US & Canada Physical Geography: Landforms, Rivers, Resources
advertisement

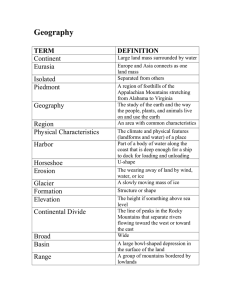
By Jack Garrity Chapter 8 Pages 131-135 The United States and Canada form a geographic region of enormous physical variety and natural wealth This wealth includes breathtaking landforms shaped by the forces of water, wind and geology over millions of years. These landforms, such as the rugged, mountainous areas near Yellowstone National Park, have attracted adventurers and inspired writers for decades. In North America, water, wind glacial, and geologic forces shape the landscapes of the USA and Canada. The 3rd in area, North America accounts for 24.71 million km². The West coast has new sharp mountains that become plains extending across the continent to meet the older eroded mountains in the east. Tectonic plate collisions created the sharp peaked Pacific Ranges millions of years ago. These include the Sierra Nevada, These include the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range These include the Sierra Nevada, the volcanic Cascade Range, the Coast Range These include the Sierra Nevada, the volcanic Cascade Range, the Coast Range, and the Alaska Range. Mount McKinley is the highest point on the continent at 6,194 meters. The Rocky Mountains stretch for 4,828 km with some peaks more than 4,267 m tall. Dry basins and plateaus fill the area between the Pacific Ranges and Rocky Mountains. Basin a hollow or depression in the earth's surface, wholly or partly surrounded by higher land: Leaking lava formed the Columbia Plateau. Wind and water erosion have shaped the Colorado Plateau with flat-topped mesas. Wind and water erosion have shaped the Colorado Plateau with flat-topped mesas. Millions of years of water erosion with continued uplift creates the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Millions of years of water erosion with continued uplift creates the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. The Gran Canyon’s sheer walls plunge 1,829 m deep. The Great Basin cradles Death Valley, the lowest place in the US and usually the hottest place on the planet. East of the Rockies, the land falls and flattens into the Great Plains, which extent 483-1,126 km across the center The Great Plains begin at 1,829 m, yet appear flat. The Great plains slope downwards at about 2 m per km to the Central Lowlands along the Mississippi River. East of the Mississippi, the land rises slowly to the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains. The heavily eroded Appalachian Mountains are the oldes and 2nd longest 2,412 km. Glaciers eroded the Appalachian Mountains throughout the Ice Age. They average 910 m, the highest of the group is Mount Mitchell in North Carolina at 2,037 m. The Canadian Shield, a giant core of rock, anchors the continent on the edge of the Canadian Plain. This stony land makes up the eastern half of Canada and northeastern USA. The Canadian Shield descends to Hudson Bay. Churchill Canada on the Hudson Bay Coastal lowlands lie east and south of the Appalachians. The Piedmont, an area of rolling hills, runs between the mountains and lowlands. In the south east, the Gulf Coastal Plain extends to Texas The Hawaiian Islands are volcanic. Lava accumulations created the 8 major and124 smaller Islands of the State. The Ellesmere Islands are part of the continent. Greenland, the world’s largest island 2.2 million km2, remains part of Denmark. Newfoundland, Prince Edward Island and Cape Breton slands are economic ports on the east coast of Canada. Vancouver Island is Canada’s main port to Asia. New York City’s Manhattan Island is the main world economic center. Lakes and rivers in North America continue to be important to economic development. Major rivers, the super highways of the past, connected the cities of the continent. The Continental Divide determines which way rivers flow. West of the Continental Divide rivers flow towards the Pacific Ocean. The Colorado and Rio Grande have their headwaters in the Rocky Mountains. Dozens of smaller tributary rivers connect with them. A tributary is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean East of the Continental Divide Rivers flow towards the Atlantic Ocean, and Hudson Bay. They flow into the Mississippi River, which runs North South. They flow into the Mississippi River flows 3,782 km towards the Gulf of Mexico. It’s headwater is so thin that you can jump across it in Minnesota. It reaches a width of 2.4 km as it empties into the Gulf of Mexico. It drains 31 US states and 2 Canadian Providences, making it one of the world’s busiest commercial waterways. The St. Lawrence River flows for 1.207 km from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrence. The Canadian cities of Quebec, Montreal, and Ottawa depend on the St. Lawrence for trade and transportation. Niagara Falls forms another part of the boarder with the Horseshoe Falls on the Canadian side and the American Falls on the US side. Glacial dams created Great Bear Lake and Great Slave Lake. Area: 31,153 km² Surface elevation: 156 m Mean depth: 72 m Glacial erosion tore the Canadian Shield leaving huge basins. These filled with water from melting glaciers, becoming the Great Lakes. The Great Lakes — Superior, Huron, Michigan, Ontario and Erie. The Great Lakes make up the largest body of fresh water on Earth, accounting for one-fifth of the freshwater surface on the planet at 6 quadrillion gallons. Area: 244,106 km² Area: 244,106 km² UAE 83,600 km² Abundant natural resources have made the US and Canada wealthy, especially as they were not sent to Europe. United States has 8,133.5 metric tons of gold. metric ton noun a unit of weight equal to 1,000 kilograms (2,205 lb). 25 metric tons of silver The United States is currently third in food production, but still produces so much it throws half away. 1 Russia 10,500,000 2 Saudi Arabia (OPEC) 10,000,000 3 United States 9,200,000 4 Iraq (OPEC) 4,300,000 5 China, People's Republic of 4,100,000 6 Canada 3,800,000 7 Iran (OPEC) 3,500,000 8 United Arab Emirates (OPEC) 2,700,000 9 Kuwait (OPEC) 2,500,000 10 Venezuela (OPEC) 2,400,000 75,212,696 World[8] 1 United States 18,561,930 — European Union[n 1][8] 16,518,723 2 China[n 2] 11,391,619 3 Japan 4,730,300 4 Germany 3,494,900 5 United Kingdom 2,649,890 6 France 2,488,280 7 India 2,250,990 8 Italy 1,852,500 9 Brazil 1,769,600 10 Canada 1,532,340 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the broadest quantitative measure of a nation's total economic activity. More specifically, GDP represents the monetary value of all goods and services produced within a nation's geographic borders over a specified period of time. 1 Qatar 132,870 2 Luxembourg 99,506 3 Singapore 85,382 4 Brunei 79,508 5 Kuwait 70,542 6 Norway 68,591 7 United Arab Emirates 67,217 8 Ireland 65,806 9 San Marino 62,938 10 Switzerland 58,647 — Hong Kong 56,878 11 United States 56,084 12 Saudi Arabia 53,802 13 Netherlands 49,624 14 Bahrain 49,601 15 Sweden 48,199 Rank Country US$ 1 Luxembourg 149,160 2 Switzerland 80,603 3 Norway 74,598 4 Qatar 68,940 5 Ireland 61,206 6 United States 56,084 7 Singapore 52,888 8 Denmark 52,139 9 Australia 51,181 10 Iceland 50,277 11 Sweden 50,050 12 San Marino 49,615 13 United Kingdom 43,902 14 Austria 43,724 15 Netherlands 43,603 16 Canada 43,413 17 Finland 42,413 — Hong Kong 42,295 18 Germany 40,952 19 Belgium 40,529 20 United Arab Emirates 38,650 Average annual wages, 2015 Country constant prices at 2015 USD PPPs United States 58,714 United Kingdom 41,384 Switzerland 58,389 Sweden 40,909 Spain 36,325 South Korea 33,110 Slovenia 33,085 Slovak Republic 22,031 Portugal 24,105 Poland 23,998 Norway 50,908 Netherlands 50,670 Mexico 14,867 Luxembourg 60,369 Japan 35,780 Italy 34,140 Israel 29,794 Ireland 46,074 Hungary 19,999 Greece 25,211 Germany 44,925 France 41,252 Finland 40,731 Estonia 21,564 Denmark 50,024 Czech Republic 21,689 Canada 47,843 Belgium 47,702 Austria 46,084 Australia 50,167 Next time, Cultural Latin America end