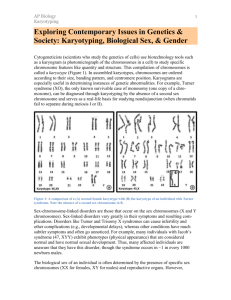
Name: _________________________ Virtual Karyotyping LESSON OBJECTIVE: In this lesson, you will analyze human karyotypes to determine if medical patients have a genetic disease. Go to the class website, and follow the link for What is a Karyotype? READ the information thoroughly before answering any of the related questions: 1. Define the term karyotype: 2. Explain HOW a cytogeneticist prepares a karyotype for analysis: 3. Differentiate between an autosome and a sex chromosome: 4. How are chromosomes numbered? Follow the link for Diagnosis of Chromosome Abnormalities and READ this information thoroughly. 5. What types of chromosome problems does a cytogeneticist look for when karyotyping? 6. Explain the phone book analogy to karyotyping: 7. What types of information does the molecular approach to karyotyping provide? Go to the class website, and follow the link for University of Arizona Karotyping Activity. Read the introduction and answer the following questions. 1. During mitosis, the 23 pairs of human chromosomes condense and are visible with a ______________ 2. T or F The dyed bands on a chromosome represent a single gene. 3. List the three identifying characteristics of chromosomes that you will identify in this assignment: a. b. c. Click the button “PATIENT HISTORIES ►” 4. How old is patient A’s mother?________________ 5. Why did patient B have his chromosomes checked?_________________________ 6. What two birth defects did patient C have when born?________________________ Click “Complete Patient A’s Karyotype”. Read the instructions and match each chromosome to its homologous chromosome. When you are finished matching all of the chromosomes, read the paragraph “Interpreting the karyotype”. 7. What notations/abnormalities would you make for patient A’s karyotype? Read the paragraph “Making a diagnosis”. 8. What is Patient A’s diagnosis? (Hint: use the table and patient karyotype at the bottom of the screen.) Click the button “PATIENT B►”. Read the instructions and match each chromosome to its homologous chromosome. When you are finished matching all of the chromosomes, read the paragraph “Interpreting the karyotype”. 9. What notation/abnormalities would you for patient B? 10. What diagnosis would be given to patient B? 2 Click the button “PATIENT C►”. Read the instructions and match each chromosome to its homologous chromosome. When you are finished matching all of the chromosomes, read the paragraph “Interpreting the karyotype”. 11. What notation/abnormalities would you for patient C? 12. What diagnosis would be given to patient C? Use your chromebook to research the following related questions: 13. Extra chromosomes can render a fetus inviable. What does this mean? 14. Trisomy 21 nondisjunction is one of the causes of Down Syndrome. What is meant by trisomy 21 nondisjunction? 15. Why does the chance of having a child with Down Syndrome increase with mother’s age? 16. What are the effects of Down Syndrome? 17. Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs as a result of a random error that causes a male to be born with an extra Sex chromosome. It isn't an inherited condition. What are the effects of Klinefelter Syndrome? 18. Turner’s syndrome occurs as a result of a random error that causes a female to be born with only 1 Sex chromosome. It isn't an inherited condition. What are the effects of Turner’s Syndrome? 19. Describe how crossing-over, independent assortment, and random fertilization lead to genetic variation. 3 CK-12: Genetic Disorders-- Huntington’s Disease Go to the class website, and follow the link for cK-12 Huntington’s Disease. READ the information thoroughly before answering any of the related questions: 1. Explain what is meant by the term “genetic disorder”: 2. Can you be a “carrier” of an autosomal recessive genetic disorder? EXPLAIN. 3. Can you be a “carrier” of an autosomal recessive genetic disorder? EXPLAIN. 4. Contrast the chance of a child inheriting an autosomal recessive genetic disorder versus an autosomal dominant genetic disorder: 5. One parent is a carrier of the cystic fibrosis gene while the other parent doesn’t carry the allele. Can their child have cystic fibrosis? EXPLAIN. 6. The class will watch a video clip explaining the symptoms and effects of Huntington’s disease. Please summarize what you learn from the video: 4