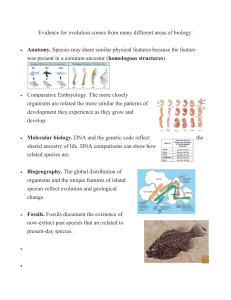
Evidence for Evolution Natural Selection Variation exists in the populations There is a selection pressure exerted on the population, e.g. competition for food. More offspring are produced than can survive Those offspring that are better adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce Favourable adaptations are passed onto the next generation Over time favourable adaptations will increase in the population. Species A species is defined by the ability to interbreed and produce fertile viable offspring. - Different species develop by the accumulation of microevolutionary changes over time → genetic isolation Isolation is critical for the species of an e… Comparative Embryology Comparative Paleontology Palaeontology (Transitional Forms) Fossils or organisms that show the intermediate states between ancestral for and that of its descendants are referred to as transitional forms Evidence that supports Transitional fossils demonstrate intermediary forms that occurred over the evolutionary pathway taken by a single genus. They establish the links between species by exhibiting traits common to both an ancestor and its predicted descendants As new fossils are discovered, new evolutionary patters are emerging, therefore supporting the theory of evolution. E.g. archaeopteryx → dinosaur → bird Comparative anatomy Comparing structural similarities of organisms to determine their evolutionary relationships. specie which share many similarities are closely related by a relatively recent common ancestor. similar body parts may be homologous structures or analogous structures. i.e. the pentadactyl limbs of humans and apes which are homologous structures. Evidence Limitations There are only a few transitional fossils that have been discovered: This is as the formation of fossils require particular conditions (e.g. an environment where sedimentary accumulation can occur) Some organisms are more successful u forming fossils due to hard parts (teeth, shell, bone) which are able to withstand the weathering of the chemical and physical assaults from the surface of the Earth Some transitional fossils may have not been found yet. Fossils may have been destroyed due to tectonic place movement. Some parts of the animal fossils cannot be found. Therefore, limitations I no. of fossils available. doesn’t prove the theory of evolution on its own assumes the theory of evolution in order to support it. Questions Palaeontology Study of fossils they come from common ancestor, Analogous structures are structures in unrelated organisms that are similar, i.e. wings in birds and bats Absolute dating (radiometric dating) Enables the actual age of a specimen to be determined using the radioactive elements that are present in the specimen Fission-type dating Used to establish he age of a mineral sample from its uranium content. Microscope used to coudn th tracks left behind by uranium fission fragments – conc. Determined by bombarding the sample with neutrons can be used to date volcanic minerals. potassium-argon dating used to determine the age of a rock by measuring the ratio of radioactive argon to radioactive potassium in the rock sample. Relative dating relies on the assumption that fossils found up higher in rock strata are younger than the lower fossils, so fossils are dated relative to one another. → Stratigraphy Relies on sedimentary rocks being formed in layers with the oldest rocks being at the bottom and and youngest on top. Biochemical sequencing → Paleomagnetism Study of the record of Earth’s changing magnetic field in rock sediments. Compares different molecular features Many different types of bases that any (e.g. nucleotide sequence of genes) to show how evolutionarily related species are. Biogeography The study of the geographical distributions of the biological organisms which provides evidence about how and when specie may have evolved. Biochemical DNADNA Hybridisation Comparative Embryology Comparison of the developmental stages of different species. Fossils Evidence provided by biogeography includes the discovery/recovery of fossils, Fossils which resemble modern organisms are found in regions separate from locations currently uninhabited. This supports the hypothesis of how species evolve from common ancestors. Different climates changed characteristics Different selection pressures Molecular fossils had commonalities with each other. Evolutionary changes will be reflected in changes in the base pairs of DNAs. Species not closely related share some of the same molecules from DNA to proteins. Amino acids make up proteins, most organisms have the same set of amino acids. Fish, amphibians, birds and mammals all show the presence of gill slits, tails and distinct muscle blocks during embryonic development. Thus, the prediction is that their early developmental stages. variation in bases cannot accurately indicate major differences. Alterations such as duplications, deletions and inversions can affect large segments of DNA. It is all based on hypotheses. Technique is inaccurate for the comparison of closely related species. Large range of data/huge margin of error These drawings are now considered to be inaccurate; they were not an accurate representation of the embryos but were interpretive.