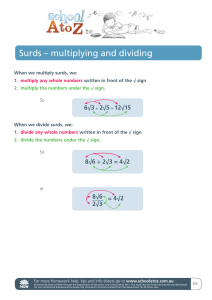
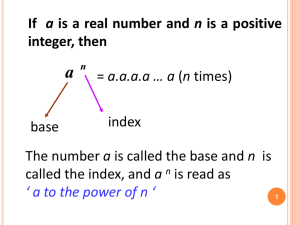
IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Global Jaya School Virastuty . on Friday, Sep 27, 2019 at 10:14 PM Teachers Virastuty ., Ranto Sarindo Hinsa S, Sanjay Batt, Krisna Budiarti, Yusak Pariang Pasaribu Subject Standard mathematics Shared grades Year 10/MYP Year 5 Course part Start Date Week 3, August Duration 9 weeks 27 hours INQUIRY Key Concept Form is the shape and underlying structure of an entity or piece of work, including its organization, essential nature and external appearance. Related Concepts Mathematics Representation Conceptual Understanding Conceptual lens: Number System and Properties Concepts in the unit: Scientific Notations, Radical and Surds, Sequences and Series Process concepts: Representation, problem-solving, mathematical instruments The number system is very important to represent the result and solution of scientific research. Global Context & Explorations Scientific and technical innovation Rounding numbers to a certain degree of accuracy in the process of measurement to get a significant solution. Explorations to develop • Processes and solutions Statement of Inquiry Numbers can be represented in the different forms to show the reasonableness of the solutions in scientific research and innovation. Inquiry Questions Factual Standard mathematics How do we write a very big number? How do we write a very small number? Scientific Notations Factual Standard mathematics How do we simplify surds with integer denominator? Radical and Surds To what extent does number system influence the development of the scientific innovation? Conceptual Standard mathematics Number System Debatable Standard mathematics When is the result from the calculator inaccurate? IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Reasonableness of Results STREAM 1 Additional Practices of radicals and surds Added by Virastuty . on August 26, 2019 2 MYP 5 For International Students Haese and Harris Added by Virastuty . on August 26, 2019 Textbook 3 Surds Added by Virastuty . on August 26, 2019 Simplifying the surds 4 MYP Investigation Practice Added by Virastuty . on September 25, 2019 Finding the pattern of sequences 5 Sequences and Series Added by Virastuty . on September 4, 2019 The main material for Sequences and Series. RESOURCES SEP 2 Unit test: Radicals and Surds Summative Class test Monday at 7:40 AM Topics covered : Radicals and Surds (Textbook chapter 3) and Standard Form (from the additional resources) SEP 2 Unit test: Radicals and Surds IB MYP Unit Planner Summative YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Class test Monday at 7:40 AM SEP 2 Year 10 Summative Criteria A: Radicals & Surds Summative Class test Monday at 7:45 AM Topics covered : Radicals and Surds (Textbook chapter 3) SEP 30 Year 10 Investigation Task Criteria B, C: Sequence & Series Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM SEP 30 MYP Investigation: Sequences and Series Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM Investigating problems with Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series. SEP 30 MYP Investigation: Sequences and Series Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM Investigating problems with Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series. Weekly Plan Year 10 - Term 1 Added by Virastuty . on August 17, 2019 Please read carefully about our plan in term 1 so that you can prepare the upcoming assessment. Measurement Added by Virastuty . on August 17, 2019 We are going to use this resource for scientific notations and rounding numbers. This is the basic concept of the number system. Scientific Notation https://www.cimt.org.uk/projects/mepres/allgcse/pr1-es.pdf Added by Virastuty . on August 17, 2019 Additional practice of scientific notations. IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit CURRICULUM MYP Objectives • A: Knowing and understanding • i. select appropriate mathematics when solving problems in both familiar and unfamiliar situations • ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving problems • iii. solve problems correctly in a variety of contexts • B: Investigating patterns • i. select and apply mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover complex patterns • ii. describe patterns as general rules consistent with findings • iii. prove, or verify and justify, general rules • C: Communicating • i. use appropriate mathematical language (notation, symbols and terminology) in both oral and written explanations • ii. use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to present information • iii. move between different forms of mathematical representation • iv. communicate complete, coherent and concise mathematical lines of reasoning • v. organize information using a logical structure • D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts • i. identify relevant elements of authentic real-life situations • ii. select appropriate mathematical strategies when solving authentic real-life situations • iii. apply the selected mathematical strategies successfully to reach a solution • iv. justify the degree of accuracy of a solution • v. justify whether a solution makes sense in the context of the authentic real-life situation Content & Skills Content Scientific Notations Rounding Numbers to Decimal Places and Significant Figures Percentage errors Radicals and Surds Sequences and Series Skills Representing numbers in the scientific notations. Rounding numbers to a certain of accuracy of decimal places and significant figures. Finding the percentage error of a measurement. Simplifying radicals and surds. Rationalizing radicals and surds with integer denominator. Solving equation involving radicals and surds. Determining the nth term of the arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. Determining the sum of first n terms of the arithmetic and geometric series. Solve application problems by using the concepts of the arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit IB MYP Unit Planner ASSESSMENT Tasks SEP 2 Unit test: Radicals and Surds Summative Class test Monday at 7:40 AM Topics covered : Radicals and Surds (Textbook chapter 3) and Standard Form (from the additional resources) SEP 2 SEP 2 5/8 A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Unit test: Radicals and Surds Summative Class test Monday at 7:40 AM 3/8 A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Year 10 Summative Criteria A: Radicals & Surds Summative Class test Monday at 7:45 AM Topics covered : Radicals and Surds (Textbook chapter 3) SEP 30 4/8 A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Year 10 Investigation Task Criteria B, C: Sequence & Series Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM IB MYP Unit Planner SEP YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit N/A A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts MYP Investigation: Sequences and Series 30 Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM Investigating problems with Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series. SEP N/A A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts MYP Investigation: Sequences and Series 30 Summative Investigation Monday at 7:40 AM Investigating problems with Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series. N/A A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Formative assessment Quiz Students are doing quizzes in a short time to check their basic understanding. Homework Students do independent study at home and the teacher will check informally during class time. Teacher observation IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit The teacher does observation during exercise time. Peer and self assessment Peer Assessment Students can correct their peer work. Standardization and moderation The teacher in charge will set a paper test one week prior to the assessment. Other teachers will check the criteria and skills assessed and give feedback to improve the quality of the test paper, they also set up the standard of the expectation. After the assessment, all the year 10 teachers will gather to set up the standardization. Each teacher will give 6 papers for the standardization, 2 below, 2 average, 2 above. Teachers will exchange and re-marking for the all 30 papers in total, then after finishing correction, we set up the standard of each strand of each criterion. MYP Assessment criteria Mathematics Standard mathematics 5/8 A: Knowing and understanding N/A B: Investigating patterns N/A C: Communicating N/A D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts * - Class mean of Assessed Criteria LEARNING EXPERIENCES Prior learning experiences Prior Knowledge: Students understand the number system and properties and the characteristics of each type of numbers. Students are able to find the next term from simple number pattern. Teaching Strategy: The teacher gives a diagram and by brainstorming asks students about the character of each type of numbers. IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Number System Diagram The teacher also exposes some simple number pattern and ask students to determine the next term of the sequence and the pattern of the sequence. Here is the link for simple number pattern. Learning experiences Here is the file of weekly lesson objectives. Year_10_Weekly_Planner_Term_1_2019-2020_Std_with_ATL.pdf Aug 18, 2019 Differentiation Peer teaching ("TEACH UP") Students can discuss with their peer in a pair so that students can explain with their own words without misunderstanding. The teacher allows students to discuss when doing mathematics practice in the class. Differentiated Math Instruction Strategies and Examples The teacher gives different instructions and example for students having difficulty in understanding mathematical concepts. Personal Consultation Session The teacher gives time for a personal consultation during class time and after school time. Relate Math to Personal Interests and Everyday Examples Use real-life comparisons to help some learners grasp new concepts. IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit CONNECTIONS Approaches to Learning Communication I. Communication skills Reading, writing and using language to gather and communicate information • Understand and use mathematical notation Understand and use correct mathematical notations of scientific number (very big numbers and very small numbers), radical and surds, the nth term of arithmetic and geometric sequences and series, exponents, and logarihtms. Self-management III. Organization skills Managing time and tasks effectively • Bring necessary equipment and supplies to class • Select and use technology effectively and productively V. Reflection skills (Re-)considering the process of learning; choosing and using ATL As IB Diploma requirements, students have to be familiar with technology. Therefore, students must bring a graphic display calculator to learn Mathematics in the class. Students must be responsible to bring necessary equipment, such as rulers, textbooks, pencils and GDC to the class. The assessment will also involve technology for problem solving. skills • Develop new skills, techniques and strategies for effective learning • Identify strengths and weaknesses of personal learning strategies (self-assessment) Thinking VIII. Critical thinking skills Analysing and evaluating issues and ideas • Use models and simulations to explore complex systems and issues • Identify trends and forecast possibilities X. Transfer skills Utilizing skills and knowledge in multiple contexts • Apply skills and knowledge in unfamiliar situations Students are able to form a best fit model of real life application by using sequences and series. For example: the model of bank saving, population growth and decay. Students are able to use the model to forecast possibilities, such as finding the population of the world in 2050? What is the impact of resources in 2050? IB Learner Profile • Knowledgeable: The teacher exposes the problems about the population and resources then the teacher asks students to analyze the problems and extend their concepts and skills to solve the problems. Then the teacher builds awareness of how scientific and technical innovation can contribute to solving the problems by giving some article or research journal of scientific and technical innovation. • Communicators: The teacher emphasizes students to write answers and solutions in the correct mathematical forms and notations. International Mindedness Some countries use different units of measurement. USA, Myanmar, and Liberia still apply the Imperial units, meanwhile, other countries use the Metric System. Therefore, we need to be careful to interpret the unit of measure of a product, such as in USA sugar is sold in 4 lb equivalent to 3 g. The different format writing of decimals. In most European countries use a comma to separate decimals, however, in the US, UK, New Zealand, and Australia use a point to separate decimals. This also affects the format writing in Indonesia. Dutch ever colonized IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Indonesia for 350 years. Therefore, in Indonesia, people use a comma for separating decimals instead of a point because of the heritage from Dutch. Academic honesty Seat arrangement during tests and summative assessments. Language development For students having the language barrier, teacher gives the list of command terms and the description used in this unit. Interdisciplinary links Not applicable Service as Action • Work collaboratively with others: Helping classmates to understand the concepts of Mathematics in this unit. REFLECTIONS 2019 - 2020 Prior to studying the unit • Why do we think that the unit or the selection of topics will be interesting? • What do students already know, and what can they do? • What have students encountered in this discipline before? Number is one of the branches of Mathematics. Number system and properties are very important for students to build a strong foundation for learning Mathematics further. Scientific notation is important to represent numbers in the international standard form. The very big numbers and the very small numbers can be written in the form of scientific notations, such as the radius of the earth, the diameter of a galaxy, the radius of a cell, etc. After students have a good foundation in representing number scientific notation, students need to learn radicals and surds. The radicals and surds belong to irrational numbers. An engineer usually uses the radicals and surds to measure the exact values of an object. Students should understand how to work with radicals and surds to get an accurate result without a calculator. Then students need to learn the exponential and logarithmic numbers which are very applicable in real-life situations. The function of population growth, decay, compound interest, and depreciation uses the concepts of exponents and logarithms. In the previous students learn about the basic laws of exponents. They simplify exponential expressions. Students also learn about simplifying the surds by using prime factor trees. Logarithm will be a new topic for students. Therefore, teachers need to ensure that students really understand how to use the exponent laws to simplify the exponential expression before teaching logarithms. Last year teachers found that logarithm is a difficult topic to teach. The students felt confused about when using roots and when using logarithm as both root and logarithm are the inverse operations of exponents. In this topic teachers need to do diagnostic assessment how far the students understand the exponents and roots. During the unit • • • • • • • What difficulties did we encounter while completing the unit or the summative assessment task(s)? What resources are proving useful, and what other resources do we need? What student inquiries are emerging? What can we adjust or change? What skills need more practice? What is the level of student engagement? How can we scaffold learning for students who need more guidance? IB MYP Unit Planner YEAR 10 - TERM 1 - NUMBER SYSTEM AND PROPERTIES Current Unit Radicals and Surds Teachers should recall the basic algebra expansions such as quadratic algebra expressions and difference of two squares: Then teachers can start explaining why the surds are prohibited for the denominator. The denominator may not contain surds, therefore teachers should explain the importance of algebra to change surd denominator to integer denominator. The textbook is useful for students. There is a lot of explanation and the worked example that students can use to strengthen their concepts. Students feel comfortable with additional practices to prepare for the unit test. Students can find the root of a root by using the rule: (√a+√b)2=(a+b)+2√ab