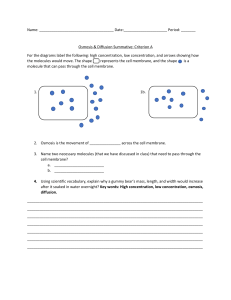
Cell Transport Notes _________________ – When the particles of one substance are uniformly distributed in another substance. ___________________ – A substance that can dissolve another substance. ___________________ – A substance that is dissolved in a solvent. Molecular Movement All the substances important to life are usually part of a solution. The solvent makes up the ______________________ of this solution. (REMEMBER: the substance dissolved in the solvent is the solute.) ________________________ is the solvent of most solutions involved in cellular activities. Molecules of matter are in constant motion. In liquids and gasses, molecular motion is ____________________________. The constant random movement of molecules is _______________________________________. Diffusion ______________________ is the process by which molecules of a substance move from areas of _______________ concentration to areas of ______________ concentrations. (Ex: movement of materials in and out of a cell across the membrane.) The diffusion of water is called __________________. When describing diffusion into and out of a cell or organelle, the movement of molecules occurs across a ___________________________________________ The difference in the concentration of molecules from the highest concentration to the lowest concentration is the _______________________ Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate 1. concentration (higher = ____________________) 2. _________________________________ 3. pressure (warmer = faster) (__________________________________ = faster) Diffusion Across Membranes Characteristics of Cell Membranes Cell membranes are selectively permeable, which means that they only allow certain things to enter and leave the cell. The cell membrane is composed of: 1. Two layers of _______________________________ 2. Proteins 3. __________________________________ 4. Carbohydrate chains Fluid Mosaic Model Lipids are fluid so some of the proteins move about within the lipid layers. Osmosis and Living Cells _________________________ is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Water makes up 70-95% of a living cell, so osmosis is a very important transport mechanism. The cell has ______________________ over osmosis. Water will move in and out until the concentration is equal on both sides of the _______________ Types of Solutions Isotonic Solution = the concentration of solutes outside of the cell is _____________________________of the cell. Ex: Red blood cell placed in an isotonic solution would ___________________ in size. Hypotonic Solution = the concentration of solutes outside the cell ____________________ inside of the cell. Ex: Red blood cell placed in a hypotonic solution would __________________. Hypertonic Solution = The concentration of solutes outside the cell ____________________ inside of the cell. Ex: Red blood cell placed in a hypertonic solution would ___________________. “iso” = equal “hypo” = less than “hyper” = more than Other means of transport: Osmosis and diffusion are __________________ _________________ because they do not use any energy to move materials across the membrane. -Sometimes movement of materials requires assistance from the cell or needs energy. (2 types) Carrier and channel proteins- part of the cell membrane and transport ____________ molecules that cannot dissolve in the lipids of the cell membrane, IF: NO Energy is required called Facilitated diffusion-substances move with the concentration gradient from high to low, but carrier molecules ___________ ______ the movement of diffusing substances. ENERGY IS REQUIRED is called ________________ _______________, the movement of materials from low to high across the concentration gradient.