Acid-Base Questions
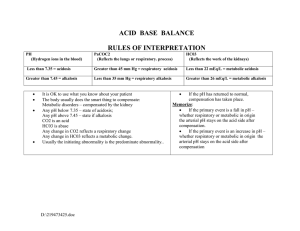
Necessary Memorization
!
Acute Resp acidosis/ Chronic Resp Acidosis
!
!
!
Kidney s response to chronic resp acidosis- spill amonium!
!
Expected PCO2 = 1.5 (HCO3) + 8]+/-2
Non Anion Gap (NAG) or Anion Gap (AG)
!
!
!
!
Rise in HCO3 3.5meq/10meq of PCO2-
Winter s formula
!
!
10/.08
10/.03
AG= Na –(Cl+HCO3) nl AG= 9-12
Effect of albuminMUDPILES
The Delta-Delta- nl ratio approx. 1:1
!
Unmeasured anions (ie Anion Gap) generate one proton per anion- this has many
assumptions involved.
!
!
No loss of anions- DKA
No buffering of H+- Lactic Acidosis
Step-wise process
!
Check internal consistency of data:
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
H+=24 x HCO3/PCO2
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
If alkalemic is respiratory or metabolic?
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
Diagnosis?
Question 1:
!
!
!
A 38 y/o male is admitted with weakness,
anorexia, wt loss and progressive anemia.
Bp 180/112 temp 37 C resp 20/min
Labs:
135
101
5.4
12
ABG: 7.32/24/104
Question 1:
Is the patient acidemic/alkalemic?
!
acidemic
!
What is the primary acid base disorder?
!
Since HCO3 is low and would cause academia and PCO2 is also low would cause
alkalosis.
Thus primary problem is metabolic acidosis
!
!
What type of metabolic acidosis Anion Gap or Non Anion Gap?
!
Na –(Cl+HCO3)= 22
Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis.
!
!
What is the delta anion gap?
!
Calculated AG- Nl AG= 22- 12 or 10.
These 10 unmeasured anions generated 10 protons then the serum HCO3 concentrated
with these 10 unmeasured anions added to it is near normal or 22 thus this a pure
metabolic anion gap acidosis.
!
!
!
Is the compensation adequate?
!
!
!
!
Winters formula {expected PCO2 +1.5 (HCO3) + 8]+/-2
Yes compensation is adequate
What circumstances caused this: MUDPILES
Ketoacidosis due to poor po intake in this case.
Question 2
!
!
!
A 72 y/o female admitted from NH with a one
week history of diarrhea and fever
Bp 100/60
Hr 100 lying
BP 70/40
HR 125 standing
133
118
2.5
5
ABG: 7.11/16/94
Question 2:
Is the patient academic/alkalemic ?
!
!
Acidemic
What is the primary acid base disorder?
!
!
Since HCO3 is low and would cause academia and PCO2 is also low
would cause alkalosis. Thus primary problem is metabolic acidosis.
What type of metabolic acidosis Anion Gap or Non Anion
Gap?
!
!
Na –(Cl+HCO3)= 10 thus, Non Gap Metabolic Acidosis
(hyperchloremic).
Is the compensation adequate?
!
!
!
Winters formula {expected PCO2 +1.5 (HCO3) + 8]+/-2
Yes compensation is adequate
What circumstances caused this:
!
!
Diarrhea Causes NON gap hyperchloremic Metabolic Acidosis.
Causes of Non Gap Acidosis
!
HCO3 loss
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
Diarrhea or other intestinal losses
(eg, tube drainage)
Type 2 (proximal) renal tubular
acidosis (RTA)
Posttreatment of ketoacidosis
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Ureteral diversion (eg, ileal loop)
Decreased renal acid excretion
Chronic kidney disease
!
!
!
Some cases of chronic kidney
disease
Type 1 (distal) RTA
Type 4 RTA (hypoaldosteronism)
FUSEDCARS:
! Fistula (pancreatic),
! Uretogastric conduits,
! Saline administration,
! Endocrine (hyperparathyrdoism),
! Diarrhea,
! Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
(acetazolamide),
! Ammonium chloride,
! Renal tubular acidosis,
! Spironolactone
Question 3
!
A 68 y/o male admitted with a 70 pack year
history and chronic analgesic abuse admitted
with severe bronchitis.
LABS:
:
!
140
101
5.0
15
ABG: 7.11//51
Question 3
Is the patient acidemic/alkalemic
!
!
Acidemic
What is the acid base disorder?
!
!
Since HCO3 and PCO2 are moving in opposite directions this suggestions a mixed acid
base disturbance. There is a metabolic acidosis and a respiratory acidosis.
What type of metabolic acidosis: Anion Gap or Non Anion Gap?
!
!
Na –(Cl+HCO3)= 24thus, Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis.
Is the compensation adequate? NO-"Respiratory Acidosis.
!
!
Winters formula {expected PCO2 +1.5 (HCO3) + 8]+/-2
What is the delta anion gap:
!
!
!
Calculated AG- Nl AG= 24- 12 =12.
These 12 unmeasured anions generated 12 protons then the serum HCO3 concentrated
with these 12 unmeasured anions added to it is near normal or 27 thus this a pure
metabolic anion gap acidosis.
What circumstances caused this:
!
!
High AG due to Uremia recall MUDPILES and a Respiratory acidosis due to COPD.
Question 4
!
!
A 64 y/o female admitted to hospital the day
before w/ a psychiatric disorder . Found
apneic and pulsless in bed by nurse. CPR is
begun.
LABS:
141
105
6.0
8
ABG: 6.99/34/60
Answer to Question 4
Is the patient acidemic?
!
!
What is the acid base disorder?
!
!
Since HCO3 is low this would suggest that the patient has a primary metabolic acidosis
at least…
What type of metabolic acidosis Anion Gap or Non Anion Gap?
!
!
Na –(Cl+HCO3)= 28 thus, High Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis.
What is the delta anion gap:
!
!
!
Calculated AG- Nl AG= 28-12 =16.
These 16 unmeasured anions generated 16 protons then the serum HCO3 concentrated
with these 16 unmeasured anions added to is it normal or 24 thus this a pure metabolic
anion gap acidosis.
Is the compensation adequate?
!
!
!
!
!
Yes- Severely
Winters formula {expected PCO2 +1.5 (HCO3) + 8]+/-2
No in this case the expected PCO2 should be 20 and the patients actual PCO2 is higher
thus the compensation is inadequate and
they have a concomitant respiratory acidosis
What circumstances caused this: AG acidosis due to Lactate and w/ concomitant
resp acidosis
Question 5
!
!
A 47 y/o female with SLE and Chronic Renal
failure has had shaking chills and LLQ pain for
36 hrs.
LABS:
136
106
124
5.5
8
6.8
ABG: 7.44/12/108
Answer to question 5
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
Is this resp or metabolic?
!
!
!
!
AG= Na –(Cl+HCO3) = 22 thus AG acidosis
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
Hco3- decreased c/w metabolic acidosis but PCO2 increased c/w respiratory
alkalosis
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
!
!
Alkalosis
AG22- nl AG 12= 10,
These 10 unmeasured anions generated 10 protons then the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 10 unmeasured anions added to it is only 18 thus there
must be a concomitant metabolic non gap acidosis also
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate? No is a primary resp alkalosis
Diagnosis? Respiratory alkalosis and a mixed ag and non gap acidosis from
renal failure
Question 6
!
!
A 64 y/o male with severe COPD has had
unrelenting watery diarrhea for 3 days.
LABS:
136
105
53.3
19
ABG: 7.09/65/48
Answer Question 6
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
!
!
AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) = 12 so NAG hyperchloremic from
diarrhea
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
!
!
acidemic
Expected PC02=1.5 (HCO3) +8 -/-2 = 35+/-2
Acute resp acidosis
Diagnosis? Hyperchloremic NAG Acidosis from
diarrhea w acute resp acidosis due to COPD
Question 7
!
!
!
A 58 y/o male has been vomiting for several
days and brought to the ER by his wife who
claims he passed out and is weak and breathing
funny.
BP 70/40 Pulse 140, Resp 24 and deep
LABS:
127
75
3.1
3
ABG: 6.7/12/108
Answer to Question 7
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
!
!
!
AG- nl AG= Delta HCO3= 37
These 37 unmeasured anions generated 37 protons thus the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 37 unmeasured anions added to it is 40, thus there must
be a concomitant metabolic alkalosis
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
!
AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) = 49
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
Acidemic
Expected PC02=1.5 (HCO3) +8 +/-2 =12.5 +/-2
Diagnosis? Mixed AG Acidosis w and Metabolic alkalosis w appropriate resp
compensation (see next page)
!
Note if Lactic acidosis using delta AG:delta HCO3 of 1.6:1.0 ratio then
predominantly a Severe Ag metabolic Acidosis
The Delta- Delta and Lactic Acidosis
!
In LA the ratio rise in the AG is not proportional in a
1:1 ratio to the fall in HCO3 due to buffering of bone
of H+
!
!
!
!
The buffering of bone is not acute so sz, arrest so it will be
1:1 acutely
In LA the ratio approaches 1.6 :1 so that a rise change in AG
of 16 would account for a change in hco3 of 10
The more Lactate produced the farther out from 1:1 this ratio
become
Delta-Delta in DKA may actually be 1:1 or less ie (1:.8)
!
Urinary excretion of Anion leading to protons generated but
loss of the unmeasured anions via the urine.
Question 8
!
!
A 28 y/o male w/ a severe closed head injury
has had a prolonged ileus. He has been on
NG suction for several days. His I/O an daily
wts suggest that his volume deplete
LABS:
144
84
3.2
42
ABG: 7.52/52/90
Answer to Question 8
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
Is resp or metabolic?
!
!
!
alkalemic
PCO2 elevated c/w a resp acidosis
HCO3 elevated- primary metabolic alkalosis
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
In metabolic alakalosis PCO2 rises .7 for every 1meq of
HCO2
!
!
Thus: Change in HCO3 is 18- and change in PCO2 should be 12-13
and is appropriate
Diagnosis? HCl loss due to prolonged NG suctioning.
Causes of Metabolic Alkalosis
!
Gastrointestinal hydrogen Loss
!
!
!
Renal hydrogen loss
!
!
!
!
!
Primary mineralocorticoid excess
Loop or thiazide diuretics
Posthypercapnic alkalosis
Hypercalcemia and the milk-alkali syndrome
Intracellular shift of hydrogen
!
!
!
Vomiting or nasogastric suction
Antacids in advanced renal failure
Hypokalemia
Alkali administration
Contraction alkalosis
!
!
!
!
Massive diuresis
Vomiting or nasogastric suction in achlorhydria
Sweat losses in cystic fibrosis
Villous adenoma or factitious diarrhea
Question 9
!
!
A 46 y/o female is brought to the ER
unresponsive and found down after an
apparent suicide attempt. On exam she is
stuporous and tachypneic.
Labs
140
106
4.1
10
ABG: 7.54/12/106
Answer to Question 9
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
Is resp or metabolic the primary cause?
!
!
!
Alkalemic
HCO3 is down so a metabolic acidosis
PCO2 is decreased c/w resp alkalosis
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
!
AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) = 24
!
!
!
!
So AG metabolic acidosis
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate? Primary respiratory
alkalosis
Diagnosis? Primary respiratory Alkalosis with AG metabolic
acidosis
!
Salicylate ingestion
ASA Overdose:
!
!
OD uncommon in children since Reyes syndrome
Acetylsalicylic Acid converted to Salycylic Acid (HS)
!
!
!
!
!
Mechanism of action
!
!
!
!
Toxic levels- 40-50ng/dL (early symptoms)
Therapeutic level 10-30ng/dL
Fatal dose 3 g in children, 10-30g in adults
90% plasma bound stays intravascular, peak levels w/in 1hr.
Inhibit COX- decreased PG, PC and TXA
Medulla- chemoreceptor causing N/V and respiratory center
Inhibit cellular metabolism- metabolic acidosis
Clinical features:
!
!
!
Tinnitus, vertigo, n/v and diarhhea
Late change in MS, and death
RESP ACIDOSIS suggests concomitant overdose…
Treatment:ASA OD
!
!
HS is a weak acid
HS#"H++ SHS crosses intracellularly and acidosis promoted
formation of HS leading to NCPE and CNS toxicity
!
Treatment directed at alkalinization resp drive is protective.
!
!
!
7.50-.55
Hyokalemia- stimulate K/H exchanger in distal tubule and
blocks urinary alkalinization
HD indications:
!
!
!
Levels >100ng/dL- absolute indication for HD
NCPE, Mental status changes, renal insufficiency, volume overload
Deterioration despite supportive care.
Question 10
!
A 27 y/o female pregnant alcoholic with insulin
dependant DM is admitted one week after stopping
her insulin and beginning a binge drinking episode.
She has had severe nausea and vomiting for several
days.
!
!
!
BP 120/80
BP 108/80
LABS:
HR 124 supine
HR 160 upright
136
70
3.6
19
ABG: 7.58 /21/104
Answer to Question 10
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
Alkalemic
!
Is resp or metabolic the primary cause?
!
HCO3 is down so a metabolic acidosis
! PCO2 is decreased c/w Resp Alkalosis
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
! AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) =47
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
!
!
!
AG-nl AG=35
These 35 unmeasured anions generated 35 protons thus the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 35 unmeasured anions added to it is 54, thus there must
be a concomitant metabolic alkalosis
Diagnosis? Mixed Resp and metabolic alkalosis w and AG acidosis
!
contraction alkalosis and gi loss w a combined DKA/alcoholic ketosis in
pregnancy.
Respiratory changes of Pregnancy
!
Upper airway
!
Estrogen effects
!
!
!
!
!
Nasal stuffiness common
Thorax and diaphragm
!
!
Early effects- not related to
uterus
Barrell Chest
!
!
!
Hyperemia
Increased glandularity
Increased mucus production
Fxnal
Diaphragm up by 4cm
AP diameter increased by 2cm
4cm
2cm increase
Respiratory changes of Pregnancy
At any point Pa02 will be higher
Than in non pregnant
Pa02= 100-110
Respiratory changes of Pregnancy
Increase Inspiratory Capacity accounts for increased Ve. (no change in RR)
RV, TLC, and ERV drop
FEV-1 of pregnancy unchange
ABG of Pregnancy: 7.40-7.45/27-32/100-110
Question 11
!
!
A 64 y/o female with hx of COPD on home
02 as outpt. Had the following blood gas
7.34/60/60 with a serum bicarbonate of 31.
On the day of admission he she develops a
cough, sob and confusion.
LABS:
142
100
4.0
31
ABG: 7.20/80/35
Answer to Question 11
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
Acidemic- primary respiratory acidosis
!
!
!
!
10/.03- chronic
10/.08 acute
10/.05 acute on chronic resp acidosis
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
Compensated metabolic alkalosis
!
Change in HCO3 for Change in PCO2 (3.5 /10)
!
!
Thus no.
Diagnosis? Acute on Chronic Respiratory Acidosis.
Compensation of Chronic
Respiratory Acidosis
Change in pH is only
.03
Ratio of HCO3 :PCO2
3.5:10
Due to the concomitant
Rise in HCO3
renal amonium excretion
Change in PC02 is 10
Question 12
!
!
A 22 y/o male is brought to the ER with
hyotension and fever.
LABS:
140
106
4.0
14
ABG: 7.39/24/60
Answer to question 12
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
Neither- never over compensate so 2 primary processes
!
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
! AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) =20
!
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
!
!
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
!
Expected PC02=1.5 (HCO3) +8 +/-2 = 29+/-2 suggesting a concomitant respiratory acidosis
These numbers cannot work!
!
AG- nl AG=8
These 8 unmeasured anions generated 8 protons thus the serum HCO3 concentrated with these 8
unmeasured anions added to it is 24 thus not a met. Alkalosis
Delta- delta 1:1
we must have either a resp alkalosis or a metabolic alkalosis to make the pH be normal…
IS the data internally consistent???
!
H+ = 24 x pCO2/ HCO3 (approx 40 = 24 x 24/14) not true….
Question 13
!
A 35 y/o male presents to the ED
unconscious.
LABS:
:
!
145
70
3.9
23
ABG: 7.61/23.8/ 77.5
6.1
Answer to question 13
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
Alkalemic
!
Is Resp or metabolic the primary cause?
!
HCO3 is nl unlikely metabolic
! PCO2 is decreased c/w Resp Alkalosis
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
! AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) =52
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
!
!
!
!
Ag- nl AG=40
These 40 unmeasured anions generated 40 protons thus the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 40 unmeasured anions added to it is 64 thus MUST be a
concomitant Met. Alkalosis
Delta-Delta is 40:1 "thus must have metabolic alkalosis
Diagnosis? Respiratory alkalosis w. concomitant metabolic alkalosis and a AG
Acidosis.
Question 14
!
64 y/o male w/ cirrhosis and septic shock has
following data
130
94
3.9
16
7.37/28
1.2
Answer to question 14
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
!
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
! AG = Na- (Cl+HCO3) =20
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
!
!
AG- nl AG=8
These 8 unmeasured anions generated 8 protons thus the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 8 unmeasured anions added to it is 24 thus no
Delta- delta 1:1
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
!
acidemic
Expected PCO2-1.5(hco3) +8 +/- 2= 32 +/-2
Diagnosis? Acute AG metabolic acidosis with concomitant Resp
Alkalosis
Question 15
!
!
52 y.o male admitted 2 days fever/cough w/
purulent sputum
Pulse 120 bp 80/60, rr 28
135
99
3.5
16
7.32/32/68 RA
Answer to question 15
!
Acidemic or Alkalemic?
!
!
What type of Acidosis is this AG or NAG?
!
!
!
!
AG- nl AG=8
These 8 unmeasured anions generated 8 protons thus the serum HCO3
concentrated with these 8 unmeasured anions added to it is 24 thus no
Delta- delta 1:1
Is respiratory Compensation Appropriate?
!
!
AG= Na- (Cl+HCO3)= 20
Is there a concomitant Metabolic process?
!
!
acidemic
Expected PCO2= 1.5(hco3) +8 +/-2 = 32 +/-2
Diagnosis? Pure AG acidosis.