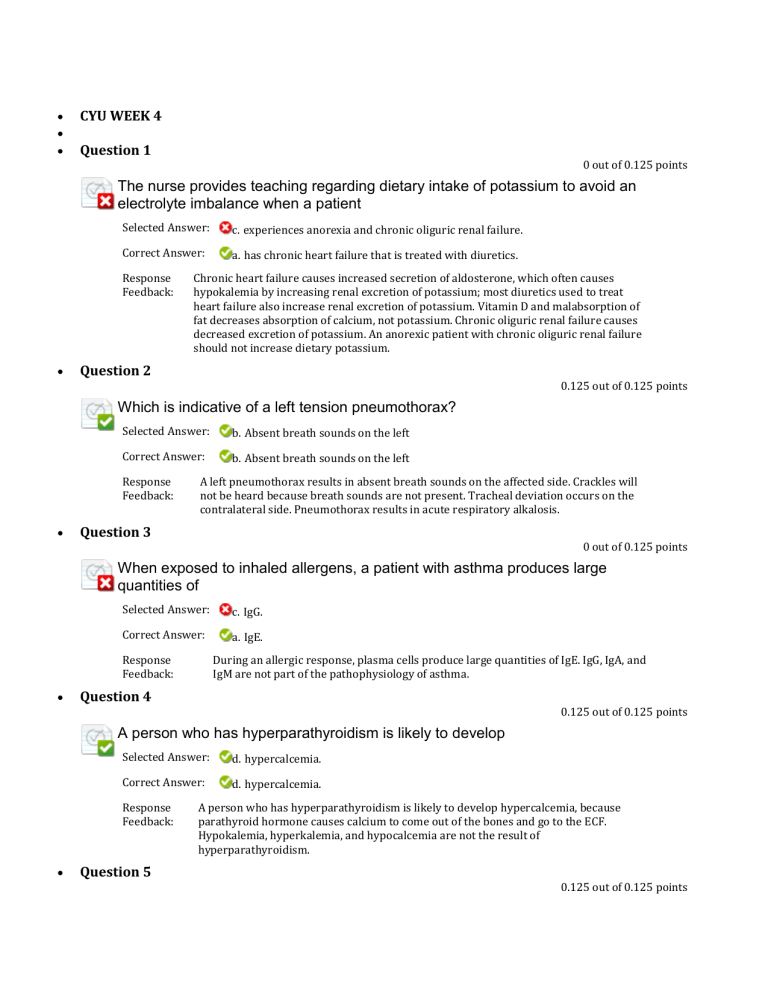
CYU WEEK 4 Question 1 0 out of 0.125 points The nurse provides teaching regarding dietary intake of potassium to avoid an electrolyte imbalance when a patient Selected Answer: c. experiences anorexia and chronic oliguric renal failure. Correct Answer: a. has chronic heart failure that is treated with diuretics. Response Feedback: Chronic heart failure causes increased secretion of aldosterone, which often causes hypokalemia by increasing renal excretion of potassium; most diuretics used to treat heart failure also increase renal excretion of potassium. Vitamin D and malabsorption of fat decreases absorption of calcium, not potassium. Chronic oliguric renal failure causes decreased excretion of potassium. An anorexic patient with chronic oliguric renal failure should not increase dietary potassium. Question 2 0.125 out of 0.125 points Which is indicative of a left tension pneumothorax? Selected Answer: b. Absent breath sounds on the left Correct Answer: b. Absent breath sounds on the left Response Feedback: A left pneumothorax results in absent breath sounds on the affected side. Crackles will not be heard because breath sounds are not present. Tracheal deviation occurs on the contralateral side. Pneumothorax results in acute respiratory alkalosis. Question 3 0 out of 0.125 points When exposed to inhaled allergens, a patient with asthma produces large quantities of Selected Answer: c. IgG. Correct Answer: a. IgE. Response Feedback: During an allergic response, plasma cells produce large quantities of IgE. IgG, IgA, and IgM are not part of the pathophysiology of asthma. Question 4 0.125 out of 0.125 points A person who has hyperparathyroidism is likely to develop Selected Answer: d. hypercalcemia. Correct Answer: d. hypercalcemia. Response Feedback: Question 5 A person who has hyperparathyroidism is likely to develop hypercalcemia, because parathyroid hormone causes calcium to come out of the bones and go to the ECF. Hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, and hypocalcemia are not the result of hyperparathyroidism. 0.125 out of 0.125 points Viral pneumonia is characterized by Selected Answer: a. a dry cough. Correct Answer: a. a dry cough. Response Feedback: No exudative fluids are produced. Viral pneumonia does not produce exudates, so the cough is non-productive. Ventilation-perfusion imbalance does not usually occur in viral pneumonia. Question 6 0.125 out of 0.125 points Pneumocystitis is a term that refers to a Selected Answer: b. fungal pneumonia secondary to HIV. Correct Answer: b. fungal pneumonia secondary to HIV. Response Feedback: Pneumocystitis is a fungal pneumonia secondary to HIV. Pneumocystitis is not a viral pneumonia found in transplant recipients, a non-infectious inflammation of the lung, or a pneumonia secondary to bladder infection. Question 7 0.125 out of 0.125 points Causes of hypomagnesemia include Selected Answer: d. chronic alcoholism. Correct Answer: d. chronic alcoholism. Response Feedback: Hypomagnesemia is common with chronic alcoholism. Hyperphosphatemia causes hypocalcemia. Oliguric renal failure and clinical dehydration reduce magnesium excretion. Question 8 0.125 out of 0.125 points Allergic (extrinsic) asthma is associated with Selected Answer: d. IgE-mediated airway inflammation. Correct Answer: d. IgE-mediated airway inflammation. Response Feedback: Extrinsic (allergic) asthma is mediated by IgE triggers. Allergic (extrinsic) asthma involves hyperresponsiveness of the airways. Antigens are the precipitating factors. Airway obstruction is reversible. Question 9 0.125 out of 0.125 points Abnormalities in intracellular regulation of enzyme activity and cellular production of ATP are associated with Selected Answer: d. hypophosphatemia. Correct Answer: d. hypophosphatemia. Response Feedback: Question 10 Phosphate is an important component of ATP. Hypophosphatemia results in decreased ATP to cells. Hyponatremia, hypocalcemia, and hypokalemia do not affect ATP production. 0.125 out of 0.125 points Which electrolyte imbalances cause increased neuromuscular excitability? Selected Answer: b. Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia Correct Answer: b. Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia Response Feedback: Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia both cause increased neuromuscular excitability. Hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hypophosphatemia, hypercalcemia, and hypermagnesemia do not cause increased neuromuscular excitability. Question 11 0.125 out of 0.125 points A patient diagnosed with chronic compensated heart failure reports that, “My feet swell if I eat salt but I don’t understand why” The nurse’s best response is Selected Answer: c. “Salt holds water in your blood and makes more pressure against your blood vessels, so fluid leaks out into your tissues and makes them swell.” Correct Answer: c. “Salt holds water in your blood and makes more pressure against your blood vessels, so fluid leaks out into your tissues and makes them swell.” Response Feedback: Salt holds water in the ECV, thus increasing capillary hydrostatic pressure. Gravity leads to feet swelling, but it does not explain what the patient is asking. Salt does not cause vasodilation, nor does it bind to blood proteins and change osmotic pressure. Question 12 0.125 out of 0.125 points Which assessment would support a diagnosis of type A COPD rather than type B COPD Selected Answer: d. Normal PaCO 2, scant sputum, accessory muscle use, barrel chest Correct Answer: d. Normal PaCO2, scant sputum, accessory muscle use, barrel chest Response Feedback: Barrel chest and obvious respiratory effort that maintains near normal blood gases are consistent with type A COPD in the early stages. Copious sputum, dyspnea, and cor pulmonale are consistent with type B COPD. Noisy breath sounds, fatigue, high PaCO 2, and overweight are consistent with type B COPD. Barrel chest, productive cough, cyanosis, and very decreased PaO 2 are not consistent with type A COPD. Question 13 Excessive antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion can cause _____ concentration. 0.125 out of 0.125 points Selected Answer: b. decreased serum sodium Correct Answer: b. decreased serum sodium Response Feedback: Excessive ADH stimulates excessive water reabsorption by the kidneys, which dilutes the blood, thus decreasing the serum sodium concentration. Excessive ADH secretion does not cause increased serum sodium or potassium concentrations, or decreased serum potassium concentration. Question 14 0 out of 0.125 points Which is true about epiglottitis? ( Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: c. Is characterized by pain with swallowing d. Can be caused by bacterial infection e. Usually occurs in children Correct Answers: a. Is usually caused by H. influenzae type B c. Is characterized by pain with swallowing d. Can be caused by bacterial infection e. Usually occurs in children Response Feedback: Epiglottitis is usually caused by H. influenzae type B, but can be caused by bacteria. It usually occurs in children and is characterized by pain with swallowing. This condition is a medical emergency and requires immediate intervention. Question 15 0.125 out of 0.125 points The characteristic x-ray findings in tuberculosis include Selected Answer: a. Ghon tubercles. Correct Answer: a. Ghon tubercles. Response Feedback: Tuberculosis results in Ghon tubercles that show up as nodules with infiltrates. Diffuse white-out, basilar infiltrates, and tracheal deviation are not characteristic x-ray findings in tuberculosis. Question 16 0.125 out of 0.125 points What is likely to lead to hyponatremia? Selected Answer: b. Frequent nasogastric tube irrigation with water Correct Answer: b. Frequent nasogastric tube irrigation with water Response Feedback: Question 17 Sodium is lost from gastric secretions when nasogastric tubes are irrigated with water. The sodium diffuses into the irrigating water and is then lost when the aspirate is withdrawn. Excessive ADH would lead to hyponatremia by retention of water in the body, thus diluting the sodium. Excess aldosterone would increase serum sodium. Normal saline is an isotonic solution and will not alter the serum sodium. 0.125 out of 0.125 points All obstructive pulmonary disorders are characterized by Selected Answer: b. resistance to airflow. Correct Answer: b. resistance to airflow. Response Feedback: Obstructive lung diseases are characterized by increased resistance to airflow. Only asthma is characterized by hyperresponsiveness. Increased residual volume is common in obstructive pulmonary disorders. Emphysema is characterized by increased lung compliance caused by a loss of alveoli and elastic tissue. Question 18 0.125 out of 0.125 points Clinical manifestations of severe symptomatic hypophosphatemia are caused by Selected Answer: a. deficiency of ATP. Correct Answer: a. deficiency of ATP. Response Feedback: Clinical manifestations of severe symptomatic hypophosphatemia are caused by a deficiency of ATP. Phosphate is an important component of ATP, which is the major source of energy for many cellular substances. Severe symptomatic hypophosphatemia does not cause excess protein accumulation, damage the kidneys, or cause hypocalcemia. Question 19 0.125 out of 0.125 points The primary cause of infant respiratory distress syndrome is Selected Answer: c. lack of surfactant. Correct Answer: c. lack of surfactant. Response Feedback: The primary cause of this disorder is lack of surfactant. While premature infants may demonstrate this disorder, the actual cause is lack of surfactant. It is a syndrome seen in premature infants. Maternal illegal drug use during pregnancy and umbilical cord compression are not the primary causes of infant respiratory distress syndrome. Question 20 0.125 out of 0.125 points What age group has a larger volume of extracellular fluid than intracellular fluid? Selected Answer: b. Infants Correct Answer: b. Infants Response Feedback: Question 21 Infants have a larger volume of extracellular fluid than intracellular fluid. Adolescents, young adults, and older adults have a larger volume of intracellular fluid than extracellular fluid. 0.125 out of 0.125 points When a parent asks how they will know if their 2-month-old baby, who is throwing up and has frequent diarrhea, is dehydrated, the nurse’s best response is Selected Answer: b. “If the soft spot on the top of his head feels sunken in and his mouth is dry between his cheek and his gums, then he is probably dehydrated.” Correct Answer: b. “If the soft spot on the top of his head feels sunken in and his mouth is dry between his cheek and his gums, then he is probably dehydrated.” Response Feedback: Checking whether the head feels sunken and the mouth is dry between check and gums are useful assessments of ECV deficit in an infant, which is an important part of clinical dehydration. It is true that clinical dehydration is the combination of extracellular fluid volume deficit and hypernatremia, but it does not address the question Mr. Worry is asking. Although the diaper information provides a useful assessment, neck veins are not a reliable assessment in an infant. Drowsiness and fatigue are not reliable assessments for dehydration. Question 22 0.125 out of 0.125 points When a parent of a toddler recently diagnosed with pneumococcal pneumonia asks why their child is so much sicker than a classmate was when they were diagnosed with pneumonia, the nurse replies Selected Answer: c. “It sounds like your child has a case of bacterial pneumonia, while the classmate had viral pneumonia.” Correct Answer: c. “It sounds like your child has a case of bacterial pneumonia, while the classmate had viral pneumonia.” Response Feedback: Viral pneumonia does not produce exudate so the cough is non-productive. In general, symptoms of viral pneumonia are less severe than those of bacterial pneumonia. The uncle’s case of viral pneumonia has less acute symptoms than the children’s case of bacterial pneumonia. Pneumococcal pneumonia is not necessarily more severe in children. The children most likely have bacterial pneumonia, which is why their symptoms are more acute than the classmate’s case of viral pneumonia. Question 23 0.125 out of 0.125 points Clinical manifestations of hyponatremia include Selected Answer: a. confusion, lethargy, coma, and perhaps seizures. Correct Answer: a. confusion, lethargy, coma, and perhaps seizures. Response Feedback: Clinical manifestations of hyponatremia include confusion, lethargy, coma, and perhaps seizures, as they are manifestations of CNS dysfunction. Weak pulse, low blood pressure, and increased heart rate are characteristic of clinical dehydration. Hyponatremia does not cause thirst, dry mucous membranes, and diarrhea. Cardiac dysrhythmias, paresthesias, and muscle weakness are manifestations of electrolyte imbalances. Question 24 0.125 out of 0.125 points A major risk factor for the development of active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) disease is Selected Answer: a. immunosuppression. Correct Answer: a. immunosuppression. Response Feedback: Immunosuppressed individuals, such as those with HIV, are at high risk for active TB disease. Contaminated water and gender are not major risk factors for pulmonary tuberculosis. Excessive use of antibiotics can lead to opportunistic yeast and fungal infections or cause bacterial resistance to available antibiotics, but it is not a major risk factor for TB. Question 25 0.125 out of 0.125 points The imbalance that occurs with oliguric renal failure is Selected Answer: a. hyperkalemia. Correct Answer: a. hyperkalemia. Response Feedback: Oliguric renal failure decreases potassium excretion, which causes hyperkalemia. Oliguric renal failure decreases acid excretion and causes metabolic acidosis (not alkalosis). Oliguric renal failure does not cause hypokalemia or hypophosphatemia. Question 26 0.125 out of 0.125 points Which alterations can lead to edema? Selected Answer: b. Decreased lymphatic flow Correct Answer: b. Decreased lymphatic flow Response Feedback: Lymphatic obstruction prevents the drainage of accumulated interstitial fluid and proteins, which can lead to severe edema. Decreased capillary hydrostatic pressure would push less fluid into the interstitial space. Increased capillary colloid osmotic pressure would remove fluid from the interstitial space. Decreased capillary membrane permeability would allow less fluid movement into the interstitial space. Question 27 0.125 out of 0.125 points A patient exhibiting respiratory distress as well as a tracheal shift should be evaluated for Selected Answer: a. pneumothorax. Correct Answer: a. pneumothorax. Response Feedback: Pneumothorax leads to a tracheal shift to the side opposite the pneumothorax. Pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pulmonary embolus do not lead to tracheal shift. Question 28 0.125 out of 0.125 points The fraction of total body water (TBW) volume contained in the intracellular space in adults is Selected Answer: a. two thirds. Correct Answer: a. two thirds. Response Feedback: Approximately two thirds of TBW is contained inside the cells. Two thirds, not three fourths, of TBW is contained inside the cells. Two thirds, not one-half, of TBW is contained inside the cells. One-third of the TBW is extracellular in adults. Question 29 Signs and symptoms of clinical dehydration include 0.125 out of 0.125 points Selected Answer: b. decreased urine output. Correct Answer: b. decreased urine output. Response Feedback: One clinical manifestation of dehydration is decreased urine output. Skin turgor and blood pressure decrease in clinical dehydration. Heart rate increases in clinical dehydration. Question 30 0.125 out of 0.125 points Airway obstruction in chronic bronchitis is because of Selected Answer: a. thick mucus, fibrosis, and smooth muscle hypertrophy. Correct Answer: a. thick mucus, fibrosis, and smooth muscle hypertrophy. Response Feedback: Airway obstruction in chronic bronchitis is as a result of thick mucus, fibrosis, and smooth muscle hypertrophy. Loss of alveolar elastin, pulmonary edema, and hyperplasia and deformation of bronchial cartilage are not part of the pathophysiology of chronic bronchitis. Question 31 0 out of 0.125 points The inward-pulling force of particles in the vascular fluid is called _____ pressure. Selected Answer: d. interstitial osmotic Correct Answer: b. capillary osmotic Response Feedback: Capillary osmotic pressure is the inward-pulling force of particles in the vascular fluid. Capillary hydrostatic pressure is an outward-pulling. The question pertains to vascular fluid rather than interstitial fluid. Interstitial hydrostatic pressure is an outward-pulling force. Question 32 0.125 out of 0.125 points Air that enters the pleural space during inspiration but is unable to exit during expiration creates a condition called Selected Answer: c. tension pneumothorax. Correct Answer: c. tension pneumothorax. Response Feedback: Air that enters the pleural space during inspiration but is unable to exit during expiration causes a tension pneumothorax. The question does not describe open pneumothorax, pleural effusion, or empyema. Question 33 0.125 out of 0.125 points The electrolyte that has a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid than in the intracellular fluid is _____ ions. Selected Answer: d. sodium Correct Answer: d. sodium Response Feedback: Extracellular fluid has a higher sodium ion concentration than does intracellular fluid. Intracellular fluid has a higher phosphate, magnesium, and potassium ion concentration than does extracellular fluid. Question 34 0.125 out of 0.125 points After evaluation, a child’s asthma is characterized as “extrinsic.” This means that the asthma is Selected Answer: a. associated with specific allergic triggers. Correct Answer: a. associated with specific allergic triggers. Response Feedback: Extrinsic asthma is also referred to as allergic asthma, which is triggered by antigens. The underlying pathogenesis of extrinsic asthma is an allergic in nature. Intrinsic asthma is associated with respiratory infections. Intrinsic asthma is associated with psychological factors. Question 35 0.125 out of 0.125 points The hypersecretion of mucus resulting for chronic bronchitis is the result of Selected Answer: a. recurrent infection. Correct Answer: a. recurrent infection. Response Feedback: Mucus provides a hospitable environment for bacterial colonization and recurrent infection. Destruction of alveolar septa and reduced inflammation are not complications of chronic bronchitis. Hypersecretion of mucus does not contribute to barrel chest. Question 36 0.125 out of 0.125 points Chronic occupational lung disease is characterized by ( Select all that apply.) Selected Answers: b. a progressive cough and dyspnea with exercise. c. causation from long-term inhalation of inorganic material. d. possible negative chest x-ray when symptom-free. e. a latent period before symptoms occur. Correct Answers: b. a progressive cough and dyspnea with exercise. c. causation from long-term inhalation of inorganic material. d. possible negative chest x-ray when symptom-free. e. a latent period before symptoms occur. Response Feedback: Chronic occupational lung disease is caused by long-term inhalation of inorganic material. A latent period of 10 to 20 years may ensue before symptoms occur. One of the earliest manifestations is a progressive cough and dyspnea on exertion. The disease cannot be ruled out by a negative chest x-ray. Impairment of macrophage function is the primary mechanism through which inorganic particles initiate lung disease. Question 37 0.125 out of 0.125 points Decreased neuromuscular excitability is often the result of Selected Answer: b. hypercalcemia and hypermagnesemia. Correct Answer: Response Feedback: b. hypercalcemia and hypermagnesemia. Hypercalcemia and hypermagnesemia result in decreased neuromuscular excitability. Hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia result in increased neuromuscular excitability. Question 38 0.125 out of 0.125 points Osmoreceptors located in the hypothalamus control the release of Selected Answer: c. vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH). Correct Answer: c. vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH). Response Feedback: Factors that increase secretion of ADH into the blood include increased osmolality of the blood, which is sensed by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. Release of angiotensin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and aldosterone is not controlled by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus. Question 39 0.125 out of 0.125 points How is a patient hospitalized with a malignant tumor that secretes parathyroid hormone–related peptide monitored for the resulting electrolyte imbalance? Selected Answer: a. Serum calcium, bowel function, level of consciousness Correct Answer: a. Serum calcium, bowel function, level of consciousness Response Feedback: Question 40 Parathyroid hormone increases the plasma calcium concentration, and constipation and lethargy are manifestations of hypercalcemia. Parathyroid hormone increases the plasma calcium concentration, but these are signs of increased neuromuscular excitability, which occurs with hypocalcemia. Parathyroid hormone affects plasma concentration of calcium, not potassium. 0.125 out of 0.125 points The assessment findings of a 5-year-old with a history of asthma include extreme shortness of breath, nasal flaring, coughing, pulsus paradoxus, and use of accessory respiratory muscles. There is no wheezing and the chest is silent in many areas. How should you interpret your assessment? Selected Answer: c. The child may be having such a severe asthma episode that the airways are closed, so start oxygen and get the doctor immediately. Correct Answer: c. The child may be having such a severe asthma episode that the airways are closed, so start oxygen and get the doctor immediately. Response Feedback: The airway inflammation, edema, and bronchoconstriction of acute asthma may occlude small airways completely, so that no air is moving, which requires emergency intervention. Alicia has a history of asthma rather than pneumonia. Asthma can occur without wheezing. This is an emergency situation that requires you to start oxygen and notify the physician.