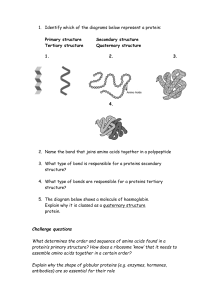
PROTEINS WORKSHEET 1. List five (5) functions of proteins along with an example of each. 2. What are the 4 main elements making up proteins? How many covalent bonds does each of these elements form? 3. What are the monomers of proteins called? How many are there? Name the 4 things bonded to the centre carbon of this monomer. 4. The main difference among amino acids is their ___________ group. What is the Rgroup on glycine? On alanine? 5. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different ______________. 6. How is a dipeptide formed? 7. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? 8. Long chains of amino acids are called ___________________ and these join together to make a ________________. 9. What is the effect of temperature on protein shape? Give an example of this. 10. Hydrogen bonding among individual amino acids in a chain causes what effect on the protein's shape? 11. Most proteins act as catalysts or __________________ inside of cells. 12. Sketch these two amino acids --- glycine & alanine. Circle the centre carbon, place a triangle around the amino group, and put a box around the carboxyl group. 13. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? Put a box around these bonds in the sketch you did on question 11. 14. A protein that has lost its precise three dimensional shape, has become_____________. Three things that can cause a protein to become denatured are____, ____, and _____ 15. Use the following words to describe the making of a protein (a term may be used more than once): tertiary structure, hydrophobic interactions, water,-COOH, polypeptide chain, Dehydration synthesis, -NH2, secondary structure, hydrogen bonding, covalent bonds, helix, primary structure, peptide bonds _____________ between amino acids joins –NH2 groups to -COOH groups (in the process _____ molecules are removed) to form a _______. The bonds so formed are called __________. The sequence of amino acids is called the ______. The _____ is often in the form of an alpha helix, which is due to ________ between amino acids in the chain. The _________ is the three dimensional shape of the protein as it folds back on itself. This structure is held together by ________ , __________, and ______ between R groups. The shape of the protein is determined by its ________ . The function of the protein is determined by its __________. Biochemistry of proteins R. Kalloo Page 1