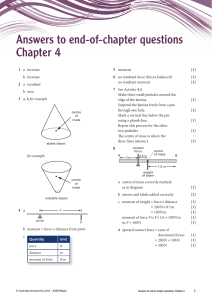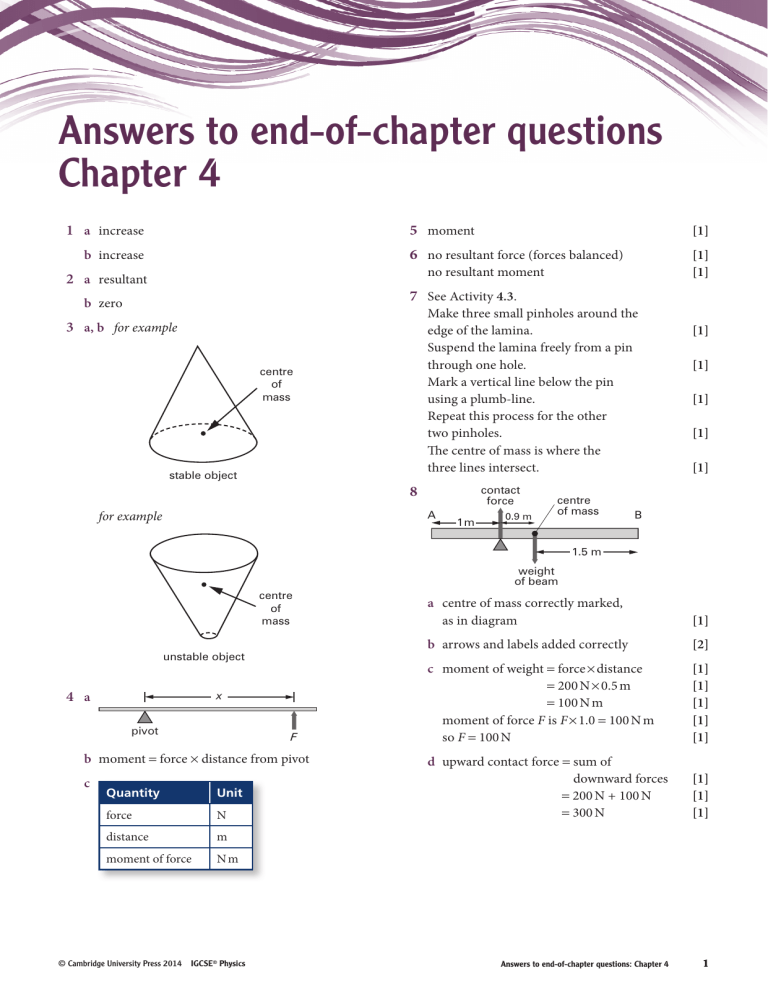
Answers to end-of-chapter questions Chapter 4 1 a increase b increase 5 moment [1] 6 no resultant force (forces balanced) [1] [1] no resultant moment 2 a resultant 7 See Activity 4.3. b zero Make three small pinholes around the edge of the lamina. Suspend the lamina freely from a pin through one hole. Mark a vertical line below the pin using a plumb-line. Repeat this process for the other two pinholes. The centre of mass is where the three lines intersect. 3 a, b for example centre of mass stable object 8 contact force A for example 1m 0.9 m centre of mass [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] B 1.5 m weight of beam centre of mass unstable object x 4 a pivot F b moment = force × distance from pivot c Quantity Unit force N distance m moment of force Nm © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE® Physics a centre of mass correctly marked, as in diagram [1] b arrows and labels added correctly [2] c moment of weight = force × distance = 200 N × 0.5 m = 100 N m moment of force F is F × 1.0 = 100 N m so F = 100 N [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] d upward contact force = sum of downward forces = 200 N + 100 N = 300 N [1] [1] [1] Answers to end-of-chapter questions: Chapter 4 1 9 a force and perpendicular distance (of force) from the point b i [1] downward force arrow at centre of bar ii 0.50 m or 50 cm [1] [1] b (1.5 + 0.6) × 10 = 21 N [1] c i stays in position [1] = 63 N m v make bar longer or move pivot/stone to the left or move pivot to left or increase mass of bar © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE® Physics [1] 30 = 0.60 kg iii moment of force = 40 × 1.2 = 48 N m [1] moment of weight = + 30 × 0.5 = 15 N m [1] total clockwise moment = 48 + 15 [1] iv F × 0.2 = 63 63 = 315 N F= 0.2 10 a mass = (1 5 × 12 ) [1] [1] ii as the parrot is rotated, both distances change in proportion so clockwise moment = anticlockwise moment [1] Answers to end-of-chapter questions: Chapter 4 2 [1] [1] [1]