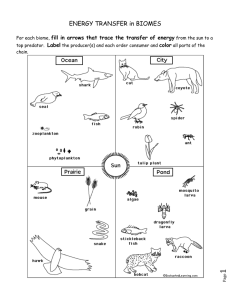
Principles of Ecology - Chapter Review 13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships I. _Ecologists_Study Relationships at Different Levels of Organization ● ● ● ● ● ● __Ecology__- the study of the interactions among living things, and between living things and their surroundings. __Organism___- one individual living thing. _Population_____- is a group of the same species that live together in one area. _Community___- A group of different species that live together in an area. _Ecosystem____- includes all of the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks, and other nonliving things in an area. _Biome_____- is a major regional or global community of organisms. A binome is usually defined by the climate and the plant communities that live in an area. II. Ecological Research Methods Include Observation, Experimentation, and Modeling. ● ● ● ___Observation__- the act of carefully watching something over time. Observation may be short or long term studies. ___Experimentation_______- An experiment in a natural setting gives a better picture of how organisms really interact. - An experiment in a_______setting______ allows for more control of variables. _____Modeling______- these can be used to explore organisms and whole ecosystems in ways that would not be possible in a natural setting. - Models use real _data_____to predict outcomes for different situations. 13.2 Biotic and Abiotic Factors I. An ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic factors ● ● ___Biotic____- factors are living things, such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria ____Abiotic_______ - factors are nonliving things, such as temperature, moisture, wind, rocks, and sunlight II. Changing one factor in an ecosystem can affect many other factors ● ● ______Biodiversity______- the variety of living things in an ecosystem. ___Keystone________Species - a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. 13.3 Energy in Ecosystems I. _______Producers_______Provide Energy for other Organisms in an Ecosystem ● ● Producers - are organisms that make their own __Food___. Plants and other photosynthesizing organisms are producers. Producers are also called ____Autotrophs_________. _Consumers____________- are organisms that get their energy by eating other organisms, including plants and animals. Consumers are also called__Heterotrophs______. II. Almost All Producers Obtain Energy from __sunlight_______ ● ● ___Photosynthesis__________- the process by which plants and protists (such as algae) make food through sunlight. These sugars are used for __cellular respiration___________. __Chemosynthesis_______- life forms that make their own food through chemicals as an energy source - not the Sun. (they can also live in Hot Springs) 13.4 Food Chains and Food Webs I. _Food Chain_____- shows the feeding relationships for a single chain of producers and consumers Example: grasses ---> rabbits -----> snakes -----> hawks II. Types of Consumers ● ● ● ● ● __Herbivores_____- eat only plants (such as rabbits) ____Carnivores____ - eat only meat (such as hawks) ____Omnivores_______ - eat both meat and plants (such as humans) ___Detritivores________ - organisms that eat dead plant and animal matter (earthworms are an example) ___Decomposers______- detritivores that break down plant and animal matter into simpler compounds. Fungi, for example, are decomposers - return nutrients to the ecosystem. ○ __Specialists____- Organisms that have a very selective diet - they can be very sensitive to population changes (example - Florida Snail Kites only eat snails) ● __Generalists_____- eat a variety of different organisms (example includes wolves). III. Trophic Levels ● ● ● ● ● __Trophic Level_______- each link of the food change - each level is called a Trophic Level. __Producers_____- bottom level - plants mostly - gain their energy from the Sun. __Primary ____Consumers - herbivores mostly that eat producers. ___Secondary_______Consumers - Carnivores and Omnivores that primarily eat Primary Producers ___Teritiary____Consumers (Apex Predators) - carnivores that eat secondary and primary consumers. IV. A Food Web Shows a Complex Network of Feeding Relationships ● ● __Food web___- Complex network of feeding relationships and the related flow of energy between trophic levels. In general, _10%__of the energy acquired in consuming a lower trophic level is passed on to the next level. 90% of the energy received will be burned off - mostly through heat. 13.5 Cycling Matter I. Water Cycles Through the Environment ● ● ___Hydrologic_____Cycle - the water cycle, is the circular pathway of water on Earth. From the Atmosphere, to the surface, and back to the Atmospheres - including all living things. Two ways that water enters the atmosphere 1. ___Evaporation______- water becoming vapor 2. ___Transpiration_______- water evaporating from plants II. Elements Essential for Life also Cycle through Ecosystems ● __Biogeochemical___________cycle - The movement of a particular chemical through the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. ● 4 types of Biogeochemical cycles: 1. _Oxygen____ Cycle - Most organisms use oxygen for cellular respiration - plants will release oxygen as a waste product. 2. ____Carbon______Cycle - Carbon is a main component of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and all of the other molecules that make up living things - Plants convert carbon dioxide from the air into carbohydrates, which get passed on as organisms eat each others. 3. __Nitrogen___Cycle - Much of the Nitrogen cycle happens underground. - Nitrogen fixation - some bacteria can turn nitrogen gas into ammonia - Nitrates are used by plants to make amino acids and proteins. 4. ___Phosphorous_____ Cycle - this cycle takes at ground level - Phosphate is released by the slow breakdown of rocks - plants take phosphates through their roots - Phosphorus then moves through the food web. 13.6 Pyramid Models I. An ___Energy Pyramid____Shows the Distribution of Energy Among Trophic Levels ● Energy Pyramid - a diagram that compares the ___energy____used by producers, primary consumers, and other trophic levels. - shows how much energy is available at each trophic level. - Energy levels are larger at the bottom and smaller at the top (as energy is lost at each level). II. Other Pyramid Models Illustrate an Ecosystem’s Biomass and Distribution of Organisms ● ● __Biomass Pyramid__________ ○ ____Biomass______- the measure of the total amount, or dry mass, or organisms in a given area. ○ A diagram that compares the biomass of different trophic levels within an ecosystem ○ Shows the mass of producers needed to support primary consumer - all the way to Tertiary Consumers. ____Pyramid of Numbers__________ ○ A pyramid of numbers gives a count of the numbers of individual organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.