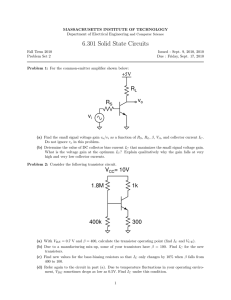
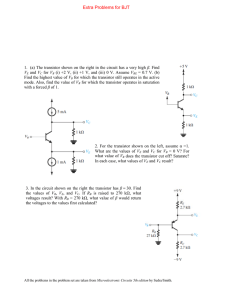
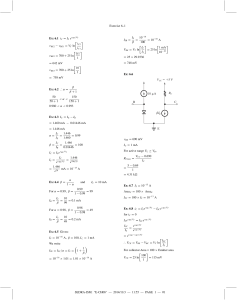
Factors Affecting the Stability of Q Point: Ideally, the Q point is expected to be "stable" i.e. should not shift up or down on the load line. But practically it is not so. In fact the Q point is quite unstable and keeps changing its position on the dc load line. The factors affecting the stability of Q point are: • Changes in temperature • Changes in the value of β • Variations of parameters from one transistor to the other. • However the Q point instability due to any reason is not desirable because it will introduce distortion in the amplified signal. Bias Stabilization: • Bias stabilization is a process of stabilizing the Q point (bias point) of the circuit • Hence we need to design a biasing circuit which will keep the position of Q point stable on the load line. • First let us understand the effects of various parameters on the stability of Q point and then discuss various biasing circuits to counter these effects. Q Point Instability due to Temperature: The junction temperature of a transistor is dependent on the amount of current flowing through the transistor. Due to increase in temperature the following parameters of a transistor will change: I. V BE 2. Β and 3. ICBO. (1) • • (2) • • (3) • • • VBE: The base to emitter voltage decreases at a rate of 2.5 mV/0C with increase in temperature. The base current IB will therefore increase and it will force Ic to change, and hence the Q point. Current gain β The Current gain βdc of a transistor is temperature dependent. As IC = βIB, changes in β will change the collector current lC. Reverse saturation current (ICBO) : The reverse saturation current of the reverse biased CB junction flows due to the minority carriers doubles for every 10 deg c, hence it is dependent on temperature. Also We know that, IC = β IB + (1+ β)ICBO Therefore change in ICBO due to temperature will force the collector current lc and hence the Q point to change. Q Point Instability due to Changes in β • The current gain β vary for a given type of transistor normally has a very wide tolerance. • The value of β may typically range from 50 to 150 or more depending on the value of lc. • The wide tolerance can seriously affect the transistor bias conditions. Q- Point Instability due to Variation in Parameters from One Device to Other: (1) Two transistors of identical number (e.g. BC 147) do not have exactly the same characteristics. Important parameters such as β will differ in value from one transistor to the other. (2) Hence if we replace one transistor by the other of same number, the Q point is going to get shifted. Stability Factors : (1)The stability of Q point of a transistor amplifier depends on the following three parameters: • Leakage current Ico • β • Base to emitter voltage VBE (2) The effect of these parameters can be expressed mathematically by defining the stability factors for the three parameters individually as follows: Stability factor indicates the degree of change in operating due to variation in temperature. There are three variables which are temperature dependent. We can define three stability factors : IC by keeping VBE and as cons tan t I CO IC S' by keeping I CO and as cons tan t VBE I S C by keeping VBE and I CO as cons tan t S • Ideally, Stability factors should be zero to keep operating point stable and fixed. • Practically, Stability factors should have the value as minimum as possible. These expressions indicate that Ic is collectively dependent on ∆ICO, ∆VBE and ∆β. The combined effect of these parameters on IC is mathematically given by, I C SI CO S ' VBE S ''