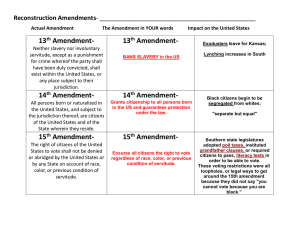
Unit 2 Study Guide 1. Early colonial era (1607-1754) (Why did Great Britain colonize the Americas?) a. New England Colonies-Worship/Religious Freedom b. Middle Colonies-Industrialization (Milling) c. Southern Colonies-Farming/Agriculture 1. French & Indian War (1754-1763) a. Effect of French and Indian War- Colonies start to united after F/I War b. Great Britain had a lot of debt after the war-Colonists were forced to pay for the war 2. Colonial period of unrest (1763-1775) a. Stamp Act-Any document that had a “stamp” on it was taxed b. Townshend Act-Everydays items were taxed (Lead, glass, paint, tea, etc.) c. Intolerable Act- Quartering Act (housing of soldiers), Tax on Tea, and closes the port of Boston d. Boston Massacre, Boston Tea Party 3. American Revolutionary War (1775-1783) a. Thomas Paine’s Common Sense-It’s an essay written to Americans (educated) that it just made “sense” to break away from Great Britain. b. Thomas Jefferson’s Declaration of Independence-Gave reasons to the king why he was bad and why America should “self-govern”. King obviously didn’t like this….WAR! c. Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s Social Contract (how it relates to the Declaration of Independence) i. Enlightenment belief (Rousseau)- Agreement between two “parties”. Agreement between “the people being ruled” (the citizens) and “those that rule” (the government) d. Impact of the Revolution on slaves and African Americans i. ii. iii. Slaves start to make a point that the way the King treated the colonies is the same way white people are treating slaves.****** Slave owning parts of the US are going to ignore this issue. Some parts of the US end slavery e. Impact of the Revolution on American women i. Abigail Adams-First Lady of the United States. Women helped to fight in the ii. Revolution. Role of women: During the war, women assumed jobs that men had in order to get iii. supplies out. Organized supplies and collected needed goods. Became nurses. Abigail Adams argues that these women should be given the same rights as men. The right to vote- Abigail Adams was a suffrage leader-->Pushed for the right to vote. 4. Articles of Confederation era (1777-1787)--> First Government Document/Constitution (First of Laws) a. Weaknesses→ No national currency, no national military, no power to enforce laws**** b. Shays’ Rebellion-Daniel Shays (Rev War Veteran). Tax collector comes to collect tax on his farm. Shays beats him up and tries to overthrow the government. 5. Constitution (1787-1789)---> Stronger constitution (Stronger national government). a. Debate over slavery (3/5ths Compromise)--> Some believe that slavery should expand more. Others believed it was unethical and we should end the practice of slavery. Southerns wanted more representation (in CONGRESS). A white man is counted as a person; whereas, a black/slave person will be counted as 3/5ths of a person. b. Federalist vs. Anti-Federalist arguments i. Federalist- Supporters of a strong central government. (Wanted a president or chief figure to run the country) ii. Anti-Federalist-Power should be left to the people/state governments. List of rights. (Bill of Rights) c. Understand the issue of “States’ Rights” (10th amendment) i. State’s Rights- The powers each state has over their population. The powers the states ii. have over the federal government. Ex. Driver’s license is an example of a state right because it is not mentioned iii. specifically in the constitution. Federal authority→ The federal government is the supreme authority. 6. Post Constitutional Ratification (1789-1800) a. The Bill of Rights (what were they, what did they do?) i. ii. iii. 1st Amendment -Freedom of religion, speech, press, assemble, and petition 2nd Amendment- In order to keep the country free, citizens should need to own guns. 3rd Amendment-No quartering (housing) of soldiers→ Quartering Act iv. v. 4th Amendment→ Protection against search and seizure (need a warrant) 5th Amendment- Can’t force you to incriminate yourself vi. vii. 6th Amendment-Trial by jury of peers, access to lawyer. 7th Amendment-Trial by jury in civil cases/court. viii. ix. 8th Amendment- Protection against cruel and unusual punishment 9th Amendment-> Enumerated rights (LISTED) (Rights 1-8 are NOT the only rights x. you have, they were just the ones we could come up with in 1789). 10th Amendment- Any power not given to the FEDERAL government is automatically given to the states (i.e driver’s licences). b. Washington’s Farewell Address and the concept of precedents i. Precedent- is an established tradition. 1. Presidents only ran for 2 terms (until FDR, thanks FDR). 2. Presidential Cabinet-Group of advisors to the president to run the country (Secretary of the treasury, state, defense, etc.) 3. Farewell Address-Saying goodbye to the nation before you leave office and give words of advice to the incoming president (Peaceful transition of power) 4. Beware political parties- Political parties lead to division (splitting of issues) 5. Beware foreign entanglements-Don’t get involved in other countries issues if you don’t have to. Know these terms and how they relate to the Units 1. Historical Context-The background information on the issue or time period 2. Historical Significance- Why is this important (why do we study it in American History) 3. Cause & Effect-What caused an event? What was the effect 4. Turning Point-What was the event that shifted the course of history a different way. 5. Point of View-The position of the person or being discussed 6. Intended Audience- Who is the group or audience being addressed 7. Purpose-Why is something important 8. Bias-How has someone upbringing caused their views to change over time. Example: Thomas Paine’s Common Sense and how it relates to “Point of View.” Be able to explain.