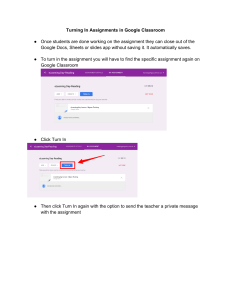
Thank you for downloading the Exploring Social Studies Digital Interactive Notebook! If you’re a pro at using Google Drive, click on the link below. If you would like to read more instructions, please keep reading this PDF! Thanks so much! Make history come alive in a new way https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1340sb nfsZbpWwIlJSeq0NqSnfhLldhDWHP1Hcop8WJ4/ copy P.S. The answer key is in this PDF. Just scroll down! ©The Teacher’s Prep What you need to get started: 1. Download Link for the Google Slide Product Link: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1340sbnfsZbpWwIlJSeq0N qSnfhLldhDWHP1Hcop8WJ4/copy 2. Have access to the Internet and a Google Account. (FREE) 3. Open the file on your own Google Drive and engage while in the edit mode. 4. Printer access to print out the finished product. (OPTIONAL) Begin your Google Slides Project: If you haven’t created a free Google account, you will need to do that before beginning the project. Each student will need their own account if they will be working on their own interactive notebook using Google Slides. Before you begin editing/filling in your digital notebook project, it is VERY important to first save a copy of the file, on your own Google Drive, and then edit the copy. You do not want to edit the original file. The slides are 8.5x11. The slides have a text box for you to highlight over and begin writing your text. Your students can add their own text boxes, too. Share the file with each of the students in your classroom and let the learning begin! P.S. The answer key is in this PDF. Just scroll down! Teacher Notes These Teacher Notes offer a guide for how to use these graphic organizers. Vocabulary 1. Chronology – the order in which events happen 2. Timeline – used to track events by date in chronological order 3. B.C.E. or B.C. – “before common era” or “before Christ” – these refer to the years before the birth of Jesus in the Gregorian calendar. 4. C.E. or A.D. – “common era” or “anno domini” – these refer to the years after the birth of Jesus in the Gregorian calendar. 5. Point of View – a personal attitude or opinion about a subject 6. Bias – a personal preference or belief about a person, event, etc. Analyzing Sources Primary Source: a primary source is a source that originated at the time an event took place or was written by someone who experienced the event. Examples: letters, speeches, photographs, film footage, architecture, diaries, government records. Secondary Source: a source created after an event has taken place. Examples: textbooks, biographies, encyclopedias, history books. Measuring Time 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Decade – a period of 10 years Century – a period of 100 years Millennium – a period of 1,000 years Period – similar to era, a large division of time Era – a large division of time, usually larger than a period. ©The Teacher’s Prep Teacher Notes Branches of History Anthropology: the study of human culture. Anthropologists study how humans adapt to their environment, how they interact with one another, and how they communicate, among other areas of human behavior. Economics: the study of how people and nations make choices about how to use the resources available them. It also refers to how society functions in reference to what is produced, how it’s produced, and for whom it’s produced. Archaeology: the study of objects, buildings, etc. left behind by people. Archaeologists dig in search of these objects to discover how people lived. Archaeologists find pottery fragments, building supplies, jewelry, weapons, bones, shells, etc. Sociology: the study of social behavior, or how people interact with each other. Elements of Geography The World in Spatial Terms: Where is a place located? Geographers use absolute location and relative location to locate places. Absolute location is the exact spot of a location on Earth using latitude and longitude coordinates. Relative location is the location of a place compared to the location of other places. Places and Regions: What are the characteristics of an area? These include physical features and human features (language, religion, architecture, etc.). A region is a group of places that share a set of common features. ©The Teacher’s Prep Teacher Notes Physical Systems: What physical systems can be found in an area? These include ecosystems, weather, physical features, and forces that create and alter Earth’s physical features. People’s lives are affected by these physical systems (types of shelter, types of food available, types of jobs, etc.) Human Systems: What do humans create or build in their environment? Human systems refer to culture, shelters, movement of people from place to place, economies, etc. Environment and Society: How do people alter the environment around them? For example, people build roads, cities, and homes. They use natural resources to create energy (hydroelectric power, for example). It’s also the study of how the environment is impacted by human actions. The Uses of Geography: How do people use the study of geography? Calendars Julian Calendar: This type of calendar was developed by Julius Caesar. It started counting dates based on the founding of Rome. At 365 ¼ days long, the Julian calendar faced challenges in accuracy. Every year, several minutes were lost, leading to a loss of a day every 128 years. As the years went by, that day added up. People realized a new calendar was needed. Gregorian Calendar: In 1582 C.E., Pope Gregory XIII started a new calendar. He began counting years from the birth of Jesus. To solve the problem of losing days, he designed the calendar so that only years divisible by 400 would be a leap year. ©The Teacher’s Prep Teacher Notes The Five Themes of Geography Location – Where a place is located. (See absolute and relative location description in the “Elements of Geography” section) Place – What are the characteristics of the place? This includes physical features (mountains, valleys, coastlines) and human features (cities, roads, homes, etc.) Regions – Places that share common characteristics. For example, some cities share common features (coasts, businesses, architecture) if they are all situated along the northeast coast. Movement – Why did people move to that area? What reasons led them to settle in a particular region? (Access to housing, food sources, and jobs are possible answers) Human-Environment Interaction – How have people changed their environment to suit their needs? How has the environment been impacted by people’s actions? Types of Maps Physical Map – a map that shows landforms and waterways Political Map – a map that shows the political boundaries of cities, states, countries, etc. Population Density Map – a map that shows the number of people who live in specific geographic locations. Climate Map – a map that shows the weather patterns of locations on Earth. ©The Teacher’s Prep Terms of Use The purchase of this Google Slides product by The Teacher’s Prep gives the user permission to use it with every student in their classroom. This resource may not be copied and distributed outside of your classroom. This resource may not be uploaded to the internet or stored in a location where others outside of your own classroom can access it. If you have any questions related to licensing, please contact The Teacher’s Prep at theteachersprep@gmail.com. Credits: Teresa Lewis ©The Teacher’s Prep