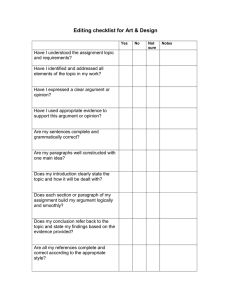
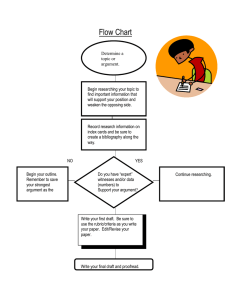
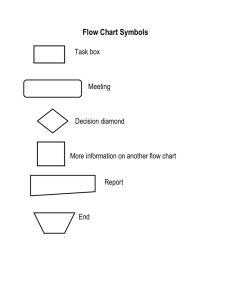
Eng Wr 302 T. Marchak Final Exam: Textbook Study Guide Review the following terms and define/explain them. Write your answers in the space left for you. (If the page numbers are off, you can look up the terms in the index at the end of the book). 1. p. 38, what is empathic listening? Answer: empathic listening is seeing the issue through the author’s eyes like you temporarily become instead of the author. 2. Ch. 1, implicit & explicit argument Answer: an explicit argument directly states its claim and supports it with reasons and evidences. An implicit argument can does not look like an argument. It can be a billboard, an advertisement, a poem, a song, and still has its different viewpoints. 3. Ch. 1, what does argument combine? (two things here) Answer: 1. A set of two or more conflicting assertions, 2. The attempt to resolve the conflictions through an appeal to reasons. 4. p. 45, define dialectic thinking. Answer: dialectic thinking is a strategy to bring text into conversation. 5. Ch. 3, define logos, pathos, ethos, kairos. Answer: logos is making the argument more logically to the audience. Pathos is the step when the writer tries to make the issue more emotionally to open the audience to the message. Ethos is trying to appear the best for the audience. Kairos is choosing the right time to have the most efficient effect on audience. 6. What is issue question? p. 64 Answer: issue question is the question which brings on an argument. It’s the core question of the argument. It doesn’t have one specific answer. 7. Define information question. Answer: information question has an obvious answer and is the truth which does not create any argument. 8. What is the claim in an essay? p. 67 Answer: claim is the main point of an argument which is created by the author and supported by many reasons to persuade the audience to their point of view. 9. What is a reason? p. 67 Answer: a reason is presented by the author in order to support the claim in an argument. 10. Define a working thesis statement, p. 69 Answer: a working thesis statement is a halfway argument written by the author to sort the argument in an order. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11. Define an enthymeme, p. 74-75 Answer: the core of an argument is an incomplete logical structure and called enthymeme. 12. Define a warrant in the Toulmin system, p.77 Answer: in Toulmin system, warrant is the value, belief, or idea that the audience has to hold it and accept it. 13. Define grounds and backing in the Toulmin system. Answer: grounds are the examples and supports to the idea to make the audience to accept the reasons. Backing is the evidence that supports the warrant in case if these is a chance for audience to attack our warrant. 14. Define the term writer’s angle of vision, p. 95 Answer: writer’s angle of vision is the perspective of the writer himself and the audience is convinced to see the issue from writer’s angle of vision. 15. Ch. 7 Define a one-sided argument. Answer: a one-sided argument is when the writer does not consider the opposing views of the issue. 16. Define a multisided argument. Answer: a multisided argument is written when the writer considers the opposing viewpoints about the issue and is not one-sided. 17. Define a dialogic argument. Answer: dialogic argument is written when the opposing viewpoint is strong, and the writer need to find some common places where he can agree with the audience so they can make an argument. 18. Explain the idea of scale of resistance, p. 125 Answer: the scale of resistance is a scale from agreement to disagreement of the audience which shows how much the audience agrees on the issue in a dialogic argument. 19. What is principle of charity in summarizing opposing views? Answer: principle of charity is summarizing opposing views fairly to avoid loaded biases and to oversimplify the opposing argument and making them essay to knock over. 20. Define delayed-thesis argument, p. 135 Answer: in delayed-thesis argument, you wait until the end of argument to state your thesis in order to reach a resistant audience. 21. Explain Rogerian Argument, p. 138 Answer: Rogerian argument is a strategy used to address the resistant audience. This argument is looking at the issue from the opposing viewpoints. 22. What is rhetoric according to most contemporary rhetoricians, p. 147? Answer: based on most contemporary rhetoricians, rhetoric is adjusting people to ideas and adjusting ideas to people. 23. Define stasis, p. 201 Answer: in Greek, stasis means to take a stand on something and it’s a type of claim in which the author presents his own approach to the argument based on the type of claim. 24. Explain definitional argument (refer to the chart). Answer: definitional argument is the type of claim which has a definition which establishes the criteria for the category. 25. Explain causal argument (chart). Answer: causal argument is the type of claim which argues about the cause of the issue and explains the links in a causal chain which goes from cause to affect. 26. Explain resemblance argument (chart). Answer: resemblance argument is the type of claim which compares two similar issues. 27. Explain evaluation & ethical argument, p. 202 (chart). Answer: evaluation and ethical argument is a claim that evaluates the value or worthiness of an issue. It questions how good or bad is the case. 28. Explain proposal argument (chart) Answer: proposal argument is a claim about how we should act about an issue. The author explains the problem and his own situation and gives a proposal to solve the problem. 29. What is a hybrid argument? Answer: a hybrid argument is a mixture of different claim types in one argument. These different claim types can be used in one argument but in separate sections. 30. Define induction as a reasoning strategy, p. 246. Answer: when we don’t have enough cases to conclude our claim with details, we use the inductive reasoning strategy and infer a general conclusion based on a limited number of specific cases.