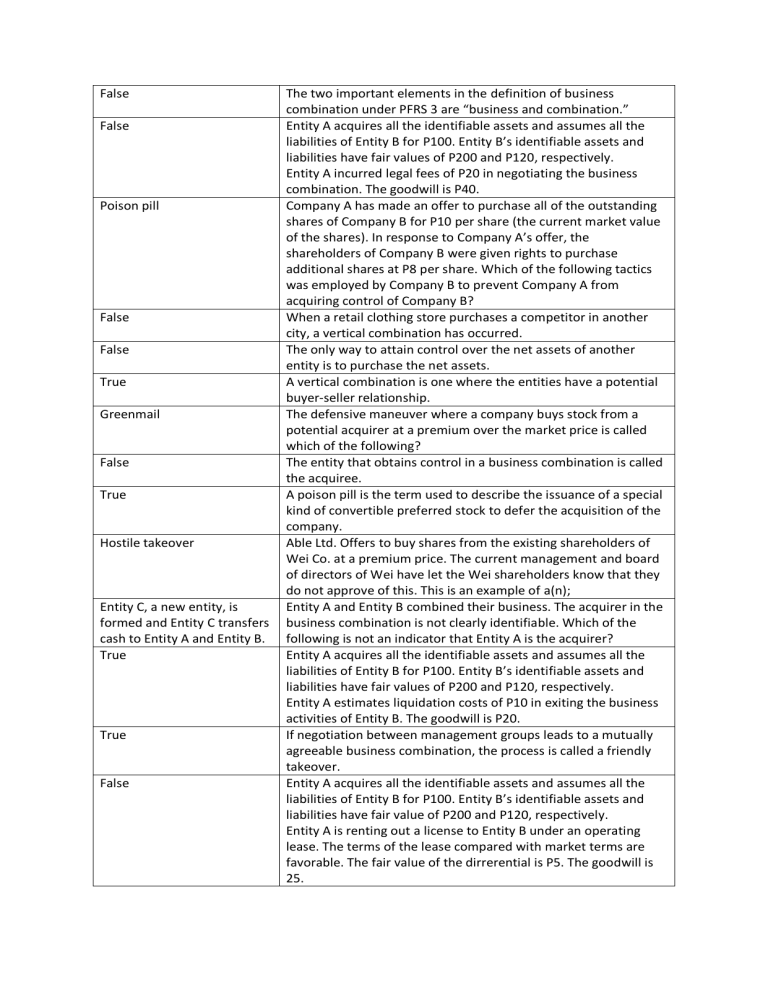
False False Poison pill False False True Greenmail False True Hostile takeover Entity C, a new entity, is formed and Entity C transfers cash to Entity A and Entity B. True True False The two important elements in the definition of business combination under PFRS 3 are “business and combination.” Entity A acquires all the identifiable assets and assumes all the liabilities of Entity B for P100. Entity B’s identifiable assets and liabilities have fair values of P200 and P120, respectively. Entity A incurred legal fees of P20 in negotiating the business combination. The goodwill is P40. Company A has made an offer to purchase all of the outstanding shares of Company B for P10 per share (the current market value of the shares). In response to Company A’s offer, the shareholders of Company B were given rights to purchase additional shares at P8 per share. Which of the following tactics was employed by Company B to prevent Company A from acquiring control of Company B? When a retail clothing store purchases a competitor in another city, a vertical combination has occurred. The only way to attain control over the net assets of another entity is to purchase the net assets. A vertical combination is one where the entities have a potential buyer-seller relationship. The defensive maneuver where a company buys stock from a potential acquirer at a premium over the market price is called which of the following? The entity that obtains control in a business combination is called the acquiree. A poison pill is the term used to describe the issuance of a special kind of convertible preferred stock to defer the acquisition of the company. Able Ltd. Offers to buy shares from the existing shareholders of Wei Co. at a premium price. The current management and board of directors of Wei have let the Wei shareholders know that they do not approve of this. This is an example of a(n); Entity A and Entity B combined their business. The acquirer in the business combination is not clearly identifiable. Which of the following is not an indicator that Entity A is the acquirer? Entity A acquires all the identifiable assets and assumes all the liabilities of Entity B for P100. Entity B’s identifiable assets and liabilities have fair values of P200 and P120, respectively. Entity A estimates liquidation costs of P10 in exiting the business activities of Entity B. The goodwill is P20. If negotiation between management groups leads to a mutually agreeable business combination, the process is called a friendly takeover. Entity A acquires all the identifiable assets and assumes all the liabilities of Entity B for P100. Entity B’s identifiable assets and liabilities have fair value of P200 and P120, respectively. Entity A is renting out a license to Entity B under an operating lease. The terms of the lease compared with market terms are favorable. The fair value of the dirrerential is P5. The goodwill is 25. Pac-man defense True True Obtaining of control True True It includes those that are retained in the combined entity. Acquisition Method True False False Closing date False Acquirer True True Company A marks a hostile takeover bid for control of Company B. In response, Company B makes a counter-offer to purchase shares from Company A’s shareholders. Which of the following best describes Company B’s response? The tender offer that is opposed by the acquiree management is called hostile bid. In an acquisition where the acquirer pays cash for the acquiree assets, the book value of the acquirer increases. This distinguishes a business combination from other types of investment transactions. When two entities competing in the same industry combine, it is called a horizontal integration. One way that a horizontal business combination can increase sales for an entity is to expand into new product markets. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the consideration transferred in a business combination? PFRS 3 requires all business combinations to be accounted for using the Conglomerate combinations are easy for the government to challenge in court. Noncontrolling interest are measures at fair value only. Horizontal business combinations are likely to occur when management is attempting to dominate a geographic segment of the market. According to PRFS 3, the acquisition date is normally the PFRS 3 requires the use for the purchase method in accounting for business combination The entity that obtains control over another business in the business combination is called the The acquisition date in a business combination is normally the closing date. A vertical business combination generally involves companies attempting to improve the efficiency of operations by purchasing suppliers of inputs or purchasers of outputs.