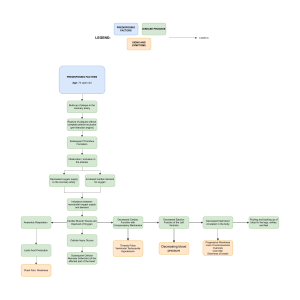
MIDTERM EXAM Question 1 0 out of 0 points Gas exchange occurs in which of the respiratory system's structures? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Trachea Alveoli The alveoli allow air to come in indirect contact with the bloodstream through the pulmonary capillary system. This alveolar membrane, which is one cell thick, allows carbon dioxide to diffuse into the alveoli from the bloodstream and oxygen to diffuse to the bloodstream from the alveoli. Sinuses are hollow spaces found in the skull. The trachea is a structure that allows passage of gases to and from the gas exchange units (alveoli). Bronchi are branches of the conducting airways that allow passage of gases to and from the gas exchange units (alveoli). Question 2 0 out of 0 points A patient with heart failure reports awakening intermittently with shortness of breath. Which terms appropriately describes this clinical manifestation? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Dyspnea Paroxysmal nocturnal Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea refers to intermittent attacks of severe dyspnea that occur during the night. Dyspnea is a general term referring to difficulty breathing. Cyanosis is the appearance of a blue or purple coloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface being low on oxygen. Bradypnea describes abnormal slowness of breathing. Question 3 0 out of 0 points What factor causes a congenital heart disease to produce cyanosis? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Left-to-right shunting of blood Right-to-left shunting of blood Disorders that result in right-to-left shunting cause cyanosis. A leftto-right shunt occurs when oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart or aorta flows back into the right side to be recirculated through the lungs. The blood reaching the systemic circulation is oxygenated and the infant is not cyanotic (acyanotic defect). However, the right side of the heart has an increased workload because of the extra shunt blood. In time, the overload of the right side of the heart can result in right ventricular hypertrophy and high right-sided heart pressures. Large ventricular septal defects may be apparent at birth because of rapidly developing right-sided heart failure and a loud systolic murmur. The majority of atrial septal defects occur at the location of the foramen ovale. The abnormal septal opening may be of variable size. Small defects (1 cm) are well tolerated. Even larger atrial septal defects may be asymptomatic for many years as long as the shunt flow is left to right and therefore acyanotic. Question 4 0 out of 0 points A patient education intervention that will help decrease the emergence of resistant infections is to instruct the patient to Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Take all the antibiotics ordered even if feeling well after a few days to prevent antibiotic defiant bacteria Take all the antibiotics ordered even if feeling well after a few days to prevent antibiotic defiant bacteria The patient should take all the antibiotics ordered, even if feeling better, to eradicate the moderately resistant microorganisms. Viruses are not impacted by antibacterial medications. Sharing antibiotics indicates that the full course of the medication isn’t being taken, and so contributing to the development of resistant microorganisms. If medication is stopped prematurely, moderately resistant organisms are selected for and become the predominant species, making it more difficult to eradicate next time. Question 5 0 out of 0 points Cellular hypoxia results in Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Failure of the sodium-potassium pump Failure of the sodium-potassium pump Hypoxia is a loss of oxygen to the cell that causes ATP activity to cease. ATP provides the power required to drive the sodiumpotassium pump. pH decreases in hypoxia (respiratory acidosis). Hypoxia is a loss of oxygen to the cell that causes ATP activity to cease. Deposits of calcium salts occur in conditions of altered calcium intake, excretion, or metabolism. Question 6 0 out of 0 points What is the underlying problem common among all types of shock? Selected Answer: Generalized vasodilation Correct Answer: Inadequate cellular oxygenation Response Feedback: Although each type of shock has specific characteristics, all are associated with a deficiency of cellular oxygen consumption. Inadequate cellular oxygenation may result from decreased cardiac output, maldistribution of blood flow, or reduced blood oxygen content. The impaired oxygen utilization by cells may lead to cell death, organ dysfunction, and stimulation of inflammatory reactions. Cardiac failure can be an outcome, but is not a common cause in all types of shock. Vasodilation occurs in only selective forms of shock. Faulty compensatory mechanisms may contribute to the seriousness of all shocks but that is not the cause of all forms of shock. Question 7 0 out of 0 points What is the name for the mRNA sequences that contain only the wanted segments? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Pre-mRNA Exon Response Feedback: An exon is the mRNA sequence that contains only the wanted segments. Introns are the unwanted areas that are removed in the nucleus by a complex splicing process, thus leaving exons. PremRNA is the original RNA transcript before removal of bases that are unnecessary. Spliceosomes are the areas of the nucleus that are a specialized RNA protein complex that removes introns. Question 8 0 out of 0 points Thrombosis in the microcirculation throughout the body is called Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) Thrombosis may also be initiated by a generalized reduction in flow and release of vasoactive substances that occur in shock states. Systemic derangement in coagulation takes place in disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), resulting in thrombosis in the microcirculation throughout the body. A stroke results from the obstruction of blood flow in or to the brain by a clot. Atherosclerosis is a circulatory condition that results in the inability of vessels to regulate blood flow as a result of the stiffening of their walls. An MI is a result of obstructed blood flow in a vessel supplying the heart muscle itself. Question 9 0 out of 0 points Which term is used to identify hypertension that has a specific disease as its cause? Selected Answer: Primary Correct Answer: Secondary Response Feedback: Secondary is the term given to hypertension that is secondary to a specific disease. Idiopathic, primary, and essential hypertension are interchangeable terms for hypertension that cannot be related to a specific disease/cause. Question 10 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true regarding the epithelial system of tissue? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Stratified epithelium is several layers thick. Stratified epithelium is several layers thick. Stratified epithelium that makes up the epidermis of the skin is several layers thick. Epithelial cells cover the majority of the external surfaces of the body and line the glands, blood vessels, and internal surfaces. Keratin is a tough protective protein that is present in the outer surface of flattened, dead epithelial cells. Pseudostratified epithelium is a single layer, but it appears to be more than one layer because of the mixture of cell shapes. Question 11 0 out of 0 points Which term refers to a state of tension that can lead to disruption or threaten physical stability? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Stress Stress Stress is defined as a state of tension that can lead to disruption or threaten homeostasis. Adaptive changes occur when a body function changes to work within its environment. Exhaustion occurs when there is a negative sequela. Homeostasis is dynamic change. Question 12 0 out of 0 points Which type of cellular adaptation is most likely to occur as the result of chronic ischemia to a region? Selected Answer: Hyperplasia Correct Answer: Atrophy Response Feedback: Ischemia is inadequate blood supply to a tissue. Chronic sublethal ischemia usually results in cell atrophy. Hypertrophy would result in an increase in cell size in response to increased physiological demand. Hyperplasia would result in an increased number of cells in response to increased physiological demand. Metaplasia is the replacement of one differentiated cell type with another better suited for the situation Question 13 0 out of 0 points Which diagnostic analysis is used to identify patients with heart failure? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide) ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) Echocardiogram Correct Answers: BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide) Echocardiogram Chest x-ray film Response Feedback: BNP is a blood test that assists in identifying patients with heart failure. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create a moving picture of the heart and is used in the diagnosis of heart failure. A chest x-ray is a physical diagnostic test that shows heart structures and is used in the diagnosis of heart failure. Complete blood count (CBC) is a blood analysis used to determine the composition of blood related to amounts of specific cells in a serum sample. The overall effect of ANP on the body is to counter increases in blood pressure and volume caused by the renin-angiotensin system. Question 14 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true about disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: It is both a bleeding and clotting disorder. It is both a bleeding and clotting disorder. Response Feedback: DIC is both a bleeding and clotting disorder. There are two types, with the chronic type being more prone to thrombotic episodes because the liver and bone marrow are functioning at a higher level and are able to produce more clotting factors and platelets. There is a rise in fibrin split products secondary to the destruction of clots. The fibrinogen level decreases as the body uses it up. Question 15 0 out of 0 points The role of the circulatory system is to do which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Transport O2 and nutrients throughout the body Remove waste products found within the body Move blood systemically from the right side of the heart Correct Answers: Transport O2 and nutrients throughout the body Remove waste products found within the body Response Feedback: The primary functions of the circulatory system include the transportation of O2 and nutrients within the body and the removal of metabolic waste products within the body. Movement of blood through the lungs is via the right side of the heart. Systemic blood flow is supplied by the left side of the heart. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood as it moves through the gastrointestinal tract via splanchnic circulation, and O2 uptake and the release of CO2 occur in the specialized vascular bed of the pulmonary circulation. Question 16 0 out of 0 points Which statement concerning the location of specific buffers is correct? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Phosphate buffers are found in the intracellular space. Hemoglobin buffers are found inside the erythrocytes. Bicarbonate buffers are found in the extracellular space. Protein buffers are found in the intracellular compartment. Correct Answers: Phosphate buffers are found in the intracellular space. Hemoglobin buffers are found inside the erythrocytes. Bicarbonate buffers are found in the extracellular space. Protein buffers are found in the intracellular compartment. Response Feedback: Bicarbonate buffers are found in the extracellular space. Phosphate buffers are found in the intracellular space and urine. Hemoglobin buffers are found inside the erythrocytes. Protein buffers are found in the intracellular and vascular compartments. Protein buffers are not found in human urine. Question 17 0 out of 0 points Restoration of effective function is the goal of which level of prevention? Selected Answer: Tertiary Correct Answer: Tertiary Response Feedback: Tertiary prevention (appropriate in the stage of advanced disease or disability) includes rehabilitative and supportive care and attempts to alleviate disability and restore effective functioning. Primary prevention is prevention of disease by altering susceptibility or reducing exposure for susceptible individuals. Clinical is a stage referred to in early disease prevention (secondary). Secondary prevention is the early detection, screening, and management of the disease. Question 18 0 out of 0 points What is the difference between capillary fluid pressure and plasma colloid osmotic pressure? Selected Answer: Capillary fluid pressure is the fluid pressure outside the capillary and is the force pushing fluid from the interstitium from the capillary; plasma colloid osmotic pressure is the primary force because of the presence of anions, which result in fluid remaining in the capillary. Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Capillary fluid pressure is the fluid pressure inside the capillary and is the force pushing fluid from the capillary into the interstitium; plasma colloid osmotic pressure is the primary force because of the presence of plasma proteins, which results in fluid remaining in the capillary. Capillary fluid pressure is the fluid pressure inside the capillary and is the force pushing fluid from the capillary into the interstitium (called hydrostatic pressure). Plasma colloid osmotic pressure is the primary force because of the presence of plasma proteins, which result in fluid remaining in the capillary. Most plasma proteins remain in the capillaries because they are such large molecules that they are unable to move easily through the capillary walls. The other options do not correctly define the terms or the processes. Question 19 0 out of 0 points Which statement(s) are true regarding post-exposure prophylaxis? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: All exposed individuals require a protease inhibitor drug regimen. Prophylaxis for a significant exposure should be started immediately. Postexposure medication treatment last at least 4 weeks, or even longer. Correct Answers: Prophylaxis for a significant exposure should be started immediately. Postexposure medication treatment last at least 4 weeks, or even longer. Two or more medications may be included in the medication regimen. Exposure, sexual or otherwise, requires similar medication protocols. Response Feedback: Significant exposure to HIV- infected blood or body fluids such as a needle stick, require that post-exposure prevention protocol be initiated immediately. The length of administration of the agents depends on multiple factors and may be 4 weeks or longer. Often post-exposure protocols involve the administration of two or three medications. This same protocol has been advocated for use as postsexual exposure prophylaxis. According to the Public Health Service and NIH, the selection of a drug regimen for HIV postexposure prophylaxis must balance the risk for infection against potential toxicities and side effects of the medication. As such, consultation with an infectious disease provider is often recommended. Treatment usually depends on if the exposure source’s viral status, viral load, or antiretroviral therapy response is known. Question 20 0 out of 0 points Which condition occurs in the presence of cellular damage? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Sodium and water move into the cell. Sodium and water move into the cell. Cellular injury causes failure of the sodium-potassium pump, resulting in migration of sodium ions into the cell. The accumulation of intracellular sodium creates an osmotic gradient that pulls water into the cell, resulting in hydropic swelling. Cells actually swell, not shrink, as a result of cellular damage. Cellular damage results in the cell’s inability to perform normal metabolic functions owing to insufficient cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Osmotic pressure increases to accommodate for swelling Question 21 0 out of 0 points A patient has a regular heart rate of 54 beats/min. The nurse would document this rhythm as Selected Answer: Bradycardia Correct Answer: Bradycardia Response Feedback: Sinus bradycardia is defined as a heart rate of less than 60 beats/min. Normal sinus rhythm is defined as an impulse rate between 60 and 100 per minute. Sinus arrhythmia is a normal finding associated with fluctuations in autonomic influences and respiratory dynamics. Sinus tachycardia is an abnormally fast heart rate of greater than 100 beats/min. Question 22 0 out of 0 points Von Willebrand disease may present itself by which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Epistaxis Ecchymoses Decreased von Willebrand factor Correct Answers: Epistaxis Ecchymoses Decreased von Willebrand factor Response Feedback: Epistaxis and ecchymoses are common clinical manifestations of von Willebrand disease, and the level of von Willebrand factor is decreased or absent. In von Willebrand disease, the platelet count and PT are normal, but aPTT is prolonged. Question 23 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true about the normal biological variations related to age? Selected Answer: There is less thirst perception in the elderly. Correct Answer: There is less thirst perception in the elderly. Response Feedback: Aging does usually result in diminished thirst perception. Adults have slower heart rates than infants. The elderly have fewer sweat glands. The elderly have diminished temperature sensations. Question 24 0 out of 0 points The condition associated with hypoxemia as a result of lung disease or living at high altitudes is called Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: secondary polycythemia. secondary polycythemia. Secondary polycythemia is the body’s response to hypoxemia from causes such as lung disease or living at high altitudes. Polycythemia vera is a high red blood cell count without associated lung disease or dehydration. It is usually associated with neoplastic disease. Relative polycythemia is associated with poor intake and dehydration. Anemia of any type is associated with a low red blood cell count. Question 25 0 out of 0 points The shift to anaerobic metabolism in shock results in Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Decreased oxygen utilization Increased lactate production When the citric acid cycle is inhibited, pyruvate accumulates in the cytoplasm. Pyruvate accumulation would quickly inhibit further glycolysis and shut down ATP production entirely except that it can be converted to a substance called lactate, which diffuses from the cell and into the extracellular fluid. A shift to anaerobic metabolism in shock does not result in metabolic alkalosis, decreased oxygen utilization, or decreased hydrogen ion production. Question 26 0 out of 0 points What gene is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: bcr-abl bcr-abl Response Feedback: The bcr-abl fusion gene is the Philadelphia chromosome and is associated with CML. TP53 is noted to have worse outcomes when associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RB is noted to have worse outcomes when associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). BRCA-1 is associated with an increase in breast cancer in women. Question 27 0 out of 0 points Which term means cause of the disease ? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Etiology Etiology Etiology is the cause or reason for a phenomenon. When the link between an etiologic factor and development of a disease is less than certain, but the probability is increased when the factor is present, it is termed a risk factor. The mechanism of disease development is called pathogenesis. The functional consequences of these changes are the clinical manifestations. Question 28 0 out of 0 points Which drug is a protease inhibitor? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Lamivudine (Epivir) Nelfinavir (Viracept) Fosamprenavir (Lexiva) Correct Answers: Nelfinavir (Viracept) Atazanavir (Reyatax) Fosamprenavir (Lexiva) Response Feedback: Nelfinavir (Viracept), atazanavir (Reyatax), and fosamprenavir (Lexiva) are protease inhibitors. Lamivudine (Epivir) and zidovudine (Retrovir) are reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Question 29 0 out of 0 points How many liters of blood are circulating in the human body at any one time? Selected Answer: 4 to 6 Correct Answer: 4 to 6 Response Feedback: There are 4 to 6 liters of blood circulating in the body at any one time. Forty-five percent of the volume is blood cells (red blood cells and white blood cells), and 55% is plasma volume (which contains nutrients and plasma proteins). 1 to 2 and 2 to 3 liters are too low a blood volume. 10 to 20 liters is an exaggerated amount of blood volume. Question 30 0 out of 0 points The kidneys excrete acids that include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Lactic Metabolic Phosphoric Hydrochloric Correct Answers: Lactic Metabolic Phosphoric Hydrochloric Response Feedback: Lactic acid is a metabolic acid. The kidneys normally excrete metabolic acids. Acids that are not carbonic acid are called metabolic acids because cells continuously produce them during normal metabolism. The kidneys normally excrete metabolic acids. Phosphoric acid is a metabolic acid. The kidneys normally excrete metabolic acids. Hydrochloric acid is a metabolic acid. The kidneys normally excrete metabolic acids. The kidneys can excrete any acid from the body except carbonic acid, which is excreted solely by the lungs. If a metabolic acid begins to accumulate in the blood, the kidneys increase their acid excretion mechanisms to correct the problem. Question 31 0 out of 0 points Which electrolyte is essential in ensuring a negative resting membrane potential? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Sodium Potassium The major determinant of the resting membrane potential is the difference in potassium ion concentration across the membrane; thus the negative value of the resting membrane potential (RMP) is determined by the ratio of intracellular to extracellular potassium ion concentration. At rest, the membrane is permeable to K+, but not to other positively charged cations, including calcium. At rest, the membrane is permeable to K+, but not to other positively charged cations, including sodium. Magnesium is not involved in the resting membrane potential. Question 32 0 out of 0 points Anemia of chronic renal failure is caused by the lack of Selected Answer: Erythropoietin Correct Answer: Erythropoietin Response Feedback: Erythropoietin is secreted by the kidney in response to hypoxia caused by a low hemoglobin concentration. Erythropoietin stimulates the bone marrow to produce mature red blood cells. The tissue of the diseased kidney has difficulty producing this hormone. A lack of adrenaline, thyroid hormone, and parathyroid hormone are not factors in anemia of chronic renal failure. Question 33 0 out of 0 points An increase in which of these characteristics would be present in cells that demonstrate hypertrophy? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Size of cells Size of cells Hypertrophy is defined as an increase in cell mass (cellular enlargement). A lipofuscin is a yellow to brown, granular, ironnegative lipid pigment found particularly in muscle, heart, liver, and nerve cells; it is the product of cellular wear and tear, accumulating in lysosomes with age. A vacuole is a small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water (hydropic swelling), food, or metabolic waste. Cells that are capable of mitotic division generally increase their functional capacity by increasing the number of cells by hyperplasia Question 34 0 out of 0 points A child with ill-fitting shoes developed a vesicle (small blister) that burst, releasing clear watery fluid. The school nurse would document this drainage as Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Serous Serous Serous exudate is watery fluid such as that which collects under a blister. This type of exudate generally accompanies mild inflammation. Purulent exudate is called pus. Purulent exudate generally occurs in severe inflammation accompanied by bacterial infection. Large pockets of purulent exudate, called abscesses, must generally be removed or drained for healing to take place. Fibrinous exudate is sticky and thick and may have to be removed to allow healing; otherwise, scar tissue and adhesions may develop. Hemorrhagic exudate has a large component of red blood cells. This type of exudate is usually present with the most severe inflammation. Hemorrhagic exudate occurs with severe leakage from blood vessels or after necrosis or breakdown of blood vessels. Question 35 0 out of 0 points Which term is used to describe an excess of red blood cells? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Polycythemia Polycythemia Polycythemia is an excess of red blood cells. Anemia is a deficiency of red blood cells. Pancytopenia is a decrease in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Granulocytopenia is a decrease in platelets. Question 36 0 out of 0 points Which statement(s) are true regarding replication of the HIV virus? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: HIV viruses that enter the cells must be converted to doublestranded DNA. The DNA is a template copied by the DNA polymerase to make a second DNA strand. The process of HIV replication is responsible for the ineffectiveness of many antiviral drugs. Correct Answers: Accuracy of transcription is poor with multiple mutations. The conversion of the DNA is made by the reverse transcriptase from the viral DNA. The DNA is a template copied by the DNA polymerase to make a second DNA strand. The process of HIV replication is responsible for the ineffectiveness of many antiviral drugs. Response Feedback: The accuracy of DNA transcription is poor, with mutations occurring frequently. This conversion is made by the reverse transcriptase from the viral RNA. The DNA is a template, and the DNA polymerase copies it to make a second DNA strand and destroys the original RNA strands. Mutations make it difficult for antivirals to work. Once the virus enters the cell, it must be converted to single-, not double-, stranded DNA. The accuracy of DNA transcription is poor, with mutations occurring frequently. Question 37 0 out of 0 points Bacteria are categorized by which of their following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Shape Site of infection Reaction to staining Correct Answers: Shape Need for oxygen Reaction to staining Response Feedback: Bacteria are named for their shape (cocci, rod, and spirochete), their need for oxygen (aerobic or anaerobic), and their reaction to staining (Gram-positive or Gram-negative). Site of infection is related to parasites. Association with proteins and lipids is related to viruses. Question 38 0 out of 0 points Which statement is false regarding hypophosphatemia? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Hypophosphatemia is caused by factors that increase phosphate intake. Hypophosphatemia is caused by factors that increase phosphate intake. Hypophosphatemia is caused by factors that decrease phosphate intake, shift phosphate from extracellular fluid into cells, increase phosphate excretion, and cause loss of phosphate through abnormal routes. Anorexia, malaise paresthesias, and impaired cardiac functioning are classic signs of hypophosphatemia. A serum level below 2.5 mg/dl is by definition hypophosphatemia. Symptoms are seldom observable until phosphate levels fall below 1.0 mg/dl. Question 39 0 out of 0 points Which statements is true regarding serum potassium (K+) levels? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Hypokalemia is capable of causing elevated diastolic pressure. Hyperkalemia can result in weakness in the lower extremities. Hypokalemia can often cause muscle weakness. Hypokalemia can result in a paralytic ileus. Correct Answers: Hyperkalemia can result in weakness in the lower extremities. Hyperkalemia can be characterized by intestinal cramping. Hypokalemia can often cause muscle weakness. Hypokalemia can result in a paralytic ileus. Response Feedback: Both low and high levels of K+ produce skeletal muscle weakness in an ascending pattern in the lower extremities first, with flaccid paralysis. Hyperkalemia causes intestinal cramping and diarrhea. Hypokalemia results in abdominal distention, diminished bowel sounds, and a paralytic ileus. Hypokalemia results in smooth muscle relaxation which results in decreased diastolic pressure. Question 40 0 out of 0 points Which cell is from myeloid lineage? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: B cells Natural killer cells Granulocytes Correct Answers: Platelets Monocytes Granulocytes Response Feedback: Platelets, monocytes, and granulocytes are from myeloid lineage. B cells and natural killer cells are lymphoid. Question 41 0 out of 0 points Tachycardia, decreased or absent breath sounds on the affected side, hyperresonance, and sudden chest pain on the affected side are clinical manifestations of Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Sarcoidosis Pneumothorax Clinical features of a pneumothorax include tachycardia, decreased or absent breath sounds on the affected side, hyperresonance, and sudden chest pain on the affected side. General symptoms of hypersensitivity pneumonitis may include chills, sweating, shivering, myalgias, nausea, lethargy, headache, and malaise. The patient may or may not have a fever. Respiratory symptoms may include dyspnea at rest, dry cough, tachypnea, and chest discomfort. Physical findings may include cyanosis (a late sign) and crackles (rales) in the lung bases. Sarcoidosis is characterized by malaise, fatigue, weight loss, fever chest discomfort, dyspnea of insidious onset, and a dry, nonproductive cough. The clinical features of ARDS usually include a history of a precipitating event that has led to a low blood volume state ( shock state) 1 or 2 days prior to the onset of respiratory failure. The patient may complain of sudden marked respiratory distress. Early signs and symptoms include a slight increase in pulse rate, dyspnea, and a low PaO2. The initial presenting sign may be shallow, rapid breathing. Question 42 0 out of 0 points Contraction of vascular smooth muscle (referred to as vasomotor tone) is mostly accomplished via the extrinsic mechanism of the autonomic nervous system, resulting in which receptor response? Selected Answer: α-1 Correct Answer: α-1 Response Feedback: Because arteries have the most smooth muscle, they are most affected by central nervous system stimulation. The release of norepinephrine (the postganglionic neurotransmitter) results in arterial vasoconstriction via the α-1 receptors located on the vascular smooth muscle walls Although β-2 receptors on smooth muscles are affected, they only increase nutrient and oxygen supplies to skeletal muscles via vasodilation, not vasoconstriction, during times of stress. β-1 and α-2 receptor responses are not involved in this scenario. Question 43 0 out of 0 points For proper pH balance within the human body, what is the ratio of bicarbonate ions to carbonic acid molecules? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: 20 bicarbonate ions to 1 carbonic acid molecule 20 bicarbonate ions to 1 carbonic acid molecule The pH of any fluid is determined by the relative amounts of acids and bases contained in it. For the pH of the blood to be within the normal range, the ratio of bicarbonate ions to carbonic acid molecules must be 20:1. The other ratios would not maintain normal pH. Question 44 0 out of 0 points The laboratory analysis conducted on a child with chronic nasal drainage reveals an elevated number of eosinophils on a white blood cell differential. Based on this finding, which is most likely the cause of the nasal drainage? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Allergies Allergies Response Feedback: Eosinophils are particularly associated with an increase in number during allergic reactions, particularly with sinus infections. Neutrophils, not eosinophils, are seen to increase in numbers related to bacterial and viral infections. Traditionally, the band count has been used to differentiate bacterial from viral infections, and a greater shift to the left is viewed as a more severe infection. Basophils are also involved in wound healing and chronic inflammatory conditions. Question 45 0 out of 0 points What occurs during an acute asthma attack? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Sputum is often thick, tenacious, scant, and viscid. Bronchoconstriction occurs. Residual lung volume increases. Forced expiratory volumes decrease. Correct Answers: Sputum is often thick, tenacious, scant, and viscid. Bronchoconstriction occurs. Residual lung volume increases. Forced expiratory volumes decrease. Response Feedback: Sputum is often thick, tenacious, scant, and viscid. Bronchospasm are experienced during asthma attacks. Air becomes trapped because of the inflammatory changes that occur so increasing residual lung volume. Forced expiratory volumes decrease during asthma attacks. Tidal does not remain constant during an asthma attack. Question 46 0 out of 0 points Which condition is an endocrine disorder that causes elevated blood pressure? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Guillain-Barré syndrome Coarctation of the aorta Cushing disease Hyperthyroidism Correct Answers: Cushing disease Hyperthyroidism Response Feedback: Endocrine disorders that result in hypertension include Cushing disease and hyperthyroidism. While Guillain-Barré syndrome results in hypertension, it is neurologic disorder. While coarctation of the aorta causes high blood pressure, it is a cardiac disorder. While pheochromocytoma causes high blood pressure, it is a tumor of adrenal gland tissue. Question 47 0 out of 0 points Activation of the renin-angiotensin system in shock causes Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Fluid retention Fluid retention Renin triggers stimulates kidney nephrons to conserve sodium and water. Renin triggers the formation of angiotensin II, which is a potent vasoconstrictor. Renin triggers stimulates kidney nephrons to conserve not shift sodium. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system does not cause glucogenesis. Question 48 0 out of 0 points The study of specific characteristics and functions of a living organism and its parts is called Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Physiology Physiology Response Feedback: Physiology is the study of the mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions of living organisms. Psychiatry is a branch of medicine dealing with mental illness. Homeostasis is a dynamic steady state. Pathophysiology refers to the disorder or breakdown of the human body’s function. Question 49 0 out of 0 points The normal adult pH in the blood is Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Between 7.35 and 7.45 Between 7.35 and 7.45 An acceptable range is 7.35 to 7.45. 7.30 is slightly below the normal range. If the blood becomes too acidic (less than 6.9) death is likely. If the blood becomes too alkaline (greater than 7.8) death is likely. Question 50 0 out of 0 points Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) can be indirectly estimated with the use of which blood pressure measurement? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure Diastolic pressure The systemic diastolic pressure is determined by the narrowing of blood vessel diameter and therefore the resistance to blood flow, whether from peripheral vascular constriction or atherosclerosis. Systolic pressure is not as influenced by the narrowing of blood vessel diameter. Pulmonary arterial pressure is generated by the right ventricle ejecting blood into the pulmonary artery. By definition, the volume of blood within a ventricle immediately before a contraction is known as the end-diastolic volume. Question 51 0 out of 0 points What is the primary cause of airway obstruction in patients with chronic bronchitis? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Mucous plugs Mucous plugs Hypertrophy of mucosal glands and goblet cells leads to increased mucous production; the mucus then combines with purulent exudate to form bronchial plugs. Thickening of bronchial smooth muscle occurs. Hyperventilation is not related to airway obstruction. While infection may be evident, it is not the cause of airway obstruction. Question 52 0 out of 0 points If the host’s immune system is compromised, resident florae may become pathogenic, resulting in Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections When normal florae are allowed to overgrow as a result of the compromise of the host’s immune system, infection can result. Salmonella requires the presence of a specific pathogen. Otitis media is not generally considered an opportunistic infection. Myocarditis is not generally considered an opportunistic infection Question 53 0 out of 0 points Which is true regarding catecholamines? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: They include epinephrine and norepinephrine. They include epinephrine and norepinephrine. Catecholamines include epinephrine and norepinephrine. Norepinephrine is secreted from the sympathetic nerves, and epinephrine is secreted from the adrenal medulla. Epinephrine and norepinephrine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. Epinephrine and norepinephrine cause increased heart rate, blood pressure, and blood flow to skeletal muscles. Question 54 0 out of 0 points Which condition explains the genetic basis for cancer development? Selected Answer: Loss of or defect in tumor suppressor genes Correct Answer: Loss of or defect in tumor suppressor genes Response Feedback: Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cancer proliferation pathways. Decreased immune function and exposure to ionizing radiation may be factors but not the basis of cancer development. Infection by oncogenic bacteria is not a factor, since bacterial infection is not relevant. Question 55 0 out of 0 points Which chromosomal abnormalities has been linked with Down syndrome? Selected Answer: Translocation Correct Answer: Translocation Response Feedback: Chromosomal translocations result from the exchange of pieces of DNA between nonhomologous chromosomes. The exchange of a long chromatid arm for a short one results in the formation of one very large chromosome and one very small chromosome This is called a Robertsonian translocation and is responsible for a rare hereditary form of Down syndrome. Extra copies of a portion of DNA is called duplication. Inversion refers to the removal and upside-down reinsertion of a section of chromosome. Loss of chromosomal material is called deletion. Question 56 0 out of 0 points Which lung zone has continuous perfusion throughout the cardiac cycle? Selected Answer: Zone 1 Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Zone 3 Zone 3 has continuous perfusion through the entire cardiac cycle. Pulmonary arterial pressure is greater than pulmonary venous pressure. Zone 1 reflects blood flow through the apices and is minimal. The alveolar pressure is higher than capillary pressure. Zone 2 has pulmonary arterial pressure greater than the pressure inside the alveoli during ventricular systole. Zone 2 has intermittent perfusion. There is no recognized Zone 4. Question 57 0 out of 0 points Characteristics of allergic purpura lesions include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Fever and itching Bleeding from the lesions Lesions located on the face Correct Answers: Fever and itching Easily palpated lesions Response Feedback: Purpura lesions are itchy and a fever is likely. They are raised and are usually easily felt. Bleeding from the lesions themselves and generalized bleeding are uncommon. The lesions tend to be found on the proximal extremities, especially on the legs and buttocks. The lesions tend to be found on the proximal extremities, especially on the legs and buttocks. Question 58 0 out of 0 points The vasoactive mediators released in septic shock contribute to increase Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Vascular permeability Vascular permeability Response Feedback: The kinin system is activated and bradykinin is released, which results in vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Histamine also increases capillary permeability, which enhances edema formation. Systemic vascular resistance is decreased in septic shock. The complement system is activated with release of C5a and C3a, which can produce microemboli and endothelial cell destruction. The coagulation system is activated and may enhance the development of microemboli. Histamine, a potent vasodilator, is released by mast cells. Question 59 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true regarding asthma? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: It is characterized by airway inflammation. It is characterized by airway inflammation. Asthma is characterized by airway inflammation. There is increased airway responsiveness to stimuli. The resulting airway obstruction is usually reversible. Extrinsic asthma is child-onset asthma. Question 60 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true regarding hypertension during pregnancy? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: More than 50% of pregnancies are complicated by high blood pressure. Cardiac output (CO) is reduced by 40% to 60% during pregnancy. CO decreases by 40% to 60% during the first two trimesters of pregnancy. Only 12% to 22% of pregnancies are complicated with hypertension. Blood pressure normally decreases during the first two trimesters and gradually returns to normal levels during the third trimester. Serious side effects of hypertension, including seizure, fetal death, and maternal death, can occur during pregnancy. Question 61 0 out of 0 points Cardiac output is the product of both Selected Answer: Stroke volume and heart rate Correct Answer: Stroke volume and heart rate Response Feedback: The product of stroke volume and heart rate provides the amount of cardiac output. None of the other options (MAP, SVR, or pulse pressure) are factors in cardiac output. Question 62 0 out of 0 points A general mechanism noted in thrombocytopenia is which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Decreased platelet production Decreased platelet survival Hemorrhage Correct Answers: Decreased platelet production Decreased platelet survival Splenic sequestration Intravascular dilution Response Feedback: In thrombocytopenia, four mechanisms are involved, including the decreased production of platelets, the decreased survival of platelets, the sequestration (pooling) of platelets in the spleen, and intravascular dilution. Hemorrhage is not one of the mechanisms involved in thrombocytopenia. Question 63 0 out of 0 points Factors released by platelets contribute to hemostasis by enhancing Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Intrinsic pathway Platelet aggregation Platelets, when activated, release factors that lead to vasoconstriction, platelet clumping, and vessel repair. Vasodilation is not caused by platelet factors. The intrinsic pathway and fibrinolysis are steps in clot formation. Question 64 0 out of 0 points Which is not one of the recognized components of the general adaptation syndrome? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Allostasis Allostasis Allostasis is a dynamic process that supports and helps the body achieve homeostasis. Alarm, resistance, and exhaustion are the three recognized components of Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome. Question 65 0 out of 0 points A contributing factor to the formation of an embolus includes which of the following?(Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Dislodged fat after long-bone surgery Air bolus introduced by IV therapy Foreign object in the blood stream An infected blood vessel Correct Answers: Dislodged fat after long-bone surgery Air bolus introduced by IV therapy Foreign object in the blood stream An infected blood vessel Response Feedback: Fat emboli can occur after long-bone surgery or trauma. Air introduced into the circulatory system can result in an air embolus. Any foreign body in the circulating in the system can be the cause of an embolus. An infection present in a vessel can trigger an embolus. Chronic blood disorders like anemia are not generally triggers for emboli. Question 66 0 out of 0 points What is the pathophysiologic phenomenon underlying disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)? Selected Answer: Clotting that leads to bleeding Correct Answer: Clotting that leads to bleeding Response Feedback: DIC is a result of widespread clot formation that consumes platelets and clotting factors, which leaves the patient at risk for serious bleeding. As the result of extensive clotting, platelet and fibrinogen levels are decreased not increased. Inadequate cardiac outcome is the fatal outcome of DIC. Mast cell degranulation is not relevant to DIC. Question 67 0 out of 0 points Which waves on the ECG is representative of depolarization of the lateral walls? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: S wave S wave The S wave is representative of lateral wall depolarization. The Q wave represents septal depolarization. The R wave represents apical depolarization. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization. Question 68 0 out of 0 points Which type of cellular adaptation would create the greatest concern if found on a biopsy report? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Dysplasia Dysplasia Dysplastic cells have significant potential to transform into cancerous cells and are usually regarded as preneoplastic lesions. Metaplasia is the replacement of one differentiated cell type with another. This most often occurs as an adaptation to persistent injury, with the replacement cell type better able to tolerate the injurious stimulation and is fully reversible when the injurious stimulus is removed. Hyperplasia is an increase in cell number usually in response to physiologic demands, hormonal stimulation or chronic cell injury. This is generally a normal adaptation, and not nearly the concern of the correct option. Hypertrophy is an increase in cell mass accompanied by an augmented functional capacity. This is generally a normal adaptation, and of little or no concern. Question 69 0 out of 0 points On which area does cortisol have an anabolic effect? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Protein Protein Cortisol has an anabolic effect on protein, leading to an increased rate of protein synthesis. Cortisol has a catabolic effect on lymphoid tissue Cortisol has a catabolic effect on muscle tissue. Cortisol has a catabolic effect on skin. Question 70 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true regarding cancer? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: The greater the undifferentiated cell count, the more aggressive the cancer. Malignant tumors have the potential to kill the host. Anaplasia means more differentiated cells. Metastasis means less differentiated cells. Correct Answers: The greater the undifferentiated cell count, the more aggressive the cancer. Malignant tumors have the potential to kill the host. Response Feedback: The greater the degree of anaplasia, the more aggressive the malignant tumor. Malignant tumors, if left untreated, have the potential to kill. Benign tumors often grow slowly than malignant ones. Anaplasia is a lack of cell differentiation. Metastasis means the invasion of cancer to distant sites. Question 71 0 out of 0 points Aging adults are more prone to dehydration as a result of lack of thirst triggers resulting from Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Decreased osmolality in intracellular fluid Increased osmolality of extracellular fluid As the kidneys age, the tubules become less responsive to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and tend to lose too much water. The excess water loss is accompanied by a decrease in thirst mechanism. As a result, the elderly person is prone to dehydration. Intracellular fluid status is not related to the thirst triggers. An increase in the osmolality of extracellular fluid would result in a risk for dehydration. Question 72 0 out of 0 points Which statement about oncogene activation is true? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Oncogenes may be introduced into the host cell by a retrovirus. Proto-oncogenes may undergo a mutation thus becoming overly active. DNA sequences that normally suppress proto-oncogene expression may be inactivated. An error may occur in the replication of the chromosome such that extra copies are produced. Correct Answers: Oncogenes may be introduced into the host cell by a retrovirus. Proto-oncogenes may undergo a mutation thus becoming overly active. DNA sequences that normally suppress proto-oncogene expression may be inactivated. An error may occur in the replication of the chromosome such that extra copies are produced. Response Feedback: At least four general ways in which proto-oncogenes can be activated: oncogenes may be introduced into the host cell by a retrovirus, a proto-oncogene within the cell may suffer a mutagenic event that changes its structure and function, a DNA sequence that normally regulates proto-oncogene expression may be damaged or lost, thereby allowing the proto-oncogene to become abnormally active, or an error in chromosome replication may occur and cause extra copies to be produced, which is called amplification. Bacteria do not carry genetic material into the cell genome, but retroviruses may. Question 73 0 out of 0 points Which is an example of active immunity? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Placental transfer of maternal antibodies Yearly flu vaccination Pneumonia vaccine Breast-feeding Correct Answers: Yearly flu vaccination Pneumonia vaccine Response Feedback: Vaccinations, such as the yearly flu and pneumonia vaccines, stimulate the host immune system to mount an immune response and produce long-lived memory cells and antibody-secreting cells that provide lasting protection, a process called active immunity. Immunity acquired by the newborn via the placenta or via breast milk and gamma globulin injections are examples of passive immunity in which antibodies produced by one individual are transferred to another. These antibodies provide only short-term protection, because the host does not produce memory cells or antibodies. Question 74 0 out of 0 points A heart that has to pump harder in order to effectively circulate blood is likely to undergo which type of cellular adaptation? Selected Answer: Atrophy Correct Answer: Hypertrophy Response Feedback: Cells hypertrophy in response to increased physiologic or pathophysiologic demands. If the heart has to pump harder than normal to meet the body s demand for oxygen and nutrients, the cardiac cells will become larger, resulting in cardiac hypertrophy. Atrophy results in cell death that would render the cells nonfunctional. Metaplasia is the replacement of one differentiated cell type with another. Muscle contraction could possibly be lost rather than enhanced. Hyperplasia would result in an increased number of cells rather than an enhanced pumping capacity. Question 75 0 out of 0 points Which statement is true regarding carbonic acid (H2CO3)? Selected Answer: If body fluids are too acidic, carbonic acid is excreted through the respiratory system in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Correct Answer: Response Feedback: If body fluids are too acidic, carbonic acid is excreted through the respiratory system in the form of carbon dioxide and water. If too much acid is present, bicarbonate (HCO3) picks up a hydrogen (H+) molecule to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), and with the help of the enzyme called carbonic anhydrase, the carbonic acid is then excreted through the respiratory system in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The other statements do not reflect effective utilization of carbonic acid (H2CO3) Question 76 0 out of 0 points The major risk factor for the development of lung cancer is Selected Answer: cigarette smoking Correct Answer: cigarette smoking Response Feedback: Tobacco smoking is the major cause (85%) of lung cancer, with approximately 160,000 deaths reported per year. While individuals older than 50 years of age have an increased risk for developing lung cancer; it is not comparable to that of a history of tobacco smoking. A family history that includes non-tobacco use related lung cancer doe have an impact on the risk for developing lung cancer; it is not comparable to that of a history of tobacco smoking. Working under conditions of asbestos exposure increases the risk for developing lung cancer; it is not comparable to that of a history of tobacco smoking. Question 77 0 out of 0 points In muscle hypertrophy, the hypertrophied cells increase in Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Size Size The cellular response to persistent, sublethal stress reflects the cell’s efforts to adapt. A common adaptive response is hypertrophy resulting in an increase in cell size. Hyperplasia is an increase in cell number. An increase in calcium would be pathological and likely result in tetany. An increase in accumulations would be pathological and likely result in cell injury Question 78 0 out of 0 points A current diagnosis of tuberculosis requires a Selected Answer: Positive sputum culture for acid-fast bacillus Correct Answer: Positive sputum culture for acid-fast bacillus Response Feedback: Three consecutive morning sputum specimens are obtained to identify the slow-growing acid-fast bacillus and confirm a current diagnosis of tuberculosis. A chest ray is used to confirm nodules with infiltrates in the lung apex and posterior segments of the upper lobes; not the definitive diagnostic result. The Mantoux test does not distinguish between current disease and past infection. Presentation of symptoms is not considered a definitive indication of the disease. Question 79 0 out of 0 points Which statement(s) are true regarding the HIV virus structure? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: There are two strands of RNA. The nucleocapsid or core is composed of p17. Between the envelope and core is a protein layer called p24. Correct Answers: There are two strands of RNA. The gag gene encodes the core antigen proteins. The pol gene encodes reverse transcriptase proteins Response Feedback: There are two strands of RNA. The gag gene encodes the core antigen proteins. The pol gene encodes reverse transcriptase proteins. The core or nucleocapsid is composed of p24, not p17. The layer between the envelope and core is protein p17, not p24. Question 80 0 out of 0 points Which terms refers to an increased speed of conduction? Selected Answer: Chronotropic Correct Answer: Dromotropic Response Feedback: Dromotropic refers to increased speed of conduction. Inotropic refers to increased contractile force. Chronotropic refers to increased heart rate. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter for the nervous system. Question 81 0 out of 0 points It is true that acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) is Selected Answer: Primarily diagnosed in children Correct Answer: Primarily diagnosed in children Response Feedback: ALL is a primarily a disorder occurring in children. All is highly curable in children, less so in adults. Peak incidence is between ages 3 and 7 years of age. A second rise occurs in middle age. Question 82 0 out of 0 points What is the marker of choice for detecting a myocardial infarction? Selected Answer: Elevated serum levels of cardiac troponin Correct Answer: Elevated serum levels of cardiac troponin Response Feedback: Two proteins that make up part of the cardiac cell contractile apparatus, troponins I and T, have become the markers of choice for detecting MI. Cardiac troponin levels become elevated in serum at about the same time as CK-MB, but they remain elevated for a longer period. ST-segment elevation is thought to represent acute cell injury and ischemia. An elevated level of serum CK-MB is a highly specific indicator of MI and considered to be diagnostic. However, CK-MB remains elevated for only 48 to 72 hours after MI. Cardiac myoglobin levels are elevated in serum very quickly after MI and may be helpful in early detection; however, cardiac myoglobin is less specific than the other markers. Question 83 0 out of 0 points What causes a shift of the oxyhemoglobin curve to the left? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Increased pH Decreased H+ ions Decreased temperature Correct Answers: Increased pH Decreased H+ ions Decreased temperature Response Feedback: The shift of the curve to the left occurs with an increase in pH, a decrease in H+ concentration, and with a decrease in temperature. The shift of the oxyhemoglobin curve to the right enhances oxygen release to the cell. The shift provides the increase in oxygen delivery that is needed during stress, chronic disease, and exercise. The shift of the curve to the left occurs with a decrease in 2,3-DPG, in some congenital hemoglobinopathies, and with carboxyhemoglobin. Question 84 0 out of 0 points Which form(s) of anemia will present with macrocytes? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Folate deficiency Iron-deficiency Thalassemia B12 Correct Answers: Folate deficiency B12 Response Feedback: Folate and B12 deficiency causes the production of macrocytes in the peripheral blood. In renal failure, the red blood cells are decreased and may have spicules. Iron-deficiency anemia is described by the presence of hypochromic and microcytic cells. Thalassemia is caused by destruction or hemolysis of red blood cells Question 85 0 out of 0 points It is true that the Epstein-Barr virus is Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Considered a cause of Burkitt lymphoma Considered a cause of Burkitt lymphoma Research has implicated that the Epstein-Barr virus is a causative factor in both Hodgkin disease and Burkitt lymphoma. Epstein-Barr virus is ubiquitous, with 90% of adults having evidence of previous infection. HIV, not Epstein-Barr, is linked to B-cell lymphoma while B-cell lymphoma, not Epstein-Barr, is linked to HIV. Question 86 0 out of 0 points Which statement(s) are true regarding hemoglobin? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Oxyhemoglobin is hemoglobin-carrying oxygen. Hemoglobin makes up 90% of dry weight of the red cell. Polypeptide chains contain iron that makes up a heme molecule. Correct Answers: Oxyhemoglobin is hemoglobin-carrying oxygen. Hemoglobin makes up 90% of dry weight of the red cell. Hemoglobin is composed of 2 pairs of polypeptide chains. Polypeptide chains contain iron that makes up a heme molecule. Response Feedback: Oxyhemoglobin is hemoglobin that is carrying oxygen molecules. Hemoglobin makes up about 90% of the dry weight of the red blood cell, and is composed of two pairs of polypeptide chains: the globins. Each globin has an attached heme molecule that is composed of iron plus a protoporphyrin molecule. There are 300, not 100, hemoglobin molecules per cell. Question 87 0 out of 0 points Which is a transport form for CO2 in the blood? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Dissolved gas As a bicarbonate ion Association with hemoglobin (Hgb) Correct Answers: Dissolved gas As a bicarbonate ion Association with hemoglobin (Hgb) Response Feedback: Carbon dioxide, a by-product of cellular metabolism, is transported in the blood as a dissolved gas, as a bicarbonate ion (HCO 3), and in association with hemoglobin (Hgb). Bivalent molecules are molecules formed from two or more atoms bound together as a single unit molecule. They are not a mechanism for transport of CO2 in the blood. Bone marrow is stimulated by a hormone growth factor called erythropoietin. It is not a mechanism for transport of CO2 in the blood. Question 88 0 out of 0 points A series of events occur during acute inflammation resulting from cellular injury. Which event occurs initially? Selected Answer: Phagocytosis results in pus formation Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Brief constriction of vessel walls Immediately after injury, the precapillary arterioles around the injured area contract briefly. When phagocytosis is incomplete, a collection of dead neutrophils, bacteria, and cellular debris, called pus, may form at the site. After edema formation, blood flows through areas of inflammation, causing neutrophils to move to the sides of the blood vessels and roll along the endothelium of the vessel wall. After vessel constrictions, the increased pressure along with increased permeability pushes fluid out of the blood vessels and into the surrounding tissue contributing to local swelling. Question 89 0 out of 0 points What stimulates the release of renin? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Renal hypoperfusion Parasympathetic activation Decreased sodium delivery Correct Answers: Renal hypoperfusion Sympathetic activation Decreased sodium delivery Response Feedback: Renal hypoperfusion, sympathetic activation, and decreased sodium delivery stimulate renin release. Increased heart rate and parasympathetic activation do not stimulate the release of renin. Question 90 0 out of 0 points A patient diagnosed with cancer presents with Cushing syndrome secondary to excessive adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion. This syndrome is described as Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Ionizing Paraneoplastic syndrome Response Feedback: Paraneoplastic syndromes are symptom complexes that cannot be explained by obvious tumor properties; they occur in 10% to 15% of patients with cancer. Many of these syndromes are associated with excessive hormone production. Ionizing is a form of cancer treatment (radiation). Hypercalcemia, an elevation of calcium ions, may occur as a result of this syndrome. Opportunistic infection is when the immune system is compromised and infections that are normally eliminated by the immune system cause infection. Question 91 0 out of 0 points If a patient has a recessive trait, what is the genotype of this patient? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: aa aa aa refers to the genotype that will produce a recessive characteristic. AA will produce the phenotype of the dominant gene. It takes only one dominant gene in the genotype to produce a phenotype that displays this dominant characteristic. Aa will produce the phenotype of the dominant gene. It takes only one dominant gene in the genotype to produce a phenotype that displays this dominant characteristic. aA will produce the phenotype of the dominant gene. It takes only one dominant gene in the genotype to produce a phenotype that displays this dominant characteristic. Question 92 0 out of 0 points Which retrovirus is believed to cause cancer? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Epstein-Barr virus Parvovirus Poxvirus Correct Answers: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Human T-lymphocyte virus type I Epstein-Barr virus Response Feedback: The HIV virus has been associated with Kaposi sarcoma. The human T-lymphocyte virus type I has been associated with T-cell leukemialymphoma. The Epstein-Barr virus has been associated with Burkitt lymphoma. Parvovirus results in fifth disease, a rash generally seen in children. Poxvirus is most commonly associated with diseases such as smallpox Question 93 0 out of 0 points When emphysema is a result of a α1-Antitrypsin disorder, assessment data is likely to include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Client age younger than 50 Elevated levels of α1-Antitrypsin Enzyme levels that are below normal Correct Answers: Client age younger than 50 No history of cigarette smoking Enzyme levels that are below normal Response Feedback: When emphysema occurs in young to middle-aged adults or before the age of 50 in a smoker, it may be associated with a deficiency of α1-antitrypsin activity in the lung. Cigarette smoking is not always a risk factor when this hereditary disorder is present. α1-Antitrypsin deficiency is a hereditary disorder characterized by low serum levels (25 to 50 mg/dl). Research does not currently support race as being a risk factor. α1-Antitrypsin deficiency is a hereditary disorder characterized by low serum levels (25 to 50 mg/dl). Question 94 0 out of 0 points Acute bronchitis can be caused by which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Influenza A Coxsackie virus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Staphylococcus pneumoniae Correct Answers: Influenza A Adenovirus Coxsackie virus Staphylococcus pneumoniae Response Feedback: Influenza A, adenovirus, Coxsackie virus, and Staphylococcus pneumoniae can cause acute bronchitis. Pseudomonas aeruginosa does not cause acute bronchitis. Question 95 0 out of 0 points Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is characterized by which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: Enlarged, painless lymph nodes Elevated granulocyte count Abdominal discomfort Weight loss Correct Answers: Elevated granulocyte count Abdominal discomfort Weight loss Response Feedback: Classic signs of CML include elevated granulocyte count, abdominal discomfort, and weight loss. Enlarged painless lymph nodes are seen with chronic lymphoid leukemia (CLL). Symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) are similar and cause bone pain. Question 96 0 out of 0 points The local warmth that occurs during an inflammatory response is the result of Selected Answer: Swelling Correct Answer: Increased blood flow Response Feedback: Because of the dilated blood vessels and open capillaries, more blood is carried to the injured area and contributes to the redness, pain, heat, and swelling of inflammation. While there may be effects on the vascular system resulting from cellular injury, it is more likely to affect vessel permeability. Leukocytosis is the recruitment and emigration of leukocytes that are focused on destroying possible pathogens. Swelling is one of the cardinal symptom of inflammation, but it is not responsible for local warmth at the injury site. Question 97 0 out of 0 points Lipid molecules cross cell membranes by Selected Answer: Using channel proteins as a membrane transport system Correct Answer: Diffusion Response Feedback: The plasma membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer that is impermeable to most water-soluble molecules, including ions, glucose, and amino acids, but permeable to lipid-soluble substances, such as oxygen and steroid hormones. Lipid-soluble molecules can directly cross the lipid bilayer of cell membranes by simple diffusion. Endocytosis is a process of cellular ingestion by which the plasma membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. Channel proteins are a form of active transport. Voltage-gated ion channels are activated by changes in electrical potential difference near the channel; these types of ion channels are especially critical in neurons, but are common in many types of cells. Question 98 0 out of 0 points When the cause of a disease is due to unintended or unwanted medical treatment, the term to describe this is Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Iatrogenic Iatrogenic Iatrogenic means that the cause was medical intervention. Genotype refers to the genetic inheritance for a condition. Idiopathic is when the cause of the condition is unknown. Ecogenetics is a struggle between genetic makeup and environment. Question 99 0 out of 0 points Which is a characteristic of cancer cells? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Poor differentiation Poor differentiation Cancer cells lose their differentiated features and contribute poorly or not at all to the function of their tissue. Cancer cells divide in an unpredictable manner. Cellular cohesiveness is lacking among cancer cells. Cancer cells do not reproduce uniformly in either size or shape. Question 100 0 out of 0 points Which enzyme is responsible for rapidly unwinding and separating the DNA strands? Selected Answer: Correct Answer: Response Feedback: Polymerase Helicase Helicase is responsible for unwinding the DNA. Polymerase binds the single strands of DNA so that they may be replicated. Telomerase is needed to help replicate the ends of the DNA fragments. The Okazaki fragments are backstitched in place by DNA ligase.