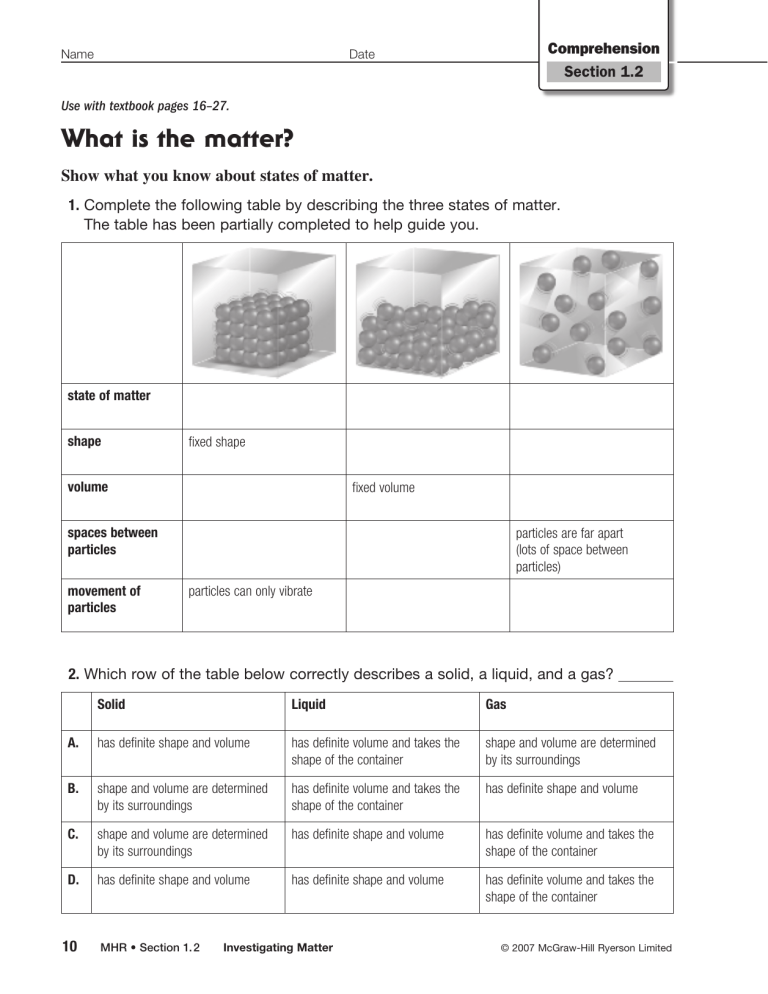
Name Comprehension Section 1.2 Date Use with textbook pages 16–27. What is the matter? Show what you know about states of matter. 1. Complete the following table by describing the three states of matter. The table has been partially completed to help guide you. state of matter shape fixed shape volume fixed volume spaces between particles movement of particles particles are far apart (lots of space between particles) particles can only vibrate 2. Which row of the table below correctly describes a solid, a liquid, and a gas? Solid Liquid Gas A. has definite shape and volume has definite volume and takes the shape of the container shape and volume are determined by its surroundings B. shape and volume are determined by its surroundings has definite volume and takes the shape of the container has definite shape and volume C. shape and volume are determined by its surroundings has definite shape and volume has definite volume and takes the shape of the container D. has definite shape and volume has definite shape and volume has definite volume and takes the shape of the container 10 MHR • Section 1. 2 Investigating Matter © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Name Cloze Activity Section 1.2 Date Use with textbook pages 16–27. Matter all around us Vocabulary boiling point change of state conductivity density elements gas heat kinetic liquid mass matter melting point movement particles properties solid states volume Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once. You will not need to use every term. 1. is anything that has mass and volume. According to the kinetic molecular theory, all matter is made of very small that are constantly moving. 2. is the amount of matter in an object. The amount of space an object occupies is its . The ratio of a material’s mass to its volume is its . 3. There are three these can change when of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Each of is added or removed. 4. The temperature at which ice turns to water is the The temperature at which water turns to water vapour is the 5. . . describes how easily electricity or heat can move through a material. 6. energy is the energy of movement. 7. Particles of a are packed so tightly together that they can only vibrate in place. Particles of a are farther apart and can slide past each other. Particles of a are very far apart and move around freely and quickly. 8. The kinetic molecular theory describes what happens to the particles of matter during a . 9. Oxygen and gold are examples of broken down or separated into simpler substances. © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.2 , which cannot be Investigating Matter • MHR 11 Name Analyzing Information Section 1.2 Date Use with textbook pages 19–20. Changes of state in gold Use the graph to help you answer the questions that follow. Temperature I gaseous gold IV II liquid gold III solid gold Energy 1. What do points I, II, III, and IV on the graph shown above represent? 2. What is removed from gaseous gold to cause it to change to a liquid? 3. What change of state occurs at point I on the graph? 4. What change of state occurs at point II on the graph? 5. What is added to solid gold to cause it to change to a liquid? 6. What happens to the temperature as solid gold turns to a liquid? 7. Describe the change in the kinetic energy as the temperature increases. 8. Describe the change in the arrangement of the gold particles as heat energy is added. 12 MHR • Section 1. 2 Investigating Matter © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Name Assessment Section 1.2 Date Use with textbook pages 16–27. C. II and III only Investigating matter D. I, II, and III Match each Term on the left with the best Descriptor on the right. Each Descriptor may be used only once. Term Descriptor 1. volume 2. density 3. state 4. conductivity 5. element A. amount of mass in a certain volume of a substance B. amount of matter in a substance or an object C. cannot be broken down into simpler substances D. amount of space that a substance or object takes up E. measure of how easily electricity or heat can pass through F. can be solid, liquid, or gas Circle the letter of the best answer. 6. Which of the following describes mass? A. state of matter B. anything with mass and volume C. amount of matter in an object D. amount of space that an object occupies 7. Which of the following are the main points of the kinetic molecular theory? 8. Which of the following describes what happens when heat is added to a substance? A. Particles lose kinetic energy and vibrate faster. B. Particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate faster. C. Particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate slower. D. Particles lose kinetic energy and vibrate slower. 9. Which of the following changes of state require the removal of heat? I. melting II. boiling A. I only B. II only C. both I and II D. neither I nor II 10. Which of the following is the temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid? A. boiling point B. melting point C. both A and B D. neither A nor B 11. Which of the following is the temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas? I. Particles are constantly moving. II. All matter is made up of very small particles. A. boiling point III. There are empty spaces between particles in a substance. B. melting point A. I and II only C. both A and B D. neither A nor B B. I and III only © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.2 Investigating Matter • MHR 13 Name Vocabulary Section 1.3 Date Use with textbook pages 28–33. Atomic structure 1. Use the vocabulary terms that follow to label the parts of an atom. Place the correct term on the line next to each part of the atom. You will not need to use all the terms. ● ● ● atom proton nucleus ● ● ● neutron electron shell (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. Complete the following table describing the three subatomic particles. Proton Neutron Electron electric charge location in the atom 16 MHR • Section 1. 3 Atomic Theory © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Name Cloze Activity Section 1.3 Date Use with textbook pages 28–33. The atom Vocabulary neutrons positive protons shells subatomic particles Rutherford Thomson Bohr Dalton electrons energy mass negative neutral Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. You can use each term more than once. You will not need to use every term. 1. suggested that matter is made up of atoms. 2. proposed that atoms contain negatively charged . particles later called 3. discovered the nucleus and its subatomic particles. He suggested that the nucleus was made up of positively charged particles called and particles with no charge called . 4. proposed that electrons are located in around the nucleus. 5. Electrons have different amounts of and forth between the energy levels. and can jump back 6. All atoms are made up of three neutrons. 7. Protons have a : protons, electrons, and charge, electrons have a charge, and have no electric charge. 8. and cluster together to form the nucleus of an atom. © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.3 Atomic Theory • MHR 17 Name Date Comprehension Section 1.3 Use with textbook pages 28–33. Contributions to atomic theory Scientist Bohr Dalton Rutherford Thomson Match each scientist to the statements describing his contribution to the atomic theory. Identify who was the first to propose these ideas. Each scientist may be used more than once. 1. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or divided into smaller particles. 2. Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells. 3. Most of the mass of the atom is in the tiny, dense, positively charged nucleus. 4. Most of the atom is empty space. 5. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. 6. All atoms of the same element are identical. 7. Atoms contain negatively charged particles. 8. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and particles with no electric charge called neutrons. 9. Different elements combine together to form compounds. 10. Electrons move around a central nucleus. 18 MHR • Section 1. 3 Atomic Theory © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Name Assessment Section 1.3 Date Use with textbook pages 28–33. Atomic theory Use the following diagram of an atom to answer questions 8 and 9. I Match each Descriptor on the left with the corresponding Scientist on the right. Each Scientist may be used more than once. Descriptor Scientist 1. A. Bohr B. Dalton C. Rutherford D. Thomson discovered the nucleus 2. suggested that all matter is made of atoms 3. proposed the “raisin bun” model of the atom 4. observed streams of negatively charged particles in gas discharge tubes 5. proposed that electrons exist in energy levels Circle the letter of the best answer. 6. Which of the following was not part of Dalton’s atomic theory? A. All matter is made of small particles called atoms. II III 8. Which of the following is the structure labelled II in the diagram? A. atom B. proton C. neutron D. electron 9. Which of the following exists in energy levels? A. I only B. II only C. III only D. II and III only 10. What is the electrical charge of the nucleus of an atom? A. neutral charge B. Atoms can be created or destroyed. B. positive charge C. Atoms of the same element are identical. C. negative charge D. Atoms of one element are different from the atoms of other elements. D. It depends on the element 7. Which of the following was not part of Rutherford’s atomic theory? A. Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in electrons. 11. The nucleus of the atom contains which of the following subatomic particles? A. electron B. proton and neutron B. Most of the atom is empty space. C. proton and electron C. The nucleus is the tiny, dense, central core of the atom. D. proton, neutron, and electron D. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. © 2007 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Section 1.3 Atomic Theory • MHR 19





