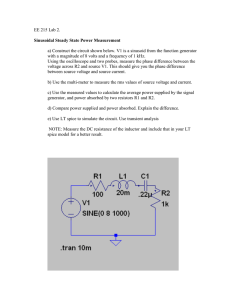
St. JOSEPH’S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Chennai -600 119 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE6009 – Power Electronics for Renewable Energy Systems MCQ with answer 1. Which of the following is a non-conventional energy source? a. Fuel cell and gas b. Petroleum and coal c. Natural gas and solar energy d. Wind energy and fuel cell 2. What is the percentage of carbon in bituminous coal a. 40 % to 60% b. 60% to 70% c. 40% to 80% d. 50% to 60% 3. Which of the following is not a fossil fuel? a. Nuclear energy b. Coal c. Oil d. Natural gas 4. The --------- is a mixture of hydrocarbon with alkanes, and sometimes a small percentage of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, or helium. a. Natural gas b. Crude oil c. antharacite d. petroelum 5. Greenhouse gas is a combination of a. Carbon-dioxide, methane and nitrogen. b. Carbon-dioxide, methane and water vapour c. methane, oxygen and water vapour d. hydrogen, oxygen and carbon-dioxide 6. The greenhouse gases that has no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerants, and electrical insulators.They are: a. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HCFCs), bromofluorocarbons (halons) b.chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), formaldehyde c.chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), acetaldehyde d. chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), acetyl-chloride. 7. The process or phenomena of radiation absorbed by the atmosphere and re-radiated towards the surface of the earth is called a. Formation of smoke and fog b. Newton effect c. Green house effect d. Darwin effect 8. What does deforestation cause to the environment? a. Gives fresh oxygen b. leads to green-house effect c. pure water is produced d. Increases rainfall 9. The most abundantly found in greenhouse gas is a. Methane b. Carbon di-oxide c. Water vapour d. Hydrogen 10. Greenhouse gases interact with what type of energy to create green house effect? a. Solar and wind b. Wind and geo-thermal c. Solar d. None of the above 11. Methanol is a. three parts hydrogen, one part oxygen and one part carbon. b.four parts hydrogen, one part oxygen and one part carbon. c. four parts hydrogen, two part oxygen and one part carbon d. four parts hydrogen, three part oxygen and one part carbon. 12. The materials used for making solar cell is a. Germanium and traces of silicon b. Silicon and traces of germanium c. Only silicon d. Silicon and germanium in equal proportion 13. The diode equation in a solar cell is given by a. I = Is (eqV/kT-1) - Is b.I = Is (eqV/kT-1) - Iph c. I = Is (eqV/kT-1) – ID d. I = Is (eqV/kT-1) – I0 14. The energy that has been derived from earth’s natural resources and that are not finite and non-exhaustible is a. Non- conventional energy or renewable energy b. conventional energy or renewable energy c. Non-conventional or non-renewable energy d. All of the above 15. The output of a Photo-voltaic cell is a. AC converted to DC b. DC converted to AC c. Only DC d. None of the above 16. The efficiency of the solar cells is a. 30% b. 40% c. 15% d. 60% 17. Select the incorrect statement from the following option. a) Fuel cells have high efficiency b) The emission levels of fuel cells are far below the permissible limits c) Fuel cells are modular d) The noise levels of fuel cells are high 18. The main components of a solar collector are a. a translucent cover, tubes which carry a coolant and an insulated back plate b. an optical cover, tubes which carry a coolant and an insulated back plate c. a transparent cover, tubes which carry a coolant and an insulated back plate d. an opaque cover, tubes which carry a coolant and an insulated back plate 19. The wind power is given by the relation a. P = ½ ρAV5 b. P = ½ ρAV2 c. P = ½ ρAV d. P = ½ ρAV3 20. Which generator coupling is preferred in wind energy extraction? a. Permanent magnet synchronous generator b. Squirrel cage induction generator c. Doubly – fed induction generator d. None of the above 21. OTEC cycle uses a Ocean thermal gradient between warmer deep and warmer shallow or surface seawaters to run a heat engine b. Ocean thermal gradient between cooler deep and warmer shallow or surface seawaters to run a heat engine and produce useful work c. Ocean thermal gradient between deep warm water and cool shallow or surface seawaters to run a heat engine and produce useful work. d. thermal gradient between cooler deep and less cool shallow or surface seawaters to run a heat engine and produce useful work. 22. The difference between open and closed OTEC cycle type is a. Closed-cycle systems use fluid with a low boiling point, such as ammonia having a boiling point around -33 °C at atmospheric pressure, to power a turbine to generate electricity b. Closed-cycle systems use fluid with a high boiling point, such as ammonia having a boiling point around -33 °C at atmospheric pressure, to power a turbine to generate electricity c. Closed-cycle systems use fluid with a medium boiling point, such as ammonia (having a boiling point around -33 °C at atmospheric pressure), to power a turbine to generate electricity d. None of the above. 23. Which of the following is the most preferred fuel cell? a. PEM fuel cell b. Methanol fuel cell c. alkaline fuel cell d. solid oxide fuel cell 24. The electrolytic solution used in a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is ____________ a) 75% KOH solution b) 25% KOH solution c) 75% NaOH solution d) 25% NaOH solution 25. The most commonly used bio-fuels are a. methanol and formaldehyde b. ethanol and bio-diesel c. formaldehyde and acetaldehyde d. methanol and crude oil 26. A stable interface between solid _________ liquid ____________ and gaseous ___________ promotes high rate of electrode processes. a) Fuel, electrolyte, electrode b) Electrode, fuel, electrolyte c) Electrode, electrolyte, fuel d) Fuel, electrode, electrolyte 27. Which of the following yield more economic and environmental returns among renewable systems? a. hybrid renewable system b. Solar energy system c. Wind energy system d. Bio-mass energy system 28. What is the by-product of fuel cell? a. Electricity, heat and water b. Electricity, methanol and water c. Ethanol, methanol and water d.All of the above 29. What uses lenses or mirrors and tracking devices to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam? a. Convoluted solar power b. Circular solar power c. Concentrated solar power d. covered solar power 30. Nacelle of a wind turbine consists of a. gears and a generator b. generator and rotor blades c. Tower with rotor blades d. all of the above 31. A space vector is represented by a complex number having a. a magnitude equal to the peak amplitude of the variable b. an angle equal to the angular position of this positive peak value. c. Each space vector is considered to have a co sinusoidal distribution around the machine periphery. d. All of the above 32. The reference frame theory commonly used in the analysis of electrical machines and power system components? a. Rotor reference frame b. Stationary reference frame c. Synchronous reference frame d. Arbitrary reference frame e. All of the above 33. Clarks transform converts a. Three phase (abc frame) to two phase in an orthogonal stationary frame(αβ) b. .Two phase in an orthogonal stationary frame(αβ) to Three phase (abc frame) c. Two phase components in the αβ frame to an orthogonal rotating reference frame (dq) d. An orthogonal rotating reference frame (dq) to Two phase components in the αβ frame 34.The Park transform converts a. Three phase (abc frame) to two phase in an orthogonal stationary frame(αβ) b. Two phase in an orthogonal stationary frame(αβ) to Three phase (abc frame) c. Two phase components in the αβ frame to an orthogonal rotating reference frame (dq) d. An orthogonal rotating reference frame (dq) to Two phase components in the αβ frame 35. Which of the following type induction machine has higher starting torque? a. Squirrel cage Induction Machine b. Slip Ring or wound type Induction Machine c. Both a and b d. None of the above 36. In the squirrel cage induction machine the rotor slots are usually given slight skew a. To reduce the magnetic hum and locking tendency of the rotor b. To increase the tensile strength of the rotor bars c. To ensure easy fabrication d. None of the above 37. A capacitor bank can be connected across the stator terminals of Induction generator and load in Wind Energy conversion system is to a. Supply reactive power to the machine as well as to the load. b. Supply Active power to the machine as well as to the load. c. Supply both active and reactive to the machine as well as to the load d. None of the above 38. The induction machine acts as a generator mode then torque and slip will be a. Positive b. Negative c. Both positive and negative d. None of the above 39. Slip of the induction machine does not depends on a. Rotor speed b. Synchronous speed c. shaft torque d. Core loss component 40. Which of the generator operated in sub and super synchronous speed for Wind Energy conversion system? a. Squirrel Cage Induction Generator b. Double Fed Induction Generator c. Permanent Synchronous Generator d. All of the above 41. Soft starters is used in SCIG based Wind Energy system to limit a. Speed b. Inrush current c. Frequency d. None of the above 42. The synchronous generators are preferred to asynchronous generators especially for a. High capacities b. Consume less reactive power compared to asynchronous c. Relatively secure and stable d. All of the above 43. Which of the following generator does not requires external magnetization especially in Standalone Wind energy conversion system a. Squirrel Cage Induction Generator b. Double Fed Induction Generator c. Permanent Synchronous Generator d. None of the above 44. Which of the following statements are correct? (Multiple answers) a. When rotor is stationary, slip =0 b. When rotor is run at synchronous speed, s=0 c. When rotor is stationary, slip =1 d. When rotor is run at synchronous speed, s=1 45. Slip speed is (Ns =Synchronous speed, Nm = Motor speed) a. b. c. d. 46. The crowbar circuit in DFIG used for a. Protection circuit against surge current b. Protection circuit for excessive speed c. Protection circuit for turbine blades d. None of the above 47. Which of the following is correct if the induction machines have? a. Positive slip - Motor, negative slip - generator and slip greater than 1 – braking b. Positive slip - Generator, negative slip - motor and slip greater than 1 – braking c. Positive slip – Motor, negative slip - braking and slip greater than 1 – Generator d. Positive slip - Generator, negative slip - braking and slip greater than 1 – motor 48. Which of the following types of PMSG cannot reach high speeds because of the limited mechanical strength? a. Inset magnet b. Surface mounted magnet c. Buried Magnet d. None of the above 49. Which of the following is not the classification of PMSG based on the direction of flux? a. Axial flux PMSG b. Radial flux PMSG c. Transverse flux PMSG d. Surface flux PMSG 50. Under which of the following conditions squirrel cage induction motor would be preferred over wound rotor induction motor a. When external voltage is to be necessarily introduced in to the rotor b. When wide range of speed controlled is desired c. When cost is the major consideration d. When high starting torque is required 51. In Induction generator, rotor frequency (fr) is related to supply frequency (fs) in term of slip (s) is a. fr = fs/s b. fr = sfs c. fr = fs-s d. None of the above 52. Which of the following is not correct in PMSG? a. Absence of mechanical commutator and brushes b. Field weakening operation is difficult due to permanent magnet c. Rotor of PMSG generator does not get heated up d. The low cost of energy density magnet 53. The electromechanical power for three phase induction machine is given a. b. c. d. None of the above 54. Which of the following is correct in PMSG with surface magnet rotor? (Xd - direct axis synchronous reactance, Xq – quadrature axis synchronous reactance) a. Xd > Xq b. Xd = Xq c. Xd < Xq d. None of the above 55. What type of rotor used in DFIG? a. Wound rotor b. Squirrel Cage rotor c. Both a and b d. None of the above 56. Doubly fed Induction generator named because a. Two generator connected in series b. Two generators connected in parallel c. Both stator and rotor fed power to the grid d. None of the above 57. If Induction generator based wind system connected to grid, then reactive power required by induction generator is supplied by (Multiple answers) a. Utility Grid b. Capacitor Bank c. Power Electronics converters d. None of the above 58. Which of the following are present in per phase equivalent circuit of Induction generator? a. Resistance and leakage reactance of the stator b. Resistance and leakage reactance of the rotor c. Equivalent core loss resistance and magnetizing reactance d. All of the above 59. The torque developed in synchronous generator is a. b. c. d. None of the above 60. The electromagnetic torque in PMSG is obtained by a. b. c. d. 61. When a line commutated converter operates in the inverter mode then a. it draws real and reactive power from the supply b. it delivers both real and reactive power to the supply c. it delivers real power to the supply d. it delivers reactive power to the supply 62. Which one of the following device is uncontrolled? a. SCR b. MOSFET c. Diode d. TRIAC 63. What is the formula for output voltage for Buck converter? a. 8D×Vin b. 5D×Vin c. 2D×Vin d. D×Vin 64. Buck-Boost acts as Buck converter for duty cycle is equal to a. .9 b. .7 c. .6 d. .4 65. If energy is taken from the AC side of the inverter and sends it back into the DC side, then it is known as a. Motoring mode operation b. Braking mode operation c. Regenerative mode operation d. None of these 66. Calculate the output voltage of the Buck converter if the supply voltage is 789 V and duty cycle value is .9. a. 711.1 V b. 710.1 V c. 722.2 V d. 713.2 V 67. For a buck converter to reduce the conduction losses in diode a. A high on - resistance switch can be added in parallel b. A low on - resistance switch can be added in parallel c. A high on - resistance switch can be added in series d. A low on - resistance switch can be added in series 68. A step - down choppers can be used in a. Electric traction b. Electric vehicles c. Machine tools d. All of these 69. The output current in PWM DC - DC converters is equal to a. Average value of the output inductor current b. Product of an average inductor current and a function of duty ratio c. Either (a) or (b) d. None of these 70. The control method used for PWM dc - dc converter is a. Voltage mode control b. Current mode control c. Hysteric control d. All of these 71. The capacity of a battery is expressed in terms of a. Current rating b. Voltage rating c. Ampere hour rating d. None of the above 72. The storage battery generally used in electric power station is a. Nickel-cadmium battery b. Zinc carbon battery c. Lead-acid battery d. None of the above 73. On over charging a battery a. It will bring about chemical change in active materials b. It will increase the capacity of the battery c. It will raise the specific gravity of the electrolyte d. None of the above 74. Ampere hour capacity of an industrial battery is based on ..........hours discharge rate a. 8 b. 12 c. 16 d. 24 75. AC voltage controllers convert a. fixed ac to fixed dc b. variable ac to variable dc c. fixed ac to variable ac d. variable ac to fixed ac 76. In AC voltage controllers the a. variable ac with fixed frequency is obtained b. variable ac with variable frequency is obtained c. variable dc with fixed frequency is obtained d. variable dc with variable frequency is obtained 77. The AC voltage controllers are used in __________ applications. a. power generation b. electric heating c. conveyor belt motion d. power transmission 78. A single-phase half wave voltage controller consists of a. one SCR is parallel with one diode b. one SCR is anti parallel with one diode c. two SCRs in parallel d. two SCRs in anti parallel 79. In the integral cycle control method of ac voltage controller a. the average power delivered to the load is controlled b. the instantaneous power delivered to the load is controlled c. the frequency of output voltage is controlled d. none of the mentioned 80. Sequence control of ac voltage controllers is employed for the improvement of a. output frequency b. input frequency c. commutation d. system power factor 81. In the three-phase bridge inverter, each step consists of a. 30° b. 60° c. 90° d. will depend on the value of the firing angle 82. In inverters, to make the supply voltage constant a. an inductor is placed in series with the load b. capacitor is connected in parallel to the load side c. capacitor is connected in parallel to the supply side d. none of the mentioned 83. External control of dc input voltage can be obtained by the use of a a. transformer b. chopper c. inverter d. converter 84. The input current waveform of a bridge controlled rectifier when the load is perfectly filtered is a. Sine wave b. Square wave c. Saw - tooth wave d. Trapezoidal wave 85. A full wave rectifier with resistive load produces a. Second harmonic b. Third harmonic c. Fifth harmonic d. Do not produce harmonics 86. In rectifiers, load current flow is a. Unidirectional b. Bidirectional c. Either (a) or (b) d. Non directional 87. In pulse width modulated inverters, the output voltage is controlled by controlling the a. input frequency b. modulating index c. amplification factor d. none of the mentioned 88. Increasing the number of pulses (N), ____________ a. reduces the output voltage amplitude b. reduces the inverter efficiency c. improves the inverter efficiency d. none of the mentioned 89. Control of frequency and voltage in 3-phase inverters is a. possible only through inverter control circuit b. possible through the control circuit of inverter and converter c. possible through inverter control of frequency and through converter control for voltage d. none of the mentioned 90. Output voltage of a single-phase bridge inverter, fed from a fixed dc source is varied by a. varying the switching frequency b. pulse-width modulation c. pulse amplitude modulation d. all of the mentioned 91. What are the classifications of wind turbines? (a)1 (b)2 (c) 3 (d ) 4 92. In future, the generators for wind turbines will be (a)Synchronous generators (b)PMSM (c) Induction generators (d)All of the above 93. According to the rotational speed of aero turbines, Wind Energy Conversion Systems are classified as (a)1 (b)2 (c) 3 (d)4 94. In standalone operation of Fixed Speed System, the fluctuations in prime mover speed can be avoided by (a)Pitch control (b)Torque control ( c)Angular control (d)None of the above 95. The main advantage of a Fixed Speed Induction Generator is (a)Increased output power (b)Reduction in capital cost ( c)Increase in efficiency (d)None of the above 96. The main disadvantages of Doubly Fed Induction Generator is (a)Increased capital cost (b)Needs periodic maintenance ( c)Both (i) & (ii) (d)None of the above 97. Stand alone operation of variable speed system uses (a)Induction generator (b)Synchronous generator ( c) Both (i) & (ii) (d)Synchronous motor 98. The Fixed Speed Induction Generators Wind Turbine is a (a)Squirrel cage induction generator (b) Slip ring induction generator ( c)Synchronous motor (d) None of the above 99. DFIG provides the access to (a)Stator windings (b)Rotor windings ( c) Commutator windings ( d)None of the above 100.In variable speed systems, which is used between the line side converter and utility (a)Step up transformer (b)Step down transformer ( c) Auto transformer (d) None of the above 101.The advantages of Fixed Speed Wind Energy Conversion systems is (a) Simple (b) Robust and reliable ( c) Low cost and easy control (d) All of the above 102.DFIG configuration allows (a)Sub synchronous operation (b)Super synchronous operation ( c)Both sub synchronous and super synchronous operation (d)None of the above 103. Which is used to control the power factor on the stator side? (a) DC link capacitor (b) Inductor (c)Resistor (d) None of the above 104. Which has the ability to work as active filter? (a) Line side converter (b) Inverter (c)Chopper (d) None of the above 105. Stand alone system is also called as (a) Dependant system (b)Autonomous system ( c) Reliable system (d)None of the above 106. A good charge rate is (a)30% of the total capacity of the battery per hour (b) 20% of the total capacity of the battery per hour (c) 10% of the total capacity of the battery per hour (d)None of the above 107.The problems related with grid connections are (a) Poor grid stability (b) Low-frequency operation ( c) Low power factor (d)All of the above 108.Which is used to avoid battery damage? (a) Charge controller (b) Inductor ( c) Resistor (d)None of the above 109. Which is used to charge the battery during day? (a) Converter (b) Photo voltaic modules (c)Inverter (d) None of the above 110. Which is used for storing energy in PV systems? (a) Batteries (b) Converter (c)Inverter (d) None of the above 111. Most of the batteries used in PV systems are (a) nickel –chromium batteries (b) Lead –acid batteries (c)Lithium batteries (d) None of the above 112.Batteries are rated in (a) Ampere-hour (b) Watt –hour (c) Kwhr (d) None of the above 113. Which is used to control the flow of electricity from PV modules to the load? (a) Converter (b) Charge controller (c)Inverter (d) None of the above 114. What are the factors affecting PV systems output? (a) Temperature (b) Dirt and dust (c)DC-AC conversion (d)All of the above 115. Which converter is used in PMSG? (a) Buck converter (b) Boost converter (c)Buck-Boost converter (d)None of the above 116. The main advantages of Induction generators are (a) Low cost (b) Low maintenance requirements (c)Reliable (d) All of the above 117. What are the types of grid-connected system? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) None of the above 118. In case of islanding the PV generators should be (a) Disconnected from mains (b) Connected to mains (c) Synchronized to mains (d) None of the above 119. What will happen if the grid is reconnected during islanding, (a) Transient over currents can flow (b) Circuit breakers damaged (c)Both (i) & (ii) (d)None of the above 120. A grid connected inverter operates in the range of (a)1-5 KHz (b)2-20 KHz (c)2-40 KHz (d)None of the above 121. The following is not a hybrid renewable energy system a. Solar+Wind b. WInd+Biomass c. Wind+Nuclear d. Solar+Biomass 122. The efficiency of a PV panel can be obtained from a. Form factor b. Fill factor c. Ripple factor d. Shading factor 123. Which of the following converter has its input current continuous? a. buck b. boost c. buck-boost d. all of the above 124. The issue in hybrid system is a. Requires battery which increases cost b. Load sharing between different sources c. A sudden change in the power output of one source affects stability d. All of the other options 125. The maximum power is delivered from a source to its load when the load resistance is ______ the source resistance. a. greater than b. less than c. equal to d. less than or equal to 126. The attached schematic shows a a. Wind+PV system with a common ac bus b. Wind+PV system with a common dc bus c. Wind+DG system with a common dc bus d. Wind+DG system with a common ac bus 127. The attached schematic shows a a. Wind+PV system with a common ac bus b. Wind+PV system with a common dc bus c. Wind+DG system with a common ac bus d. Wind+DG system with a common dc bus 128. In the attached schematic, the ac bus voltage is fixed by a. Wind system b. DG system c. PV system d. Grid 129. In the attached schematic, the dc bus voltage is fixed by a. Wind system b. PV system c. Grid d. Design 130. The dc-dc converter shown in the attached schematic helps to a. Reduce PV panel voltage to required bus voltage b. Helps to charge a battery c. Achieve MPPT d. Convert the dc voltage to grid voltage 131. The attached schematic shows a a. Stand alone wind electric system b. stand alone PV system c. stand alone hybrid system d. grid connected hybrid system 132. In the attached schematic, the charge controller a. prevents deep discharge of battery b. prevents overcharging of battery c. Maintains the dc bus voltage d. All the other options 133. In the attached schematic, the control unit a. switches from PV to Wind when irradiance is less and wind velocity is more than cut-in b. switches from Wind to PV when wind velocity is less and irradiance is present c. Helps to maintain load sharing between Wind and PV d. All the other options 134. In the attached schematic, the blocking diode of the PV panel, a. Protects array from voltage spikes b. Prevents flow of reverse current at low irradiation c. Prevents flow of reverse current at nights d. All the other options 135. Wind+PV hybrid systems are very hip since a. there is a large demand for wind energy systems b. there is a large demand for PV systems c. since wind and pv systems are complementary d. No inverters are required 136. Dump load is a load a. which is purely reactive b. which is used to waste excess energy available in the source c. which regenerates back to the source d. None of the other options 137. A diesel generator a. can operate in no load b. cannot operate at 100% load c. should operate at some minimum load d. None of the other options 138. The attached schematic refers to a. a fixed speed wind energy system b. a wind energy system with limited variation in wind speed c. a hybrid system with limited variation in wind speed d. a fixed speed hybrid system 139. The battery bank in the attached schematic helps to a. Meet load demand when there is a sudden fall in wind speed b. Meet sudden increase in load till DG start-up time c. Improve wind energy utilisation d. All the other options 140. The attached schematic of PV-Diesel hybrid system shows a. Series configuration b. Parallel configuration c. Switched configuration d. None of the above 141. The attached schematic of PV-Diesel hybrid system shows a. Series configuration b. Switched configuration c. Parallel configuration d. None of the other options 142. The schematic attached shows a. Series configuration b. Switched configuration c. Parallel configuration d. None of the above 143. In the attached schematic, the inverter a. can operate in parallel with DG b. can operate in parallel with PV c. Has to be rated for 100% capacity d. Can be rated for 50% capacity 144. In the attached schematic, a. DG can charge battery bank b. Only PV can charge battery bank c. Inverter and DG cannot operate in parallel d. Battery bank cannot supply power to load directly 145. To determine load sharing between 2 sources in parallel, the sources have to be converted to their a. Thevenin model b. Miller model c. Steinmetz model d. Cuk model 146. In the attached schematic for a PV system, a. X axis is current and Y axis is voltage b. X axis is voltage and Y axis is current c. X axis is voltage and Y axis is power d. X axis is power and Y axis is voltage 147. In fractional open circuit voltage MPPT method, a. Voltage at MPPT is 100% of open circuit voltage b. Voltage at MPPT is around 70-80% open circuit voltage c. Voltage at MPPT is around 50-60% open circuit voltage d. Voltage at MPPT is around 30-40% open circuit voltage 148. In the fractional short circuit MPPT algorithm, a. The current at MPPT is 100% of short circuit current b. The current at MPPT is around 80-90% of short circuit current c. The current at MPPT is 50-60% of short circuit current d. The current at MPPT is 30-40% of short circuit current 149. In hill climbing MPPT algorithms, a. Switching frequency is varied b. Duty cycle is varied c. Output capacitance is varied d. Output inductance is varied 150. Which of the following is a disadvantage of renewable energy? a. High pollution b. Available only in few places c. High running cost d. Unreliable supply