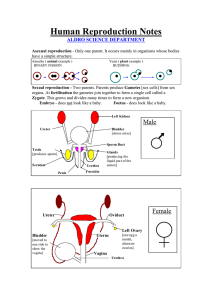
Phases of Childbirth Terms Labor – the process of giving birth Gestation- the period of pregnancy, where the foetus is developed Parturition- the process of foetus expelled from mother’s body. Also known as birth. Contraction- Shortening of uterine muscles Foetal Position Before labour Foetus’ head is settled in the mother’s pelvis Faces woman’s right/left hip bone Knee drawn up to its abdomen Legs crossed one side of head on mother’s bladder Other side of head against her bowel The Stages of Labor First Stage Second Stage Contractions cause the cervix to dilate The baby is born Third Stage The placenta is expelled from the mother’s body First Stage During final 3 months of gestation… Uterus last – weak, irregular contraction 30-40 seconds Contractions becomes stronger and frequent Contraction occurs approximately 30 minutes First Stage tive labor Starts when the cervix has dilated to 3 cm Last about 8-9 hours Contractions become stronger & more frequent Wave of contraction move from upper part of uterus to downward towards cervix (Waves similar to peristalsis) *where did we learn peristalsis? First Stage Each contraction makes uterus’ muscle fibre shortens This leads to pulling of cervix Pull on cervix leads to cervical dilation (open) What might happen to the foetus as the cervix dilates? First Stage As contraction becomes more frequent Head cervix of foetus pushed against slowly dilating Eventually cervix becomes fully dilated (approximately 10 cm) Uterus, cervix and vagina forms single, curved passage This passage is called “Birth Canal” First Stage Second Stage Involves delivery of the foetus Begins with bursting of membrane surrounding foetus – amniotic sac Stage of expulsion Gush of fluid from vagina Second Stage Cervix – fully dilated Delivery of baby begins!! Each contraction moves the foetus small amount Mother – contracts her abdominal muscles & push baby out of the uterus & through the vagina 20 minutes – 2 hours Contractions – 45-90 seconds, 3-5 minutes Typical birth – baby travels down the birth canal head first and facing the mother’s back Second Stage Once head emerges It turns sidewards and faces’ mother’s hip Rotation allows easier movement of body and shoulder through the birth canal Second Stage Third Stage Final stage Placenta is delivered Mother experiences mild contractions After 5 minutes of delivering placenta – membrane and umbilical cords are expelled Afterbirth Little blood is lost – due to placental blood vessels constricting Contraction of uterus shuts the blood vessel Third Stage Baby begins to breathe with its own lungs Placenta is still inside the the uterus Still connected placenta by umbilical cord Umbilical cord is clamped, tied in 2 places and cut between the ties The stump of the cord dries up and falls away What health issues might occur to the mother and the baby? Cesarean Delivery Sometimes called a C-section Procedure in which a doctor delivers the baby through a surgical opening in the mother’s abdomen Cesarean Delivery May be necessary: Mother’s pelvis is too small to deliver baby Fetus is in the breech/abnormal position (feet or buttocks closest to the cervix) Mother is carrying multiples Mother has preexisting medical condition that makes birth unsafe Placenta covers the opening of the uterus Long labor threatens mommy and/or baby Fetal monitor shows baby’s heart rate dropping dangerously low Breech Position Risk of Breech presentation Baby can get stuck in birth canal This will cause? Umbilical cord may be blocked or damaged This will cause? Review Questions Can you describe the 3 phases of labour? What changes occur in the uterus, cervix and vagina to allow them to function as “birth canal”? What hormone/s are involved during labour? Explain the phase and the effect Australian doctors prefer women to have their babies in the hospital. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of having a child in a hospital and homebirth. Question 1 Describe the foetal position before labour. Question 1 Describe the foetal position before labour. Foetus’ Faces Knee Legs one head is settled in the mother’s pelvis woman’s right/left hip bone drawn up to its abdomen crossed side of head on mother’s bladder Other side of head against her bowel Question 2 What stage is the baby born? Question 2 What stage is the baby born? Second stage Question 3 During first stage of labour, the wave contraction is similar to what movement? Question 3 During first stage of labour, the wave contraction is similar to what movement? Peristalsis Question 4 Describe breech position Question 4 Describe breech position feet or buttocks closest to the cervix Question 5 What are the risks of breech position? Question 5 What are the risks of breech position? Baby can get stuck in birth canal. Umbilical cord may be blocked or damaged.