliena Fatima Arjun Amir Aryan Anishka Khidab Niranjan Task 2B: Calculate the values of PE at different points A B D C TASK 2C: • Sketch two graphs to show how gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy changes for a falling object? Sinuri Mohammed Mia Julienne Aysana Advik Kavya Joerel Kristina TASK 2 Extended: Analyze the position with highest value of K.E and P.E B A C SUMMARY PLENARY Factors Affecting GPE 20 kg g = 10 N/kg Task 3: Peer-marking = PM By: (Checker’s name) 1. joule, J 2. gravity 3. 10 m high 4. Saturn 5. a) A b) C c) A d) C 6. The graph(s) should show a decreasing line for GPE and an increasing line for KE * should be able to establish the link between kinetic energy and speed – the more KE there is, the faster the object moves. Identify whether there is potential elastic energy on the spring: normal, stretched and compressed. Differentiated Task2: •What causes the jack-in-the-box to bounce up when the lid is open? •What forms of energy are involved in question number one? Answers: 1. Energy is stored in a spring when it is compressed; when the spring is released, the energy is transferred by movement; causing ‘Jack’ to bounce up. 2. Elastic potential energy and kinetic energy Differentiated Task 2: Analyse the picture involving 2 more forms of energy together with elastic potential energy. Fill in the blanks with the amount of energy: zero, minimum, maximum, low, high LO 16: Identify simple energy transfers which involve gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy and kinetic energy. All correct = DEVELOPING With any mistake = EMERGING Differentiated Task 2:Complete the energy transfer diagram of a tennis ball with appropriate form of energy. LO 20: Interpret and draw energy transfer diagrams for a range of different energy transfers, including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical energy and kinetic energy. All correct = DEVELOPING With any mistake = EMERGING Extension Task : Plan an investigation to find the minimum height of drop to burst a water balloon.