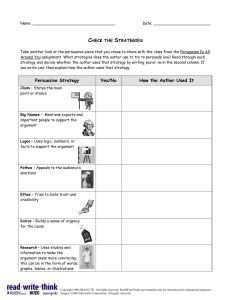
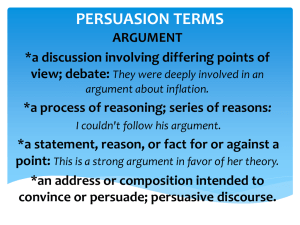
7 Quick Tips for Writing a Great Persuasive Essay Position papers. Persuasive arguments. Debate Topics. Whether you’re attending college on campus or you’re pursuing an online degree, at some point, you will need to write at least one persuasive essay. Also called a position paper, a persuasive essay is a short-length composition in which you compel the audience to share your viewpoint by presenting convincing evidence and a clear explanation that effectively supports your position. While social media makes it easier than ever for us to spout our opinions, posting a firmly worded Tweet is not really the same as building a cohesive, successful, and convincing argument. With that in mind, we offer a few quick tips that will set you on the right path. 1. State your position Everyone loves a good story, but that is not what you’re trying to write here. Avoid obscurity, ambiguity, and surprise endings. Your audience should fully understand from the start where you stand and what you intend to argue. If your reader has to guess your position, you’ve already lost them. State your position clearly from the start, and restate it as you go along. Use a strong and clearly worded thesis statement in your opening paragraph, and continue to use it as a reference point as you develop your argument. 2. Get organized If you want to persuade an audience with your argument, they need to be able to follow it. If your writing lacks organization, that’s not going to happen. Organization starts with a clear, argumentative thesis statement (as mentioned above). This should be your reference point for the whole paper. From there, your writing should develop the argument in a logical format, anchored in evidence, analysis, and counter-argument. Do not attempt to do this off the top of your head. Create an outline beforehand that identifies your thesis statement, lists major points, cites evidence-based supporting points, and makes note of potential counter-arguments. Use this as your model while you work. Not sure where to start? Get in touch with your school’s writing center. The tutors there can help you develop an airtight outline. 3. Persuade with passion This rule applies to any schoolwork: you tend to do your best work in the areas where you have the greatest interest. Arguing is no different. If you have the choice, pick a topic that you are passionate about. You’re much more likely to construct a good argument if you feel like you have some proverbial skin in the game. If you don’t have your choice of topic, that’s okay. Research what you are assigned, find a way to connect it to your passions, and develop a real sense of ownership in the argument. But even as you channel your passion, keep your emotions in check. Don’t allow anger or bias to get in the way of a compelling argument. 4. Know your audience All writing is written to someone. Writing is, after all, a medium for communication. With that in mind, it is necessary to consider your audience. Yes, your professor will be reading it. But he or she is not actually the intended audience. Think about who the writing is actually for? More specifically: Who are you trying to persuade? Every audience has its own unique needs and wants. What may work with one audience may fall completely flat with another. Dream up a hypothetical audience. Maybe you’re speaking to middle-aged conservatives, or perhaps a cross-section of liberal undergraduate millennials. Write to persuade them, not your professor. By doing so, you’ll develop an argument that could actually function in the real world. 5. Do your research At the core of any strong argument is solid evidence. The notion that you can fake your way through a persuasive argument only works until you encounter someone who actually understands the subject. Heads up: that’s why your professor was hired. If you want to write a successful persuasive argument, you need to do your research. You need to understand the topic from multiple angles. You should also be able to provide ample evidence for your claims as well as anticipate potential counter-arguments. It’s also best when your evidence comes from multiple forms of reputable sourcing, so aim for a mix of peer-reviewed academic studies, ethical news media, historical examples, and expert opinions. Don’t rely on unfounded assumptions and don’t fudge data in favor of your argument. Tell it like it is. Get to know your school library. Better yet, get to know your research librarians, as they can be immensely helpful. Not sure how to cite sources? Consult the Purdue OWL for free style guides. Bonus tip: Here’s a really bad feeling: Finding out that your argument is untenable the night before your paper is due. Taking the time to do quality research early on can prevent this catastrophe from happening. 6. Support your argument Opinions are not arguments. However, arguments stem from opinions. That’s why we construct arguments in the first place, because we have opinions. The key is that you must support your argument, with the aforementioned research, logic, and organization. Don’t be content to just state a point and expect it to win your audience over wholeheartedly. Present your argument, support it with strong evidence, analyze that evidence, and continually develop a sense of why, what, and how all of it together makes your stance the correct one. 7. Write with integrity Successful arguments build on three essential rhetorical components: logos (logical reasoning); pathos (passionate reasoning); and ethos (ethical reasoning). We’ve already covered logos and pathos here above, but ethos must be addressed. If you are making a persuasive argument, you have an ethical obligation not to manipulate or mislead your audience. Your argument should be constructed accurately, without relying on fallacies, misinformation, fear tactics, or any other rhetorical device that might somehow trick the audience into agreeing with you. You need to establish trust with your audience. While these tips are not exhaustive, they should help you get your footing while working on a persuasive essay. Remember, above all, you need to own your argument, and these tips should help you approach the task with confidence.