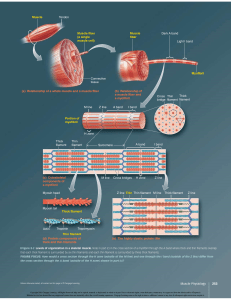
Functional Characteristics of Muscle Tissue • Electrical excitability – Autorythmic – Chemical Stimuli • Contractility – Ability to shorten forcibly when adequately stimulated • Extensibility – Smooth muscle subjected the most • Elasticity – Ability of a muscle fiber to recoil and resume its resting length after stretching Functions of Muscle • Producing body movement • Movement of substances within the body • Stabilizing body positions – Joints – Postural muscles • Produce heat – Maintain normal body heat – Shivering Attachment Nerve and Blood Supply Skeletal Muscle Anatomy of Muscle Fiber What makes the striations? • Striations – A band • H zone – M line – I band • Z line • Sarcomere Composition of Myofilaments Hierarchy of structure • • • • • Muscle Fascicle Muscle Fiber (Cell) Myofibril Myofilament Sarcoplasmic Reticulum & T Tubules Contraction: The Sliding Filament Model Sliding Filament Theory Calcium and the Regulatory Proteins Excitation-Contraction Coupling