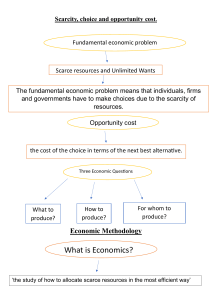
Chapter – 1 Introduction By Dr. Nadia Learning Objectives Define managerial economics and discuss briefly its relationship to microeconomics and other related fields of study such as finance, marketing, and statistics. Cite and compare the important types of decisions that managers must make concerning the allocation of a company’s scarce resources. Illustrate how economic changes affect a firm’s ability to earn an acceptable return. Compare the three basic economic questions from the standpoint of both a country and a company. Economics and Managerial Decision Making Economics: The study of the behavior of human beings in producing, distributing and consuming material goods and services in a world of scarce resources. Economics and Managerial Decision Making Management: The science of organizing and allocating a firm’s scarce resources to achieve its desired objectives. Economics+ Management = Managerial Economics Therefore: Managerial Economics: The use of economic analysis to make business decisions involving the best use (allocation) of an organization’s scarce resources. Economics and Managerial Decision Making Manager: A manager is a person who directs resources to achieve a stated / targeted goal, of a company. Economics: The science of making decisions in the present scarce resources. Managerial Economics: the study of how to direct scarce resources in the way that most efficiently achieves a managerial goal. Economics and Managerial Decision Making In making key business decisions the ‘Manager’ must answer the following questions: 1.What are the economic conditions of a particular market? Like: A.Market Structure? B.Supply and Demand? C.Technology? (Contd.) Economics and Managerial Decision Making D. Government Regulation? E. Future Conditions? F. Macroeconomic Factors? Economics and Managerial Decision Making Other questions are: 2. Should our firm be in this business? A.If yes, then at what price? B.At what output? C.How to maximize our economic profit or minimize our losses in the short-run? Economics and Managerial Decision Making 3. How can we organize and invest in our resources (land, labor, capital, managerial skills) in such a way that we maintain a competitive advantage over other firms in this market? By A.Cost-leader? B.Product Differentiation? C.Outsourcing, alliances, mergers, acquisitions? D.International dimension – regional or country focus or expansion? Economics and Managerial Decision Making 4. What are the risk involved? A.Changes in demand and supply conditions B.Technological changes and the effect of competition C.Changes in interest rates and inflation rates D.Exchange rate changes for companies engaged in international trade E.Political risk for companies with foreign operations Risk is the chance that actual future outcomes will differ from those that were expected. The Economics of a Business The economics of a business refers to the key factors that affect the firm’s ability to earn an acceptable rate of return on investment. The most important of these factors are competition technology customers Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Microeconomics is the study of the choices made by consumers, firms, and government, and how these decisions affect the market for a particular good. It focuses on the analysis of individual economic units. Especially: supply and demand pricing of output production process cost structure distribution of income Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Macroeconomics is the study of the performance of the national and global economies. Especially: national output (GDP) unemployment inflation fiscal and monetary policies trade and finance among nations Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Resources: Also referred to as factors of production or inputs. Economic analysis usually include four basic types of resources: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Scarcity is the condition in which resources are not available to satisfy all the needs and wants of a specified group of people. Because we face scarcity, we must make choices. Opportunity cost is the amount that must be sacrificed in choosing one activity over the next best alternative. Review of Economic Terms and Concepts The nature of Scarcity: Resources Land, Labor, Capital, Needs & wants Entrepreneurship & of the population Management Skills SUPPLY DEMAND Review of Economic Terms and Concepts In the presence of limited supplies compared to demands, countries must decide how to allocate their scarce resources. Allocation decisions must be made because of scarcity. Three choices: What should be produced and in what quantity? How should it be produced? For whom should it be produced? Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Q 1. What should be produced and in what quantity? If a country produces guns and butter, then in this case the above question should be answerable to – Should a country with scarce resources should produce guns or butter? And how much should it produce? Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Q 2. How should it be produced? Suppose a country decides to produce butter. Then what amount of resource (land, labor, capital and entrepreneurial efforts should it devote for this production. Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Q 3. For whom should it be produced? The meaning of this question is a decision that must be made for the distribution of a country’s output of goods and services among the members of its population. All countries must deal with these three questions because all have limited resources. Review of Economic Terms and Concepts Entrepreneurship is the willingness to take certain risks in the pursuit of goals. The effort to coordinate the production and sale of goods and services. Entrepreneurs take risk and commit time and money to a business without any guarantee of profit. Global Application Global Application: Reinventing the Corporation through Strategy and Ownership. Western Union began over a 100 years ago, when long distance communication by telegraph had just begun. Since then the changes in technology are quite obvious, therefore the company branched out from telegraph business, else it would have soon be out of business. Diversified into money transfer business. Global Application Today western union is the leading provider of money transfer services, including transactions over the Internet. Their services is spurred on by increasing number of immigrant workers in countries throughout the world who send their hard-earned money back home to their families. Western Union illustrates that a company which has experienced so much changes in its economics, can no longer rely on the corporate support of a larger entity. Global Application Another example is VNU, a Dutch publishing company. It transformed itself over the past decade into a leading global provider of marketing and media information. Publications of yellow pages, etc. VNU illustrates that it was difficult to sustain the reinvention and growth of a company operating in markets with changing customers, technology, and competition. Summary Managerial economics is a discipline that combines microeconomic theory with management practice. An important function of a manager is to decide how to allocate a firm’s scarce resources. Examples of such decisions are the selection of a firm's products or services, the hiring of personnel, the assigning personnel to particular tasks or function, the purchase of materials and equipment, and the pricing of products and services. Summary The application of economic theory and concepts helps managers make allocation decisions that are in the best economic interests of their firms. Chapter – 1 Introduction Thanking you Dr. Nadia